Geography facts for kids
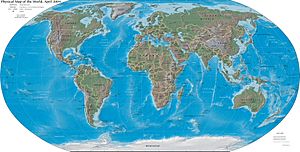
Geography is the study of our planet, the Earth. It looks at the Earth's natural features, like continents and mountains. It also studies the people and animals who live here. Geographers also learn about things that happen on Earth, such as winds and earthquakes.
The word geography comes from two Greek words. Gê means "Earth," and graphein means "to write or draw." So, geography means "to write and draw about the Earth." A scientist named Eratosthenes first used this word around 276-194 B.C.
Someone who is an expert in geography is called a geographer. Geographers work to understand the world around us. They study how different parts of the world began and how they have changed over time.
Geography has two main parts: physical geography and human geography. Physical geography focuses on the natural world. This includes things like climate and oceans. Human geography studies how people interact with the Earth. This can include how many people live in a place or how a country's economy works. There is also environmental geography, which looks at how humans affect the environment.
Maps are very important tools for geographers. They use maps to understand places and often create new ones. The skill of making maps is called cartography. People who make maps are known as cartographers.
Studying the Natural World
When geographers study the natural world, they focus on physical geography. They explore many different natural features and processes.
Some of the things they look at include:
- Climate: The usual weather patterns in a place.
- Landforms: Natural shapes on the Earth's surface, like hills.
- Continents: The large landmasses on Earth.
- Oceans: The huge bodies of saltwater.
- Soil: The top layer of the Earth where plants grow.
- Rocks: Natural solid materials that make up the Earth.
- Rivers: Natural flowing watercourses.
- Mountains: Large natural elevations of the Earth's surface.
- Endogenetic processes: Forces that shape the Earth from the inside.
- Exogenetic processes: Forces that shape the Earth from the outside.
Studying Human Life
Geographers also study the human environment. This means they look at how people live on Earth. They explore how humans use and change the planet.
Some topics in human geography are:
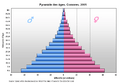
- Population: How many people live in an area.
- Countries of the world: Different nations and their borders.
- Agriculture: How people grow food and raise animals.
- Cities: Large towns where many people live.
- Industry: How goods are made and services are provided.
- Energy: How power is produced and used.
- Pollution: Harmful substances in the environment.
- Air pollution: Harmful substances in the air.
Famous Geographers
Many important people have helped us understand geography. Here are a few notable geographers:
- Eratosthenes (c. 276–c. 195/194 BC) – He was one of the first to calculate the size of the Earth.
- Ptolemy (c. 100–c. 170) – He collected Greek and Roman knowledge in his book, Geographia.
- Muhammad al-Idrisi (1100–1165) – An Arab geographer who wrote a famous book called Nuzhatul Mushtaq.
- Gerardus Mercator (1512–1594) – A mapmaker who created the mercator projection. This is a special way to draw maps.
- Alexander von Humboldt (1769–1859) – He wrote Cosmos and helped start the study of biogeography.
- Carl Ritter (1779–1859) – He held the first geography professor job at Berlin University.
- William Morris Davis (1850–1934) – He is known as the "father of American geography."
- Ellen Churchill Semple (1863–1932) – She was the first female president of the Association of American Geographers.
- Carl O. Sauer (1889–1975) – A well-known cultural geographer.
- Roger Tomlinson (1933 – 2014) – He helped create modern geographic information systems (GIS).
- Mei-Po Kwan (born 1962) – She has done important work with GPS and real-time mapping in GIS.
- Cynthia Brewer – She created ColorBrewer, a helpful tool for choosing map colors.
Images for kids
-
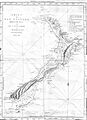
James Cook's map of New Zealand from 1770.
-
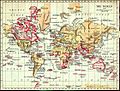
A map of the world based on Ptolemy's Geographia, written around c. 150.
-
A self-portrait of Alexander von Humboldt, an early geography pioneer.
-
A portrait of Gerardus Mercator, a famous mapmaker.
-
An example of Biogeography, the study of where living things are found.
-
Climatology and meteorology study weather, like this cyclone.
-
Geomorphology studies how landforms are created.
-
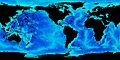
Oceanography is the study of oceans.
-
Quaternary science studies the last 2.6 million years of Earth's history.
-
Cultural geography explores human cultures and their spaces.
-
Economic geography studies how money and goods move.
-
Political geography studies countries and their power.
-
Social geography looks at how people interact in places.
-
Urban geography studies cities and towns.
See also
 In Spanish: Geografía para niños
In Spanish: Geografía para niños
 | Jessica Watkins |
 | Robert Henry Lawrence Jr. |
 | Mae Jemison |
 | Sian Proctor |
 | Guion Bluford |