List of states with nuclear weapons facts for kids
Nuclear weapons are very powerful weapons that use a special kind of energy from atoms. Eight countries in the world have publicly said they have successfully made and tested these weapons.
Five of these countries are called nuclear-weapon states (NWS) under an important agreement called the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT). These five countries are the United States, Russia (which took over from the Soviet Union), the United Kingdom, France, and China. They are listed in the order they first got nuclear weapons.
Other countries that have nuclear weapons are India, Pakistan, and North Korea. These three countries did not join the NPT when it started in 1970, and they have tested their nuclear weapons openly. North Korea was part of the NPT but left it in 2003.
Israel is also thought to have nuclear weapons, but they do not officially say so. This is called a "policy of deliberate ambiguity." It means they keep it a secret to deter (discourage) others without causing too much political trouble.
Some countries used to have nuclear weapons but don't anymore. South Africa built nuclear weapons but then took them apart before joining the NPT. The former Soviet republics of Belarus, Kazakhstan, and Ukraine had Soviet nuclear weapons, but these were moved to Russia.
As of 2024, experts estimate there are about 3,880 active nuclear warheads and 12,119 total nuclear warheads in the world. A warhead is the part of a missile or bomb that contains the nuclear explosive.
Contents
- Countries with Nuclear Weapons: A Quick Look
- Recognized Nuclear-Weapon States
- Countries Declaring Possession of Nuclear Weapons
- Countries Believed to Possess Nuclear Weapons
- Who Decides to Launch Nuclear Weapons?
- Nuclear Weapons Sharing
- Countries That Used to Have Nuclear Weapons
- Images for kids
- See also
Countries with Nuclear Weapons: A Quick Look
This section lists countries that have nuclear weapons. It also shows how many warheads they have and when they first tested a nuclear weapon. This group of countries is sometimes called the "Nuclear Club." The numbers for Russia and the United States are more certain because they have agreements to check each other's weapons. For other countries, these numbers are estimates.
| Country | Total Warheads | Deployed Warheads | First Test Date | Delivery Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5,044 | 1,770 | 16 July 1945 | Sea, Air, Land | |
| 5,580 | 1,710 | 29 August 1949 | Sea, Air, Land | |
| 225 | 120 | 3 October 1952 | Sea | |
| 290 | 280 | 13 February 1960 | Sea, Air | |
| 500 | 0 | 16 October 1964 | Sea, Air, Land | |
| 164 | 0 | 18 May 1974 | Sea, Air, Land | |
| 170 | 0 | 28 May 1998 | Sea, Air, Land | |
| 30 | 0 | 9 October 2006 | Sea, Land | |
| 90 | 0 | 1960–1979 | Unknown |
Total amount of nuclear warheads per country. Russia (45.4%) United States (42.7%) China (4.1%) France (2.4%) United Kingdom (1.8%) Pakistan (1.4%) India (1.3%) Israel (0.7%) North Korea (0.2%)
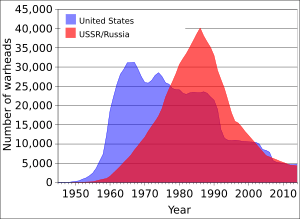
The number of nuclear weapons in the world was highest in 1986, with 70,300 active weapons. Now, in 2024, there are about 3,880 active warheads and 12,119 total warheads. Many weapons that were taken out of service were stored or partly taken apart, but not completely destroyed.
Countries use different ways to deliver nuclear weapons, like from submarines, airplanes, or missiles launched from land. Some countries have a "nuclear triad," meaning they can launch weapons from all three: land, sea, and air.
Recognized Nuclear-Weapon States
These five countries are recognized as nuclear-weapon states because they had tested a nuclear explosive before January 1, 1967. They are also the permanent members of the United Nations Security Council, which means they have special power in the United Nations.
United States
The United States developed the first nuclear weapons during World War II. They worked with the United Kingdom and Canada on a secret project called the Manhattan Project. They were worried that Nazi Germany would build them first.
The U.S. tested its first nuclear weapon on July 16, 1945, in a test called "Trinity." It is the only country to have used nuclear weapons in war. They dropped atomic bombs on the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
The U.S. was also the first country to develop the hydrogen bomb, a much more powerful type of nuclear weapon. They tested a prototype in 1952. During the Cold War, the U.S. kept making more and better nuclear weapons. At its peak in 1966, the U.S. had 31,175 nuclear warheads. Since 1992, they have focused on keeping their existing weapons safe and well-maintained.
Russia (Successor to the Soviet Union)
The Soviet Union tested its first nuclear weapon in 1949. This project was partly helped by information they got through spying during and after World War II. The Soviet Union was the second country to develop and test a nuclear weapon.
Their main reason for building these weapons was to balance the power with the United States during the Cold War. They tested their first hydrogen bomb in 1955. The Soviet Union also tested the most powerful explosive ever detonated by humans, called the "Tsar Bomba." It was so powerful that its planned strength was reduced by half before it was detonated.
After the Soviet Union broke apart in 1991, Russia officially took control of all its nuclear weapons. At its highest point in 1986, the Soviet nuclear arsenal had about 45,000 warheads.
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom tested its first nuclear weapon in 1952. The UK had done a lot of early research on the atomic bomb. They worked closely with the United States and Canada on the Manhattan Project. However, after 1945, the U.S. kept its nuclear secrets more closely. So, the UK had to develop its own way to make and detonate a bomb.
The United Kingdom was the third country to develop and test a nuclear weapon. Their goal was to have their own way to deter (discourage) the Soviet Union. They also wanted to keep their status as a major world power. The UK tested its first hydrogen bomb in 1957.
During the Cold War, the British military used special bombers and submarines to carry nuclear weapons. Today, the Royal Navy has four submarines that carry Trident II missiles, which are their nuclear weapons.
France
France tested its first nuclear weapon in 1960. Their program was mostly based on their own research. One reason was the diplomatic tension during the Suez Crisis, which involved both the Soviet Union and its allies, the U.S. and UK. France also wanted to remain a major world power after the colonial era.
France tested its first hydrogen bomb in 1968. After the Cold War, France reduced and updated its nuclear weapons. Now, their system relies on missiles launched from submarines and air-to-surface missiles carried by fighter jets.
France joined the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty in 1992. In 2006, President Jacques Chirac said that if France was attacked with weapons of mass destruction, it would respond with nuclear weapons. In 2015, President François Hollande said that France needed nuclear weapons to stay safe in a dangerous world. He also shared that France has "fewer than 300" nuclear warheads.
China
China tested its first nuclear weapon in 1964. They developed this weapon to deter both the United States and the Soviet Union. Just two years later, China had a nuclear bomb that could be put on a missile.
China tested its first hydrogen bomb in 1967. This was only 32 months after their first nuclear test, which is the fastest known time for a country to go from a basic nuclear weapon to a hydrogen bomb. China is the only recognized nuclear-weapon state that has a "no first use" policy. This means they promise not to use nuclear weapons first in a conflict.
China joined the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty in 1992. As of February 2024, China is estimated to have about 500 nuclear warheads. Experts believe China is significantly updating and expanding its nuclear arsenal. Its stockpile is expected to grow in the coming years.
Countries Declaring Possession of Nuclear Weapons
India
India is not part of the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty. In the 1960s, Indian officials said the NPT created a world of "haves" and "have-nots." They argued it unfairly limited "peaceful activity," like using nuclear explosions for non-military purposes. India said it would not agree to international control of its nuclear facilities unless all other countries got rid of their nuclear weapons.
India tested what it called a "peaceful nuclear explosive" in 1974. This test, known as "Smiling Buddha," raised questions about how civilian nuclear technology could secretly be used for weapons. Countries that had helped India with its peaceful nuclear reactors, like Canada, were very concerned.
After its 1974 test, India said its nuclear ability was mainly "peaceful." However, between 1988 and 1990, it seems India prepared about two dozen nuclear weapons to be delivered by air. In 1998, India tested actual weaponized nuclear warheads, including a thermonuclear device (a type of hydrogen bomb). India adopted a "no first use" policy in 1998.
As of January 2023, India is estimated to have about 164 nuclear warheads.
Pakistan
Pakistan is also not a party to the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty. Pakistan secretly developed nuclear weapons over many years, starting in the late 1970s. Pakistan's Prime Minister Zulfiqar Ali Bhutto said in 1971 that if India built nuclear weapons, Pakistan would too, even if they had to "eat grass" to do it.
It is believed that Pakistan has had nuclear weapons since the mid-1980s. In 1998, Pakistan conducted six nuclear tests in response to India's tests a few weeks earlier.
In 2004, a Pakistani scientist named Abdul Qadeer Khan, who was important in Pakistan's nuclear program, admitted to leading a secret network that sold nuclear weapons technology. He had sold technology to North Korea, Iran, and Libya.
As of 2023, experts estimate that Pakistan has about 170 nuclear warheads.
North Korea
North Korea was part of the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty but announced it was leaving on January 10, 2003. This happened after the United States accused North Korea of having a secret program to enrich uranium.
In February 2005, North Korea claimed to have working nuclear weapons, but many experts doubted this because they hadn't tested one. In October 2006, North Korea said it would conduct a nuclear test to confirm its nuclear status. They reported a successful test on October 9, 2006. Most U.S. intelligence officials believed the test was only partly successful. North Korea conducted more tests in 2009 and 2013.
North Korea claimed to have tested its first hydrogen bomb in January 2016, but measurements showed it was not consistent with a hydrogen bomb. On September 3, 2017, North Korea detonated a device that caused a strong tremor, which was consistent with a low-powered thermonuclear detonation.
Kim Jong Un officially declared North Korea a nuclear weapons state on September 9, 2022. Experts believe North Korea's military nuclear program is very important to its national security. They may have assembled up to 30 nuclear weapons and could make more.
Countries Believed to Possess Nuclear Weapons
Israel
Israel is widely believed to be the sixth country in the world to develop nuclear weapons. However, it has never officially said it has them. It is thought they had basic nuclear weapons ready as early as 1966. Israel is not a party to the NPT.
Israel uses a policy called "strategic ambiguity." This means they say they would not be the first country to "introduce" nuclear weapons into the region. But they refuse to confirm or deny having a nuclear weapons program or arsenal. This policy helps them deter (discourage) enemies without causing too much political trouble.
Experts believe Israel likely has between 80 and 400 nuclear weapons. Some estimates suggest they have about 80 intact nuclear weapons. These could be delivered by missiles or by aircraft.
Who Decides to Launch Nuclear Weapons?
The decision to use nuclear weapons is usually limited to one person or a very small group of people.
| Country | Authority | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| President of the United States | The President always has a special briefcase, sometimes called the "Nuclear Football," nearby. | |
| President of Russia | Briefcases may also be given to the Minister of Defence and the Chief of the General Staff. | |
| Prime Minister of the United Kingdom | The Prime Minister and a secretly chosen 'second' person can order a launch. | |
| President of France | Other military leaders may also be involved in decisions. | |
| Central Military Commission | The Chairman of the Central Military Commission is the top military commander. | |
| Prime Minister of India | The Nuclear Command Authority includes an Executive Council and a Political Council. | |
| National Command Authority | Requires agreement from the council's members. | |
| President of the State Affairs | The President of the State Affairs is the final decision-maker for North Korea's nuclear weapons. | |
| Prime Minister of Israel | Requires agreement from the Minister of Defense and the Chief of the General Staff. |
Some countries allow military personnel to launch nuclear weapons if the main leader cannot make a decision. This is usually kept secret. For example, in the United States, some military commanders can launch weapons if there's no time to get a decision from the President. Russia has a system called "Dead Hand" that might allow military commanders to act based on certain rules. British nuclear submarine commanders are given "Letters of last resort" by the Prime Minister, which contain secret instructions.
Nuclear Weapons Sharing
Some countries share nuclear weapons, meaning one country provides weapons for another country to store and use if needed.
| Country | Base | Estimated |
|---|---|---|
| Kleine Brogel | 20 | |
| Büchel | 20 | |
| Aviano | 20 | |
| Ghedi | ||
| Volkel | 20 | |
| Incirlik | 20 | |
| 100 |
Under NATO nuclear weapons sharing, the United States has given nuclear weapons to Belgium, Germany, Italy, the Netherlands, and Turkey to keep and use. This means pilots and other staff from these "non-nuclear" NATO countries practice handling and delivering U.S. nuclear bombs. They also adapt their airplanes to carry these bombs.
However, all U.S. nuclear weapons have special safety devices called Permissive Action Links. This means the host countries cannot easily arm the bombs without special codes from the U.S. Department of Defense. As of April 2019, the United States kept about 100 nuclear weapons in Europe.
| Country | Air base | Warheads |
|---|---|---|
| Probably Lida | ~130 |
Since June 2023, the leaders of Russia and Belarus have said that some nuclear weapons are located in Belarus, but they are still owned by Russia. Russia plans to give Belarus two ways to deliver these weapons: Iskander-M missile systems and training for Belarusian Su-25 aircraft to carry nuclear weapons.
Russia's President Vladimir Putin said that putting Russian weapons in Belarus is similar to how American nuclear weapons are placed in NATO countries in Europe.
Countries That Used to Have Nuclear Weapons
Nuclear weapons have been in many countries, often as storage places controlled by other powers. But only one country has given up nuclear weapons after having full control of them. When the Soviet Union broke apart, some former Soviet republics had nuclear weapons on their land. However, they didn't have full control over them, as they needed codes from Russia.
South Africa
South Africa made six nuclear weapons in the 1980s. But they took them apart in the early 1990s.
In 1979, there was a possible secret nuclear test detected in the Indian Ocean, called the Vela incident. Many people have thought it was a test by Israel, working with South Africa, but this has never been confirmed.
South Africa joined the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty in 1991.
Former Soviet Republics
- Kazakhstan had 1,400 Soviet-era nuclear weapons on its land. It transferred all of them to Russia by 1995, after joining the NPT.
- Ukraine had as many as 3,000 nuclear weapons on its land when it became independent from the Soviet Union in 1991. This was like having the third-largest nuclear arsenal in the world. When Ukraine joined the NPT in December 1994, it agreed to get rid of all nuclear weapons on its territory. The warheads were removed from Ukraine by 1996 and taken apart in Russia.
- Belarus also had single warhead missiles on its land in the 1990s when it was part of the Soviet Union. When the Soviet Union collapsed in 1991, 81 single warhead missiles were in Belarus. All of them were moved to Russia by 1996. Belarus was a member of the NPT from May 1992 until February 2022. Since 2023, Belarus has started hosting Russian nuclear weapons again.
When these three countries joined the NPT, they were promised that their independence and land would be respected. This promise was made in an agreement called the Budapest Memorandum on Security Assurances. However, Russia has broken this agreement since the Russo-Ukrainian War began in 2014.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Países con armas nucleares para niños
In Spanish: Países con armas nucleares para niños