Salvador Fidalgo facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Salvador Fidalgo
|
|
|---|---|
| Born |
Salvador Fidalgo y Lopegarcía
August 6, 1756 |
| Died | September 27, 1803 (aged 47) Tacubaya, Mexico
|
| Nationality | Spanish |
| Occupation | explorer |
Salvador Fidalgo y Lopegarcía (born August 6, 1756 – died September 27, 1803) was a brave Spanish explorer. He led important trips for Spain to places like Alaska and the Pacific Northwest. These journeys happened in the late 1700s.
Contents
Salvador Fidalgo was born in La Seu d'Urgell, a town in Catalonia, Spain. His family was from a noble background. He joined the Spanish Navy as a young cadet, called a guardiamarina, in Cádiz.
He finished his training in 1775. After that, he became an Alférez de Fragata, which is like a junior officer.
Fidalgo was chosen to work with Vicente Tofiño de San Miguel, a famous mapmaker. They helped create the first detailed map book of Spain's ports and coastlines. He served in the Mediterranean Sea and fought in battles against British and Portuguese ships. In 1778, he was promoted to Teniente de Navío (Lieutenant). He was then sent to the Spanish naval base in San Blas, Mexico.
Spain's Claims in the Pacific Northwest
Spain believed it owned the lands in Alaska and the Pacific Northwest. This belief came from old agreements like a papal bull from 1493 and the Treaty of Tordesillas from 1494. These agreements said Spain had the right to explore and settle most of the Western Hemisphere.
In 1513, the Spanish explorer Vasco Núñez de Balboa was the first European to reach the Pacific coast of Panama. He claimed the entire Pacific Ocean for Spain. This included all the lands touching it, like the west coast of North America.
For about 250 years, Spain didn't explore or settle much of the northwest coast. But in the late 1700s, Spain heard that Russian and British explorers were arriving there. This made Spain worried about its claims. So, they decided to send expeditions to see how far the Russians and British had gone.
Fidalgo's 1790 Expedition to Alaska
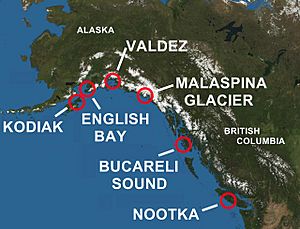
In 1790, the Viceroy of New Spain asked Salvador Fidalgo to lead an expedition. Fidalgo sailed from Nootka Sound, which is near today's Vancouver Island.
In May 1790, Fidalgo's ship reached what is now Cordova, Alaska. They looked for signs of Russian presence but found none. They traded with the local native people. On June 3, 1790, Fidalgo and his crew landed at Orca Inlet. There, they held a special ceremony. Fidalgo put up a large wooden cross and claimed the area for Spain. He named it Puerto Córdova.
Fidalgo continued exploring the Alaskan coast. He reached Gravina Point and performed the same ceremony. On June 15, 1790, they found a new port. They named it Puerto Valdez, after the Spanish Navy Minister.
On July 4, 1790, Fidalgo's team met Russians for the first time. This happened on the Kenai Peninsula. Fidalgo named this spot Puerto Revillagigedo. The expedition then went to the main Russian settlement on Kodiak Island. Fidalgo invited the Russians onto his ship. The next day, July 5, 1790, he held another ceremony. This was near the Russian outpost of Alexandrovsk, southwest of today's Anchorage.
Fidalgo led the expedition back to San Blas, arriving on November 15, 1790.
Establishing a Post at Neah Bay
In 1792, Salvador Fidalgo was given a new task. He was to set up a Spanish outpost at Neah Bay, Washington. This place is on the coast of the Strait of Juan de Fuca in the U.S. state of Washington.
Fidalgo arrived on his ship, the Princesa, on May 28, 1792. The new outpost quickly had a garden, a place for farm animals, and a strong fence with a small group of soldiers.
This outpost was set up during talks between Spain and Britain. These talks were about who owned the land after a disagreement called the Nootka Crisis. Spain was thinking about moving its main base from Nootka Sound. Fidalgo's work at Neah Bay was to prepare for this possible move.
Later in 1792, there was a conflict between the Spanish and the Makah people, who lived at Neah Bay. Fidalgo's second-in-command was killed. In response, Fidalgo ordered an attack on the Makah, and many people were hurt. Fidalgo was later criticized by his leaders for this action. The outpost at Neah Bay was then closed, and Fidalgo was called back to Nootka Sound.
Later Life and Death
In 1794, Salvador Fidalgo was promoted to Capitán de Fragata (Frigate Captain). In 1795, he sailed to the Philippines to deliver important diplomatic papers. In 1801, he helped stop a Native American rebellion on Tiburón Island in the Gulf of California.
Salvador Fidalgo died on September 27, 1803. He passed away in Tacubaya, which is near Mexico City.
Legacy
Fidalgo Island, located near Puget Sound in Washington State, was named in his honor.
See also
In Spanish: Salvador Fidalgo para niños