- This page was last modified on 26 February 2026, at 14:35. Suggest an edit.
iOS facts for kids
For other uses, see IOS (disambiguation).
| iOS | |
|---|---|
 |
|

Home screen of iOS 26, the most recent version
|
|
| Developer | Apple |
| Written in | C, C++, Objective-C, Swift, assembly language |
| OS family | Unix-like, based on Darwin (BSD), macOS |
| Working state | Current |
| Source model | Closed, with open-source components |
| Initial release | June 29, 2007 |
| Latest release | 26.3 (February 11, 2026; 15 days ago) |
| Latest preview | 26.4 beta 2 (23E5218e) (February 23, 2026; 3 days ago) |
| Repository |
|
| Marketing target |
|
| Available in | 41 languages |
|
List of languages
Arabic, Bulgarian, Catalan, Chinese Simplified, Chinese Traditional (Hong Kong), Chinese Traditional (Taiwan), Croatian, Czech, Danish, Dutch, English (Australia), English (United Kingdom), English (United States), Finnish, French (Canada), French (France), German, Greek, Hebrew, Hindi, Hungarian, Indonesian, Italian, Japanese, Kazakh, Korean, Malay, Norwegian, Polish, Portuguese (Brazil), Portuguese (Portugal), Romanian, Russian, Slovak, Slovenian (iOS 18), Spanish (Latin America), Spanish (Spain), Swedish, Thai, Turkish, Ukrainian, Vietnamese
|
|
| Update method |
|
| Supported platforms |
|
| Kernel type | Hybrid (XNU) |
| Default user interface |
Multi-touch GUI |
| License | Proprietary software except for open-source components |
| Articles in the series | |
| iOS version history | |
iOS (which used to be called iPhone OS) is a special computer program, like the brain, for Apple's iPhone smartphones. It helps your iPhone run all its apps and features. Apple first showed it in January 2007 with the very first iPhone. It became available in June 2007.
Apple releases big new versions of iOS every year. The newest stable version, iOS 26, became available to everyone on September 15, 2025.
iOS is also the foundation for other Apple operating systems. These include iPadOS for iPads, tvOS for Apple TV, and watchOS for Apple Watch. Before iPadOS was created in 2019, iOS also ran on iPads. It also powered iPod Touch devices until they were no longer made. iOS is the second most popular mobile operating system in the world, right after Android. As of December 2023, the App Store has over 3.8 million apps for iOS devices.
iOS is built on ideas from macOS, which is the operating system for Apple's computers. It uses parts of the Mach microkernel and FreeBSD. This makes it a Unix-like operating system. While some parts of iOS are available for others to use and change (called open source), most of iOS is owned by Apple (called proprietary software).
Contents
- The Story of iOS: How It Began
- Key Features of iOS
- Processors That Power iOS Devices
- Devices That Use iOS
- How iOS Is Developed
- Apple's Control Over iOS
- Security and Privacy: Keeping You Safe
- See also
The Story of iOS: How It Began
In 2005, Steve Jobs, who was the head of Apple, started planning the iPhone. He had to decide if they should make the Mac computer's software smaller or the iPod's software bigger. Jobs chose to make the Mac software smaller. He had two teams compete to create the best system. Scott Forstall's team won by creating what was then called iPhone OS.
This decision was important because it made it easy for many computer programmers to create apps for the iPhone. They already knew how to write software for Mac computers. Forstall also helped create a special kit for programmers to build iPhone apps. He also helped create the App Store inside iTunes.
Apple showed the operating system with the iPhone on January 9, 2007. It was released in June of that year. Steve Jobs first said the iPhone ran "OS X" (the Mac operating system). But when the iPhone came out, the system was named "iPhone OS." At first, you couldn't install apps made by other companies. Jobs thought people could use web applications through the Safari web browser instead. In October 2007, Apple announced they were making a software development kit (SDK) for app makers. They released it on March 6, 2008.
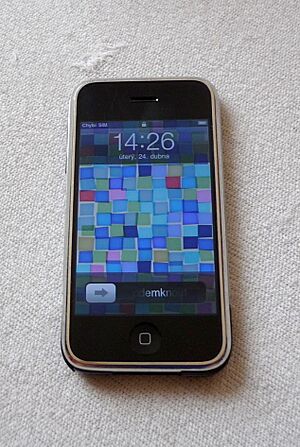
A first-generation iPhone (2007), the first device to run iOS, then called iPhone OS
The iOS App Store opened on July 10, 2008, with 500 apps. It grew very quickly. By October 2013, there were 1 million apps. By June 2016, there were 2 million apps. These apps have been downloaded over 130 billion times.
In September 2007, Apple introduced the iPod Touch. It looked like an iPhone but was for music and apps. On January 27, 2010, Apple launched the iPad. It had a bigger screen for browsing the web, watching videos, and reading. It also used multi-touch gestures. The iPad could use most existing iPhone apps.
In June 2010, Apple changed the name from iPhone OS to "iOS." Apple got permission from Cisco, a company that already used "IOS" for its network devices.
The Apple Watch smartwatch was announced on September 9, 2014. It focused on health and fitness tracking. It came out on April 24, 2015. It uses watchOS, which is based on iOS.
In October 2016, Apple opened its first iOS Developer Academy in Naples, Italy. This academy teaches students how to create and manage apps for Apple devices. It also covers business skills and designing app interfaces. By 2020, nearly a thousand students had graduated. They worked on 400 app ideas and published about 50 apps on the App Store.
On June 3, 2019, Apple announced iPadOS. This was a special version of iOS made just for the iPad. It launched on September 25, 2019.
On June 9, 2025, Apple introduced iOS 26. The version number now matches the year after its introduction. This helps keep all Apple operating systems' version numbers in sync.
Key Features of iOS
User Interface: How You Interact
The iOS user interface lets you control your device by touching the screen. You use multi-touch gestures like swiping, tapping, pinching, and reverse pinching. You also use sliders, switches, and buttons. Some apps use the device's accelerometers. This means they react if you shake the device (like to undo something) or turn it (like to switch between tall and wide views). iOS also has many accessibility features to help users with vision or hearing challenges.
When you turn on your iOS device, you see the lock screen. It shows the time and special widgets with information from your apps. On iPhones, it also has two buttons, usually for the flashlight and camera. You can change these buttons. After unlocking, you go to the home screen. This is where you find your apps and widgets. Widgets show live, updating content like the weather forecast or news.
At the top of the screen is the status bar. It shows things like battery level and signal strength. You can pull down from the top right (on iPhones with Face ID) or swipe up from the bottom (on iPhones with Touch ID) to open the Control Center. This lets you quickly change settings like brightness, volume, and Wi-Fi.
Swiping down from the top left (or top to bottom on iPhones with Touch ID) opens the Notification Center. It shows all your alerts, grouped by app. You can sometimes reply to messages right from a notification. Important alerts, like emergency alerts, show up on the lock screen with a special sound.
You can take a screenshot by pressing the home and power buttons at the same time on iPhones with Touch ID. On iPhones with Face ID, you use the volume-up and power buttons.
The camera app used to have a closing shutter animation. Since iOS 7, it just has a quick black screen effect. Over time, features like HDR photos and "live photos" (short videos with each picture) were added.
In iOS 13, "context menus" were added. These show helpful actions when you touch and hold an item.
iOS uses the San Francisco font. It's designed to be easy to read, even in small sizes. App icons are 180x180 pixels on larger iPhones and 120x120 pixels on smaller ones.
Organizing Apps on the Home Screen
The home screen, managed by something called SpringBoard, shows your app icons. There's also a dock at the bottom for your most-used apps. The home screen appears when you unlock your device or press the home button. A status bar at the top shows information like time and battery. If you have a passcode, you must enter it to get to the home screen.
In iPhone OS 3, Spotlight was added. This lets you search for media, apps, emails, contacts, and more. In iOS 7 and later, you can access Spotlight by pulling down on the home screen. In iOS 9, it also included Siri suggestions for apps and news. In iOS 10, Spotlight moved to the "Today" panel.
With iPhone OS 3.2, you could set a wallpaper for your home screen. This feature came to iPhones and iPod Touches with iOS 4.
iOS 7 added a cool "parallax effect." This makes your wallpaper and icons shift slightly when you move your device. It creates a 3D look, making icons seem to float.
System Fonts: A Clear View
iOS first used Helvetica as its main font. For the iPhone 4 and its sharp screen, Apple switched to Helvetica Neue. With iOS 9, Apple changed the font again to San Francisco. This font was designed by Apple to be very easy to read across all its products.
Folders: Keeping Things Tidy
iOS 4 introduced folders. You can create a folder by dragging one app icon on top of another. You can then add more apps to it. iOS automatically suggests a name for the folder, but you can change it. If apps inside a folder have notifications, the folder shows the total number of new alerts. Folders on iPhones can hold many apps across multiple pages. On iPads, folders can hold even more apps per page.
Notification Center: Your Alerts in One Place
Before iOS 5, notifications appeared in a pop-up window and disappeared quickly. In iOS 5, Apple created Notification Center. This lets you see a history of all your notifications. You can tap a notification to open its app or clear it. Notifications now appear as banners at the top of the screen. If an app sends a notification when it's closed, a red badge appears on its icon. This badge shows how many new alerts that app has.
Applications: The Heart of Your Device
iOS devices come with many preinstalled apps from Apple. These include Mail, Maps, TV, Music, FaceTime, Wallet, and Health.
Applications, or "apps," are programs you can install on your iOS device. You download them from the official App Store. Apps in the App Store are checked for security before they are available. Apps are made using the iOS Software Development Kit (SDK) and tools like Xcode. Programmers use languages like Swift and Objective-C.
At first, Apple didn't plan to let other developers make native apps. They wanted people to use web apps instead. But this idea didn't become popular. So, in October 2007, Apple announced the SDK, which was released on March 6, 2008.
The SDK is a free download for Mac computer users. It includes tools like an iPhone simulator to test apps. To test apps on a real device, get help, and sell apps in the App Store, developers need to join the Apple Developer Program.
Over the years, the App Store grew hugely. It passed milestones like 50,000, 100,000, and eventually over 2 million apps. The billionth app was installed on April 24, 2009.
App Library: Smart App Organization
The App Library automatically sorts your apps into folders. It groups them based on what they do, like social media or productivity. It also has an alphabetical list of all your apps. You can quickly find apps using the search bar. You can also hide certain home screen pages to focus on your most-used apps.
Storage: Keeping Your Files Safe
iOS keeps apps separate from each other for security and privacy. Apps usually can only access their own files. To access other files, iOS uses tools like document pickers and file providers.
iOS 8 introduced Document Picker and Document Provider extensions. These let apps open, save, and work with documents stored in a central place or in cloud services.
With iOS 11, Apple added the Files app. This app gives you a central place to manage your files. Other apps can connect with the Files app to make their documents available there.
You can expand your device's storage using iCloud. This is Apple's cloud storage service. It gives all users 5GB of storage for free. You can pay for more storage. iCloud Drive lets you store documents, presentations, and other files in the cloud. You can access these files on any of your devices if you're signed in with the same Apple ID.
Accessibility: Making iOS for Everyone
iOS has many features to help people with vision and hearing challenges. VoiceOver is a major feature. It reads information on the screen aloud, like buttons, icons, and links. Users can navigate the device using gestures. Apps made with Apple's standard tools often work with VoiceOver automatically. For example, VoiceOver can describe a photo scene when you hold up your iPhone to take a picture.
Apple also created a "Made for iPhone" program with iOS 7 in 2013. This allows special third-party hearing devices to connect to iPhones and iPads. They can stream audio directly to a user's ears. These products also offer features like battery tracking and adjustable sound settings.
With iOS 10 in 2016, Apple added even more accessibility features. VoiceOver got a new pronunciation editor. A Magnifier setting lets you enlarge objects using the camera. Software TTY support helps deaf people make phone calls. Apple also provided guides for developers to add accessibility to their apps.
In 2012, Liat Kornowski from The Atlantic said the iPhone was a huge step forward for accessibility. In 2016, Steven Aquino of TechCrunch praised Apple for leading in assistive technology. Sarah Herrlinger, an Apple manager, said, "We see accessibility as a basic human right." She added that building accessibility into products helps create an inclusive world.
Multitasking: Doing More at Once
Multitasking means running more than one app at a time. It first came to iOS in June 2010 with iOS 4. Only certain devices, like the iPhone 4 and iPhone 3GS, could multitask then. The iPad got multitasking later with iOS 4.2.1.
iOS multitasking lets apps do some things in the background. For example, an app can keep playing audio or video even if you switch to another app. It can also check your location or receive notifications.
Switching Between Applications
In iOS 4.0 to iOS 6.x, you double-clicked the home button to open the app switcher. A scrolling bar appeared at the bottom, showing app icons. Tapping an icon switched to that app.
With iOS 7, the app switcher changed. Double-clicking the home button showed screenshots of open apps. You could scroll sideways to see them. You could close apps by swiping their screenshots upwards.
iOS 9 brought another visual change to the app switcher. App icons became smaller and appeared above the screenshots. The app "cards" overlapped, creating a rolodex effect as you scrolled. The home screen appeared at the far right. In iOS 11, the app switcher was redesigned again. On the iPad, the Control Center and app switcher were combined.
Closing Apps
In iOS 4.0 to iOS 6.x, you held down app icons in the switcher until they "jiggled." Then you tapped a red minus circle to close them.
Since iOS 7, closing apps is faster. You just swipe the app's screenshot upwards off the screen. You can close up to three apps at once.
Finishing Tasks in the Background
Task completion lets apps keep working on a task even after you switch away from them. Since iOS 4.0, apps can ask for up to ten minutes to finish a task in the background.
Siri: Your Voice Assistant
Siri is a virtual assistant built into iOS. You can talk to Siri using your voice. It answers questions, suggests things, and performs actions by using online services. Siri learns how you speak and what you like over time.
Siri started as a separate app for iOS in February 2010. Apple bought it two months later. It was then built into the iPhone 4S when it came out in October 2011. The separate Siri app was then removed from the App Store.
Siri can do many things. It can make phone calls, check information, schedule events, manage settings, search the internet, help you navigate, and find entertainment. It also works with many iOS apps. With iOS 10 in 2016, Apple let some other apps use Siri, like messaging, payment, and ride-sharing apps. iOS 11 gave Siri clearer, more human-like voices. It also learned to answer follow-up questions and translate languages. iOS 17 made it possible to activate Siri by just saying "Siri," though "Hey Siri" still works.
Game Center: Play with Friends
Game Center is an online "social gaming network" from Apple. It lets you invite friends to play games, start multiplayer games, track your achievements, and compare your high scores on leaderboards. Since iOS 5, you can also add profile photos.
Apple announced Game Center on April 8, 2010. It was released on September 8, 2010, with iOS 4.1. It came to the iPad with iOS 4.2.1. Older devices like the iPhone 3G and original iPhone did not get Game Center.
Processors That Power iOS Devices
iOS runs on ARM processors. Currently, it supports different versions of the ARMv8 and ARMv9 architectures. Before iOS 7 in 2013, iOS only worked with 32-bit ARM processors. But iOS 7 added full support for 64-bit processors. This happened when Apple started using 64-bit ARMv8-A processors with the Apple A7 chip. Since 2015, all new apps and app updates in the App Store must support 64-bit. iOS 11, released in 2017, stopped supporting all older 32-bit iOS devices and apps. This made iOS a 64-bit-only operating system.
Devices That Use iOS
iOS powers almost all of Apple's mobile devices. It is used for all iPhones and iPod Touch devices. Also, Apple Watches, Apple TVs, and iPads either use iOS for some models or use operating systems that are based on iOS for others.
| Timeline of iOS devices: iPhone, iPod Touch, iPad, Apple TV, and Apple Watch models |
|---|
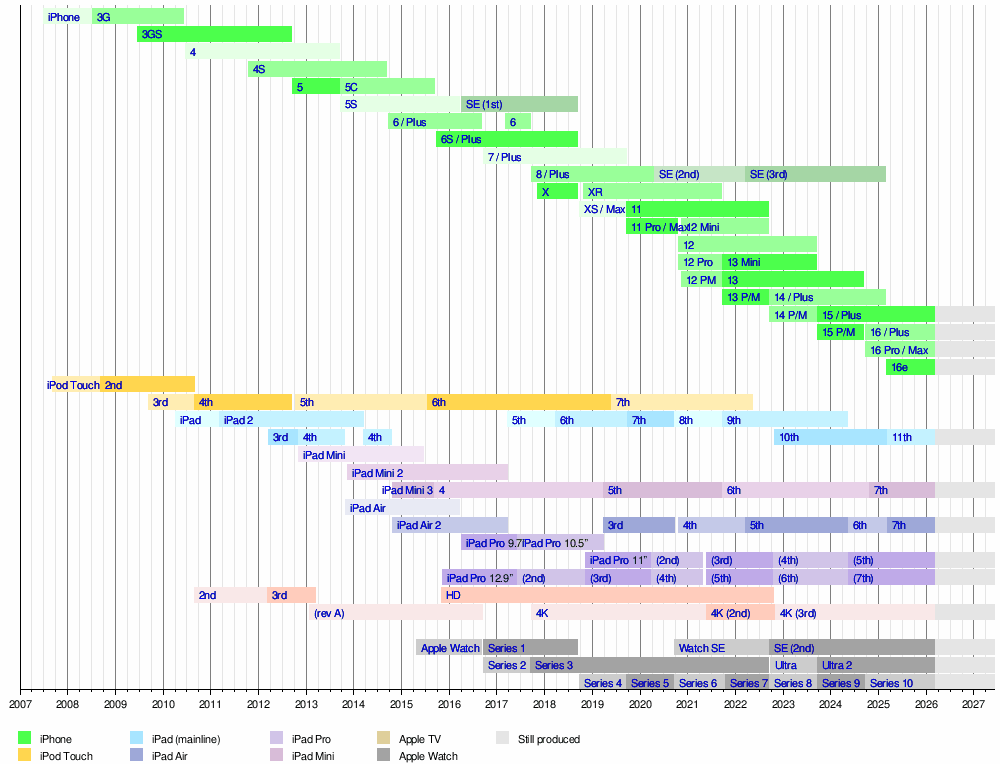 Sources: Apple Inc. Newsroom Archive, Mactracker Apple Inc. model database
|
How iOS Is Developed
The iOS software development kit (SDK) is a set of tools that lets people create mobile apps for iOS.
When Steve Jobs was first developing the iPhone before 2007, he didn't want other developers to make native apps. He wanted them to create web applications for the Safari web browser instead. But many developers wanted to make native apps. So, in October 2007, Jobs announced that Apple would release an SDK. It became available on March 6, 2008.
The SDK is free to download for users of Mac computers. It's not available for Microsoft Windows PCs. The SDK gives developers access to many features of iOS devices. It also includes an iPhone simulator to test apps on a computer. New versions of the SDK come out with new versions of iOS. To test apps on a real device, get help, and sell apps through the App Store, developers need to join the Apple Developer Program.
With tools like Xcode, the iOS SDK helps developers write apps using languages like Swift and Objective-C. Other companies also have tools to create iOS apps using their own programming languages.
Updates and How They Happen
iPad platform usage as measured by the App Store on January 21st, 2025 iPadOS 18 (71%) iPadOS 17 (14%) iPadOS 16 and earlier (15%)
Apple releases big updates to iOS every year. Since iOS 5, you can get these updates over-the-air, meaning directly on your device. You can also update using iTunes on older macOS and Windows computers. On newer macOS, you use Finder, and on Windows, you use the Apple Devices app.
Your device regularly checks for updates. If enabled, updates download and install automatically. Otherwise, you can install them manually or allow them to install overnight when plugged in and connected to Wi-Fi.
In the past, iPod Touch users had to pay for system updates. This changed in September 2009, and iPod Touch updates became free.
Apple has made iOS devices supported for updates for much longer over the years. Early iPhones only received two updates. Newer models have been supported for five, six, or even seven years.
The XNU Kernel: iOS's Core
iOS uses the XNU kernel, which is the core part of the Darwin operating system. This same kernel is also used by macOS and other Apple operating systems like iPadOS, watchOS, and tvOS. iOS 18, a recent stable version, uses version 24 of Darwin. Parts of Darwin and XNU are open source software.
Since iOS 6 in 2012, the kernel uses a security technique called kernel address space layout randomization (KASLR). This makes it harder for bad software to find weaknesses in the system's memory.
Jailbreaking: Customizing Your Device
Since iOS first came out, some people have found ways to change their devices beyond what Apple allows. This is called "jailbreaking." Before the iOS App Store opened in 2008, people jailbroke to install apps not approved by Apple.
Apple has said it doesn't release updates just to stop jailbreaking. However, new iOS updates often fix the ways people used to jailbreak.
When a device is jailbroken, it means its core software (the kernel) has been changed. If a jailbreak is "untethered," the device stays jailbroken even after you turn it off and on again. If it's "tethered," you need to connect it to a computer to re-jailbreak it each time it restarts. There are also "semi-tethered" and "semi-untethered" methods that offer more flexibility.
People jailbreak for various reasons. They might want to change how their device looks, get more control over its files, or install apps that aren't in the App Store. On some devices, jailbreaking can even allow installing other operating systems like Android.
In 2010, the Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF) helped make it legal in the U.S. to jailbreak iPhones. This was specifically for installing *legally obtained applications* not from the App Store. This rule doesn't change Apple's warranty policies. The EFF also helped make it legal to "unlock" an iPhone.
Unlocking: Using Different Phone Companies
Many phone companies used to "lock" iPhones. This meant you could only use the iPhone with that specific company's service. However, companies like AT&T eventually allowed iPhone owners to unlock their devices after meeting contract requirements. Apple provides instructions, but the phone company must authorize the unlock. This lets you use your iPhone with other phone companies that use the same technology.
There are also unofficial ways to remove these locks. However, Apple does not support these methods. Unlocking is different from jailbreaking, but sometimes a jailbreak is needed for unofficial software unlocks. The legality of unofficial unlocking depends on the country. In the U.S., it was allowed for devices bought before January 26, 2013.
Apple's Control Over iOS
Some people believe that Apple has too much control over iOS. They point to things like how Apple manages purchased media, how developers must pay a yearly fee to distribute apps, and how Apple approves all apps. They also mention that Apple can remotely disable or remove apps.
Some in the tech community worry that this strict control might limit new ideas in software. However, others praise how iOS keeps apps separate from each other (called sandboxing), which helps with security.
Security and Privacy: Keeping You Safe
iOS has many features built into both its hardware and software to keep your device and your personal information safe and private.
See also
 In Spanish: IOS para niños
In Spanish: IOS para niños
- Comparison of mobile operating systems

