Victoria Island facts for kids
|
Native name:
Kitlineq
|
|
|---|---|
 |
|
 |
|
| Geography | |
| Location | Northern Canada |
| Coordinates | 70°25′N 107°45′W / 70.417°N 107.750°W |
| Archipelago | Arctic Archipelago |
| Area | 217,291 km2 (83,897 sq mi) |
| Area rank | 8th |
| Length | 700 km (430 mi) |
| Width | 564–623 km (350–387 mi) |
| Highest elevation | 655 m (2,149 ft) |
| Highest point | Unnamed |
| Administration | |
|
Canada
|
|
| Territories | Northwest Territories Nunavut |
| Largest settlement | Cambridge Bay, Nunavut (pop. 1,760) |
| Demographics | |
| Population | 2,168 (2021) |
| Ethnic groups | Inuit |
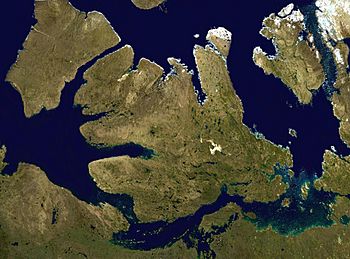
Victoria Island (Inuinnaqtun: Kitlineq) is a very large island in the Arctic Archipelago of Canada. It sits right on the border between Nunavut and the Northwest Territories. This island is the eighth-largest island in the world. It is also Canada's second-largest island, covering about 217,291 square kilometers (83,897 sq mi).
To give you an idea of its size, Victoria Island is almost twice as big as Newfoundland (111,390 km²). It is also a bit larger than the island of Great Britain (209,331 km²). However, it is smaller than Honshū in Japan (225,800 km²).
The western part of the island is in the Inuvik Region of the Northwest Territories. The rest of the island is part of Nunavut's Kitikmeot Region. About 2,168 people live on Victoria Island. They live in two main towns. The bigger town is in Nunavut, and the other is in the Northwest Territories.
The island is named after Queen Victoria. She was the Queen of Canada from 1867 to 1901. Features named "Prince Albert" are named after her husband, Prince Albert.
Contents
Exploring Victoria Island's Past
Victoria Island has been home to people for a very long time. The Thule culture lived here in the past. These were the ancestors of today's Inuit people. Scientists found five old qamutiik (sleds) on the Wollaston Peninsula. These sleds belonged to the Neoeskimo culture and are from between 1250 and 1573 CE.
The local Inuit people call the island Kitlineq. The people themselves are known as Kitlinermiut, also called the Copper Inuit.
Early European Explorers
European explorers began to map Victoria Island in the 1800s.
- In 1826, John Richardson was the first European to see the southwest coast. He named it "Wollaston Land."
- In 1839, Peter Warren Dease and Thomas Simpson explored the southeast coast. They called it "Victoria Land."
- Later, in 1851, John Rae mapped the entire southern coast. He connected the two "lands" that had been found.
- Between 1850 and 1851, Robert McClure sailed around most of Banks Island. This showed that Banks Island was separate from Victoria Island. His team also mapped the northwest and west coasts of Victoria Island.
- In 1905, Godfred Hansen, who was with Roald Amundsen, mapped part of the east coast.
- From 1916 to 1917, Storker T. Storkerson mapped the northeast coast. He was part of Vilhjalmur Stefansson's Canadian Arctic Expedition. He even sighted the Storkerson Peninsula, which is named after him.
Modern Journeys Across the Island
In 2008, Clark Carter and Chris Bray became the first people known to walk all the way across Victoria Island. They had tried in 2005 but didn't finish. So, they came back in 2008 and completed the remaining 660 kilometers (410 miles) of their journey.
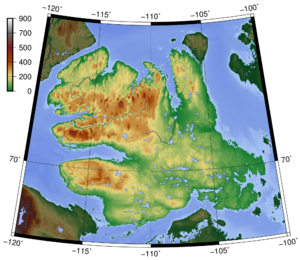
Victoria Island's Geography
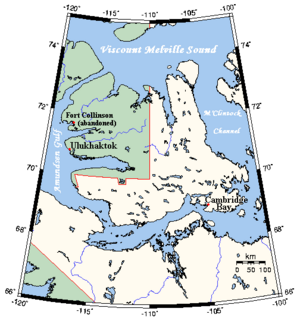
Victoria Island is surrounded by many important waterways.
- To the north is Viscount Melville Sound.
- To the east are the M'Clintock Channel and Victoria Strait.
- To the west are Amundsen Gulf and Banks Island. Banks Island is separated from Victoria Island by the Prince of Wales Strait.
- To the south are the Dolphin and Union Strait, Austin Bay, Coronation Gulf, and the Dease Strait.
These southern waterways, and sometimes the Prince of Wales Strait, are part of the Northwest Passage. This is a sea route that connects the Atlantic and Pacific oceans through the Arctic. Canada says these waters are its own, but some other countries see them as international waters.
Peninsulas and Lakes
Victoria Island has a very jagged coastline with many deep bays and peninsulas.
- In the east, pointing north, is the Storkerson Peninsula. It is separated from Stefansson Island by the Goldsmith Channel.
- Hadley Bay is a large inlet that separates the Storkerson Peninsula from the island's north-central areas.
- Another wide peninsula in the north is the Prince Albert Peninsula. It reaches out to the Prince of Wales Strait.
- In the south, pointing west, is the Wollaston Peninsula. It is separated from the island's middle by Prince Albert Sound.
The highest point on Victoria Island is 655 meters (2,149 feet) high. It is found in the Shaler Mountains in the north-central part of the island. The largest lake on the island is Tahiryuaq (also called Ferguson Lake). It is in the southeast, near Cambridge Bay, and covers 562 square kilometers (217 sq mi).
Some people say that Victoria Island looks like a stylized maple leaf. The maple leaf is a main symbol of Canada.
Victoria Island's Climate
Victoria Island has a polar climate. This means that no month has an average temperature of 10°C (50°F) or higher. Summers are usually cool and rainy. Days can be pleasant, but nights are chilly. Winters are very cold, dark, and long. October often has the most snowfall. Snow and frost can happen at any time of the year.
Most rain falls in the summer months. This is when the temperature rises above freezing for a short time. Then, it drops back down for about nine months of winter. Spring is often sunny but still very cold. Autumns are short and crisp. Clouds start to appear more often in August, and September is almost always cloudy.
In Cambridge Bay, the sun stays below the horizon during the polar night. This happens from about November 30 to January 11. The sun stays above the horizon during the midnight sun from May 19 to July 22.
| Climate data for Cambridge Bay (Cambridge Bay Airport) WMO ID: 71925; coordinates 69°06′29″N 105°08′18″W / 69.10806°N 105.13833°W; elevation: 31.1 m (102 ft); 1981–2010 normals |
|||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high humidex | −5.0 | −9.7 | −4.1 | 3.9 | 10.5 | 25.3 | 30.8 | 28.6 | 16.3 | 5.8 | −1.4 | −3.5 | 30.8 |
| Record high °C (°F) | −4.9 (23.2) |
−9.4 (15.1) |
−4.0 (24.8) |
6.1 (43.0) |
11.5 (52.7) |
23.3 (73.9) |
28.9 (84.0) |
26.1 (79.0) |
16.4 (61.5) |
6.9 (44.4) |
0.0 (32.0) |
−3.4 (25.9) |
28.9 (84.0) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | −28.5 (−19.3) |
−28.9 (−20.0) |
−25.3 (−13.5) |
−16.3 (2.7) |
−5.6 (21.9) |
5.8 (42.4) |
12.8 (55.0) |
9.8 (49.6) |
2.5 (36.5) |
−7.3 (18.9) |
−18.8 (−1.8) |
−24.9 (−12.8) |
−10.4 (13.3) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −32.0 (−25.6) |
−32.5 (−26.5) |
−29.3 (−20.7) |
−20.8 (−5.4) |
−9.3 (15.3) |
2.7 (36.9) |
8.9 (48.0) |
6.8 (44.2) |
0.3 (32.5) |
−10.4 (13.3) |
−22.3 (−8.1) |
−28.3 (−18.9) |
−13.9 (7.0) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −35.4 (−31.7) |
−36.1 (−33.0) |
−33.2 (−27.8) |
−25.3 (−13.5) |
−13.0 (8.6) |
−0.3 (31.5) |
4.9 (40.8) |
3.8 (38.8) |
−1.9 (28.6) |
−13.5 (7.7) |
−25.7 (−14.3) |
−31.8 (−25.2) |
−17.3 (0.9) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −52.8 (−63.0) |
−50.6 (−59.1) |
−48.3 (−54.9) |
−42.8 (−45.0) |
−35.0 (−31.0) |
−17.8 (0.0) |
−1.7 (28.9) |
−8.9 (16.0) |
−17.2 (1.0) |
−33.0 (−27.4) |
−43.9 (−47.0) |
−49.4 (−56.9) |
−52.8 (−63.0) |
| Record low wind chill | −73.4 | −72.6 | −69.8 | −60.1 | −43.2 | −29.2 | −7.9 | −13.1 | −28.6 | −49.4 | −60.7 | −66.3 | −73.4 |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 5.8 (0.23) |
4.9 (0.19) |
7.1 (0.28) |
5.7 (0.22) |
7.0 (0.28) |
13.6 (0.54) |
24.1 (0.95) |
25.7 (1.01) |
19.1 (0.75) |
14.7 (0.58) |
8.0 (0.31) |
6.1 (0.24) |
141.7 (5.58) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
1.0 (0.04) |
10.0 (0.39) |
23.9 (0.94) |
23.9 (0.94) |
12.7 (0.50) |
0.6 (0.02) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
72.1 (2.84) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 6.7 (2.6) |
5.9 (2.3) |
8.4 (3.3) |
6.9 (2.7) |
7.2 (2.8) |
3.8 (1.5) |
0.1 (0.0) |
1.8 (0.7) |
6.8 (2.7) |
15.9 (6.3) |
9.8 (3.9) |
6.8 (2.7) |
80.2 (31.6) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.2 mm) | 7.3 | 6.8 | 9.2 | 6.8 | 7.1 | 8.0 | 10.7 | 13.1 | 11.9 | 12.1 | 9.0 | 7.9 | 109.8 |
| Average rainy days (≥ 0.2 mm) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.9 | 5.9 | 10.7 | 12.5 | 7.1 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 37.8 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.2 cm) | 7.4 | 6.9 | 9.8 | 7.1 | 7.3 | 3.4 | 0.1 | 1.2 | 6.3 | 12.5 | 9.5 | 8.3 | 79.8 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 65.3 | 66.4 | 70.5 | 76.2 | 83.8 | 77.2 | 68.2 | 73.6 | 82.3 | 86.2 | 76.5 | 70.0 | 74.7 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 7.3 | 73.7 | 169.6 | 275.9 | 245.1 | 291.6 | 333.8 | 186.6 | 71.7 | 56.8 | 17.6 | 0.0 | 1,729.7 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 11.7 | 35.4 | 47.1 | 57.7 | 36.6 | 40.5 | 45.9 | 33.6 | 17.8 | 20.0 | 13.5 | 0.0 | 30.0 |
| Source: Environment and Climate Change Canada Canadian Climate Normals 1981–2010 | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Ulukhaktok (Ulukhaktok/Holman Airport) Climate ID: 2502501; coordinates 70°45′46″N 117°48′22″W / 70.76278°N 117.80611°W; elevation: 36.0 m (118.1 ft); 1981–2010 normals |
|||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high humidex | −7.2 | −9.4 | −7.6 | 6.9 | 10.6 | 23.0 | 27.9 | 24.5 | 17.1 | 5.1 | 0.1 | −3.2 | 27.9 |
| Record high °C (°F) | −4.0 (24.8) |
−6.5 (20.3) |
−5.0 (23.0) |
4.5 (40.1) |
11.5 (52.7) |
22.5 (72.5) |
29.0 (84.2) |
23.5 (74.3) |
15.8 (60.4) |
5.9 (42.6) |
1.1 (34.0) |
−3.0 (26.6) |
29.0 (84.2) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | −24.3 (−11.7) |
−24.9 (−12.8) |
−21.4 (−6.5) |
−12.6 (9.3) |
−3.2 (26.2) |
7.8 (46.0) |
12.8 (55.0) |
9.3 (48.7) |
3.1 (37.6) |
−6.2 (20.8) |
−16.5 (2.3) |
−21.6 (−6.9) |
−8.1 (17.4) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −28.0 (−18.4) |
−28.8 (−19.8) |
−25.6 (−14.1) |
−17.0 (1.4) |
−6.6 (20.1) |
4.6 (40.3) |
9.0 (48.2) |
6.4 (43.5) |
0.9 (33.6) |
−8.9 (16.0) |
−19.8 (−3.6) |
−25.2 (−13.4) |
−11.6 (11.1) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −31.8 (−25.2) |
−32.6 (−26.7) |
−29.8 (−21.6) |
−21.4 (−6.5) |
−10.0 (14.0) |
1.4 (34.5) |
5.2 (41.4) |
3.4 (38.1) |
−1.3 (29.7) |
−11.4 (11.5) |
−23.1 (−9.6) |
−28.6 (−19.5) |
−15.0 (5.0) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −47.5 (−53.5) |
−49.0 (−56.2) |
−45.0 (−49.0) |
−42.1 (−43.8) |
−26.5 (−15.7) |
−12.5 (9.5) |
−3.5 (25.7) |
−5.5 (22.1) |
−15.5 (4.1) |
−36.8 (−34.2) |
−37.5 (−35.5) |
−42.8 (−45.0) |
−49.0 (−56.2) |
| Record low wind chill | −59.8 | −59.2 | −61.9 | −45.6 | −31.0 | −18.3 | −6.8 | −11.1 | −21.9 | −44.7 | −51.3 | −51.2 | −61.9 |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 8.4 (0.33) |
7.5 (0.30) |
7.3 (0.29) |
5.3 (0.21) |
7.4 (0.29) |
8.0 (0.31) |
22.4 (0.88) |
32.2 (1.27) |
19.8 (0.78) |
17.1 (0.67) |
11.5 (0.45) |
8.5 (0.33) |
155.3 (6.11) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
1.1 (0.04) |
6.9 (0.27) |
22.2 (0.87) |
30.2 (1.19) |
13.2 (0.52) |
0.6 (0.02) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
74.2 (2.92) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 8.5 (3.3) |
7.5 (3.0) |
7.5 (3.0) |
5.3 (2.1) |
6.4 (2.5) |
1.2 (0.5) |
0.2 (0.1) |
2.0 (0.8) |
6.6 (2.6) |
16.9 (6.7) |
12.3 (4.8) |
8.9 (3.5) |
83.3 (32.8) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.2 mm) | 5.3 | 5.2 | 4.9 | 3.9 | 4.8 | 4.7 | 7.8 | 11.0 | 9.3 | 9.5 | 7.3 | 5.3 | 78.9 |
| Average rainy days (≥ 0.2 mm) | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.6 | 3.9 | 7.8 | 10.5 | 6.3 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 29.4 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.2 cm) | 5.3 | 5.2 | 5.0 | 3.9 | 4.4 | 1.0 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 3.5 | 9.4 | 7.4 | 5.4 | 51.5 |
| Source: Environment and Climate Change Canada | |||||||||||||
Animals of Victoria Island
Victoria Island is home to special animals. The Dolphin-Union caribou herd lives here. These caribou are also known as Island Caribou. They are a type of barren-ground caribou that live in Canada's High Arctic and the nearby mainland. They are found only in Canada.
These caribou travel across the Dolphin and Union Strait. They move from their summer feeding grounds on Victoria Island to their winter areas on the Nunavut-Northwest Territories mainland. It's quite rare for North American caribou to cross sea ice like this. The only other caribou that do this are the Peary caribou. Peary caribou are smaller and have smaller populations. They also live on Victoria Island.
Victoria Island is also famous for having the world's largest island within an island within an island. This means there's a lake on an island, and in that lake, there's another island, and on that island, there's another lake with another island!
People Living on Victoria Island
In the 2021 Canadian census, 2,168 people lived on Victoria Island. About 1,760 people lived in Nunavut, and 408 lived in the Northwest Territories.
There are two main towns on the island:
- Cambridge Bay is the larger town. It is on the southeast coast and is in Nunavut.
- Ulukhaktok is on the west coast and is in the Northwest Territories.
Some old trading posts, like Fort Collinson on the northwest coast, are now empty.
Towns and Their Populations
| Name | Population |
|---|---|
| Cambridge Bay | 1,760 |
| Ulukhaktok | 408 |
Maps of Victoria Island and Nearby Areas
- Viscount Melville Sound - 74°15′N 105°00′W / 74.250°N 105.000°W
- M'Clintock Channel - 72°00′N 102°00′W / 72.000°N 102.000°W
- Victoria Strait - 69°31′N 100°30′W / 69.517°N 100.500°W
- Amundsen Gulf - 71°00′01″N 124°00′10″W / 71.00028°N 124.00278°W
- Banks Island - 72°45′02″N 121°30′10″W / 72.75056°N 121.50278°W
- Prince of Wales Strait - 72°21′14″N 118°46′57″W / 72.35389°N 118.78250°W
- Dolphin and Union Strait - 69°05′10″N 116°02′30″W / 69.08611°N 116.04167°W
- Austin Bay - 68°33′N 113°10′W / 68.550°N 113.167°W
- Coronation Gulf - 68°08′N 112°00′W / 68.133°N 112.000°W
- Dease Strait - 68°50′N 107°30′W / 68.833°N 107.500°W
- Storkerson Peninsula - 72°30′N 106°30′W / 72.500°N 106.500°W
- Goldsmith Channel - 73°10′N 106°05′W / 73.167°N 106.083°W
- Stefansson Island - 73°20′N 105°45′W / 73.333°N 105.750°W
- Hadley Bay - 72°31′N 108°12′W / 72.517°N 108.200°W
- Prince Albert Peninsula - 72°30′02″N 117°00′09″W / 72.50056°N 117.00250°W
- Wollaston Peninsula - 69°41′05″N 115°10′30″W / 69.68472°N 115.17500°W
- Shaler Mountains - 71°55′02″N 111°30′07″W / 71.91722°N 111.50194°W
- Tahiryuaq - 69°25′16″N 105°16′03″W / 69.42111°N 105.26750°W
- Cambridge Bay - 69°06′50″N 105°03′10″W / 69.11389°N 105.05278°W
- Ulukhaktok - 70°44′12″N 117°46′19″W / 70.73667°N 117.77194°W
- Fort Collinson - 71°37′02″N 117°52′09″W / 71.61722°N 117.86917°W
More to Explore
 In Spanish: Isla Victoria (Canadá) para niños
In Spanish: Isla Victoria (Canadá) para niños
 | Audre Lorde |
 | John Berry Meachum |
 | Ferdinand Lee Barnett |