Centralia, Washington facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Centralia
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|

Centralia downtown historic district
|
|||
|
|||
| Nickname(s):
Hub City, City of Azaleas
|
|||
Location of Centralia, Washington
|
|||
| Country | United States | ||
| State | Washington | ||
| County | Lewis | ||
| Government | |||
| • Type | Council–manager | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 7.81 sq mi (20.22 km2) | ||
| • Land | 7.62 sq mi (19.74 km2) | ||
| • Water | 0.19 sq mi (0.48 km2) | ||
| Elevation | 164 ft (50 m) | ||
| Population
(2020)
|
|||
| • Total | 18,183 | ||
| • Estimate
(2024)
|
19,061 | ||
| • Density | 2,386.22/sq mi (921.12/km2) | ||
| Time zone | UTC-8 (PST) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-7 (PDT) | ||
| ZIP code |
98531
|
||
| Area code(s) | 360 | ||
| FIPS code | 53-11160 | ||
| GNIS feature ID | 2409429 | ||
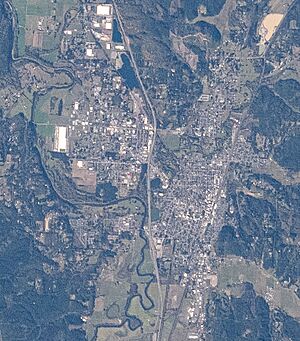
Centralia is a city in Lewis County, Washington, United States. It is located along Interstate 5, about halfway between Seattle and Portland, Oregon. In 2020, the city had a population of 18,183 people. Centralia is often called a "twin city" with Chehalis, which is located just south of Centralia.
Contents
History
The area where Centralia now stands was first settled by the Upper Chehalis people. The first non-Native American settlers arrived in 1845. In 1850, a free African-American man named George Washington moved there with his adopted parents. They left Missouri because they worried he might be forced into slavery after a new law was passed.
George Washington's adopted father bought land in 1852. He was able to sell this land to George Washington for $6,000. This was important because, unlike the nearby Oregon Territory, the new Washington Territory allowed African Americans to own land. By 1857, a major road connected the new community to other regions. In the 1850s and 1860s, the Borst Home in Centralia was a key stopping point for stagecoaches and had a toll ferry.
When the Northern Pacific Railway was expected to arrive in 1872, George Washington and his wife, Mary Jane, planned a town called Centerville. They named the streets after Bible themes and sold land lots for $10 each. They even gave a free lot to anyone who built a house. Washington also gave land for a city park, a cemetery, and a church.
By 1883, the town was renamed Centralia. This name was suggested by a new settler from Centralia, Illinois, because it was a "central" point. The town officially became a city on February 3, 1886. Its population grew quickly. However, it faced a tough time during the Panic of 1893 when the railway went bankrupt. George Washington helped the town survive by giving loans and forgiving debts, even though he faced prejudice. The city then grew again thanks to coal, lumber, and dairy farming. When Washington passed away in 1905, all businesses in town closed, and 5,000 people attended his funeral. In 2023, Centralia honored him by making August 15, his birthday, "Founder's Day."
On June 26, 1908, a large fire destroyed a block in the city's downtown area. The fire started early in the morning at the Star Saloon. Twelve buildings were lost, but only one person was reported injured.
On November 11, 1919, a sad event known as the Centralia Massacre happened. During an Armistice Day parade, a group of American Legionnaires attacked the Industrial Workers of the World (IWW) hall. The IWW members, including a veteran named Wesley Everest, defended themselves, and four Legionnaires died. Everest was captured and died while jailed. Other IWW members were also jailed. This event was reported worldwide and, along with similar actions, affected the labor movement in America for a while.
The town's name, Centralia, originally meant it was the middle point between Tacoma and Kalama. Later, it became the midpoint between Seattle and Portland, Oregon after Interstate 5 was built.
Geography
Centralia covers about 7.56 square miles (19.58 square kilometers). Most of this area is land, with a small part being water.
Landforms
Plummer Lake is a small lake near Interstate 5. It was created when glacial rock was dug up for gravel starting in 1910. The lake is named after Sydney Plummer, who owned the quarry. As of 2017, Plummer Lake is privately owned.
Climate
Centralia has a climate with warm, dry summers and mild winters. This is known as a warm-summer Mediterranean climate. Temperatures are generally mild, but Centralia can be warmer in summer and colder in winter than places further north along the Puget Sound.
| Climate data for Centralia, Washington, 1991–2020 normals, extremes 1893–present | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 68 (20) |
75 (24) |
85 (29) |
93 (34) |
98 (37) |
107 (42) |
107 (42) |
103 (39) |
100 (38) |
92 (33) |
75 (24) |
73 (23) |
107 (42) |
| Mean maximum °F (°C) | 57.1 (13.9) |
60.8 (16.0) |
69.3 (20.7) |
77.8 (25.4) |
84.8 (29.3) |
88.0 (31.1) |
93.7 (34.3) |
93.1 (33.9) |
87.6 (30.9) |
76.0 (24.4) |
62.3 (16.8) |
56.1 (13.4) |
96.8 (36.0) |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 46.1 (7.8) |
49.5 (9.7) |
54.1 (12.3) |
59.5 (15.3) |
66.6 (19.2) |
71.1 (21.7) |
77.5 (25.3) |
78.2 (25.7) |
72.6 (22.6) |
61.1 (16.2) |
50.7 (10.4) |
45.0 (7.2) |
61.0 (16.1) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 40.2 (4.6) |
41.7 (5.4) |
45.0 (7.2) |
49.3 (9.6) |
55.5 (13.1) |
60.1 (15.6) |
65.2 (18.4) |
65.5 (18.6) |
60.5 (15.8) |
51.9 (11.1) |
43.9 (6.6) |
39.4 (4.1) |
51.5 (10.8) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 34.2 (1.2) |
33.9 (1.1) |
35.9 (2.2) |
39.1 (3.9) |
44.4 (6.9) |
49.1 (9.5) |
52.9 (11.6) |
52.8 (11.6) |
48.4 (9.1) |
42.7 (5.9) |
37.1 (2.8) |
33.9 (1.1) |
42.0 (5.6) |
| Mean minimum °F (°C) | 22.8 (−5.1) |
23.2 (−4.9) |
27.0 (−2.8) |
30.8 (−0.7) |
35.3 (1.8) |
41.8 (5.4) |
45.9 (7.7) |
45.8 (7.7) |
39.8 (4.3) |
31.1 (−0.5) |
25.2 (−3.8) |
22.2 (−5.4) |
17.3 (−8.2) |
| Record low °F (°C) | −4 (−20) |
0 (−18) |
13 (−11) |
20 (−7) |
27 (−3) |
31 (−1) |
33 (1) |
35 (2) |
24 (−4) |
20 (−7) |
5 (−15) |
0 (−18) |
−4 (−20) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 5.85 (149) |
4.24 (108) |
4.39 (112) |
3.24 (82) |
2.44 (62) |
1.53 (39) |
0.50 (13) |
0.84 (21) |
1.59 (40) |
4.00 (102) |
6.53 (166) |
6.44 (164) |
41.59 (1,058) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 3.4 (8.6) |
1.4 (3.6) |
0.5 (1.3) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.0 (0.0) |
0.4 (1.0) |
0.9 (2.3) |
6.6 (16.8) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in) | 21.7 | 17.6 | 19.5 | 17.1 | 12.1 | 8.9 | 3.9 | 4.6 | 8.1 | 15.6 | 21.1 | 22.1 | 172.3 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.1 in) | 1.6 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 3.4 |
| Source 1: NOAA | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: National Weather Service | |||||||||||||
Population and People
Centralia has grown steadily over the years. In 2010, there were 16,336 people living in the city. By 2020, the population had grown to 18,183.
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1890 | 2,026 | — | |
| 1900 | 1,600 | −21.0% | |
| 1910 | 7,311 | 356.9% | |
| 1920 | 7,549 | 3.3% | |
| 1930 | 8,058 | 6.7% | |
| 1940 | 7,414 | −8.0% | |
| 1950 | 8,657 | 16.8% | |
| 1960 | 8,586 | −0.8% | |
| 1970 | 10,054 | 17.1% | |
| 1980 | 11,555 | 14.9% | |
| 1990 | 12,101 | 4.7% | |
| 2000 | 14,742 | 21.8% | |
| 2010 | 16,336 | 10.8% | |
| 2020 | 18,183 | 11.3% | |
| 2024 (est.) | 19,061 | 16.7% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census 2020 Census |
|||
2010 Census Facts
In 2010, about 85% of the people in Centralia were White. About 16% of the population was Hispanic or Latino.
The average age in Centralia was about 34.8 years old. About 24.7% of residents were under 18, and 16.6% were 65 or older.
Economy and Jobs
Centralia started as a railroad town, and its economy depended on railroads, timber, coal, and farming. At one time, five different railroad lines crossed in Centralia.
When Mount St. Helens erupted in 1980, it greatly affected the local lumber industry. Many jobs were lost, and the city's retail businesses struggled.
In 1988, a company called London Fog opened the first factory outlet store in the Northwest in Centralia. This was because Centralia is halfway between major cities. Its success led to the creation of the region's first factory outlet center, making Centralia a popular shopping spot for tourists. This also helped the downtown area become a place for antique, art, and specialty stores.
The Port of Centralia was created in 1986 to help the city's economy grow beyond lumber. It started building its facilities in 1988, and the first business moved in by 1990. As of 2016, the Port of Centralia had 30 businesses and employed 800 people.
Chehalis Mints, a company that makes mint and mint chocolate candies, was founded in Centralia in 1994. Its products are mainly sold in the Pacific Northwest.
As older industries declined, Centralia focused on businesses near the freeway, like food, hotels, and shops. It also became a hub for shipping and warehousing. This shift has helped the city's population grow by 60% since the 1980s.
TransAlta Coal Mine and Power Plant
On November 28, 2006, it was announced that TransAlta, a major employer in Centralia, would close its coal mine. This mine was the last working coal mine in Washington state. The company offered land and money to the city to help with the economic changes. Despite worries, the city did not suffer much economically from the mine's closure. Centralia continued to grow in its industrial and downtown areas. The mine site is now being restored, with land being filled, reshaped, and new trees planted. As of 2023, half of this restoration project was complete. The site might become a recreation area in the future.
The power plant, which uses coal, was built in the early 1970s. It is Washington state's last coal-powered energy factory. At its busiest, it produced enough energy to power a city as big as Los Angeles. The plant is expected to close permanently in 2025, based on an agreement made in 2011. The first part of the shutdown was completed in 2020. The energy produced until its closure is used by Puget Sound Energy (PSE). In 2022, about 14.5% of PSE's electricity came from this plant, enough for 300,000 homes. There are plans to use the site for green energy facilities, like those generating power from hydrogen.
TransAlta created a $20 million fund to help train and educate employees affected by the closures. This is part of a larger program that also provides money for energy efficiency and technology for nearby communities and schools. The land at the site is slowly being prepared for public and business use, including planting trees and maintaining wetlands.
Arts and Culture
Festivals and Events
Centralia hosts the annual Hub City Car Show, usually in late summer. It takes place in the downtown area, where the main street is closed for the event.
The Centralia Campout is a yearly gathering of folk musicians in August. It focuses on American Old-time music, with jam sessions, dances, and workshops.
The Centralia Lighted Tractor Parade is a yearly winter holiday event since 2009. It happens in early December and features decorated tractors parading through downtown. A local resident who has helped the community is chosen as the Grand marshal.
Girls Night Out is an event held twice a year to support downtown businesses and raise money for local charities. It started in 2008.
Historic Buildings and Sites
The Carnegie Library, built in 1913, is in Washington Park. It was remodeled in the late 1970s and is now part of the Timberland Regional Library system.
Centralia Union Depot was built in 1912. It has beautiful red brick, old oak benches, and detailed woodwork. This renovated train station is listed on the National Register of Historic Places and is currently used by Amtrak trains.
Fort Borst Park is home to the Fort Borst blockhouse and the Borst Home. The blockhouse is a log building from 1856, used for grain storage during conflicts with Native Americans. It was moved twice and is now in the park. Joseph Borst bought the blockhouse in 1857 and built the Borst Home next to it in 1864. The home is near where a toll ferry used to be. The site also has a recreated one-room schoolhouse and a church. The Borst Home is listed on the National Register of Historic Places.
Centralia has other historic sites listed on the National Register of Historic Places, including the George E. Birge House, the Hubbard Bungalow, and the Wesley Everest Gravesite. The Centralia Downtown Historic District is also historic and includes McMenamin's Olympic Club Hotel & Theater, a historic hotel and restaurant that opened in 1908.
Another notable building is the one-room Salzer Valley Schoolhouse. Built in 1894, it was a school until 1944.
Movie Theaters
Centralia once had the Twin City Drive-In movie theater. It started in 1933 as a single outdoor screen. In the 1950s, it was known for showing some movies that were considered a bit daring for the time. The drive-in also had a train ride for children. A second screen was added later, but the theater eventually closed. In 2002, someone bought the neon entrance sign to save it. Windstorms damaged the screens, and a fire in 2023 destroyed the remaining building. As of 2023, there are not many visible parts left of the old drive-in.
Music
The Seattle-based rock band Harvey Danger used Centralia as a metaphor in their song "Moral Centralia" from their 2005 album Little by Little.
Public Art
Many murals can be found throughout historic downtown Centralia. Some show the city's founder, George Washington, while others depict historical events like the 1919 Armistice Day Centralia Massacre.
Centralia is part of the ARTrails of Southwest Washington, a group that promotes local artists and galleries. They hold an annual studio tour in the fall. ARTrails opened a gallery in Centralia in 2015, and the Centralia Train Depot is a central point for the tour.
Theater
The Evergreen Playhouse has been Centralia's theater since 1959. It started as a small group performing in a ballroom. The organization bought its own theater building in 1972. During the Covid-19 pandemic, the 130-seat playhouse was renovated. As of 2023, the Evergreen Playhouse is a non-profit, volunteer-run theater that has always managed to operate without losing money.
Sports
Centralia had a minor league baseball team in the early 1900s. The team was known by different names, like the Midgets, Pets, and Railroaders. They won the 1911 Washington State League championship. The team stopped playing in 1912, and Centralia has not had an official minor league team since. They played their games at Riverside Park.
A bicycle event called the Centralia to Chehalis Bike Ride used to be held regularly. The route went from George Washington Park, around the Chehalis–Centralia Airport, through neighborhoods, and ended in Chehalis.
Parks and Recreation
Centralia's parks are divided into natural areas, neighborhood parks, and community parks. There are also sports fields and water parks.
George Washington Park, in downtown Centralia, is home to the Centralia Timberland Library. The park has a statue called The Sentinel and the Freedom Walk War Memorial. Both honor Centralia soldiers who died in World War I. The statue also remembers the American Legion members who died during the 1919 Armistice Day Riot. A bronze plaque honoring the deaths of members of the IWW during the Centralia Tragedy was added next to the statue in 2023. The Freedom Walk, built in 1993, lists the names of veterans who died in combat since World War I.
The Seminary Hill Natural Area is a preserve of over 80 acres (32 hectares) with more than two miles of trails. It was once the site of a seminary.
Riverside Park, about 4.5 acres (1.8 hectares), is located along the Skookumchuck River. It was donated to the city in 1983. The park has a large skate park and a covered playground.
Bob Peters Field is a sports complex at the Centralia College campus. Named after a long-time athletic director, this 4.0-acre (1.6-hectare) site has fields for baseball, softball, and soccer. It was finished in 2023.
The Veteran's Memorial Pearl Street Pool was built in the 1950s. The city owned it until the 1980s, then a local non-profit took over. Centralia got the pool back in 2008 but closed it in 2011 due to high repair costs and lack of funds. Since then, a playground and spray park have been added to the area. In 2023, the city council decided to permanently close the pool and filled it with dirt for safety reasons. Another community pool, the Centralia Community Pool, is run jointly by the city, the school district, and a local fitness company.
Fort Borst Park
Fort Borst Park is Centralia's largest park, covering 101.0 acres (40.9 hectares) at the meeting point of the Chehalis and Skookumchuck rivers. It has 2.1 miles (3.4 kilometers) of paved trails in a forested area, a dog park, and a large picnic area. Visitors can fish from the riverbanks or use a boat launch. Borst Lake in the park is stocked with rainbow trout.
The park contains the original Borst Home, a recreated schoolhouse, and a replicated pioneer church from the 1860s. The Borst Park Arboretum, created in 1960, surrounds the homestead. It has the Borst family cemetery, nearly 200 trees, and many rhododendrons. The park also hosts an annual Christmas "Drive-Through Lights" event that collects food and raises money for the park department.
Inside Fort Borst Park is Centralia's NW Sports Hub, which opened in 2014. This 76,500-square-foot (7,100 square meter) complex has indoor courts for volleyball and basketball, and fields for indoor baseball and soccer. Outside, there are baseball fields, tennis courts, more soccer fields, and the Centralia High School track stadium, which can seat 3,500 people. In 2023, the outdoor fields received new lighting and turf. The complex is used for community events, high school sports tournaments, and college scouting events.
Government and Politics
Centralia is a city with a council-manager system. This means the City Council, made up of seven members, makes decisions, and a city manager handles the day-to-day operations.
Centralia tends to be politically conservative and often supports the Republican party, similar to Lewis County as a whole.
Education
The Centralia School District is in charge of student education in Centralia.
Centralia College
Centralia College is the oldest continuously operating junior college in Washington state. It was founded on September 14, 1925.
Media
Newspaper
Centralia's main newspaper is The Chronicle. It serves most of Lewis County. There are also smaller community newspapers published twice a week, like The Lewis County News.
Radio
The Centralia area has two AM radio stations, KELA - 1470 AM and KITI - 1420 AM. The FM station, KCED - 91.3 FM, operates from within the city. You can also listen to radio broadcasts from nearby Chehalis stations KMNT - 104.3 FM and KACS - 90.5 FM.
Transportation
Air
Centralia is served by the Chehalis–Centralia Airport. The city used to co-own the airport but stopped in 2004. Centralia also once had its own Centralia Municipal Air Field, which opened in 1927 but closed by the mid-1930s due to economic difficulties.
Railroads
Amtrak, the national passenger train system, serves Centralia station at the renovated 1912 railroad depot. The southbound Coast Starlight train stops in Centralia, heading to cities like Portland, Sacramento, and Los Angeles. The northbound Coast Starlight goes to Olympia-Lacey, Tacoma, and Seattle. Amtrak Cascades trains also serve Centralia multiple times a day, traveling between Vancouver, British Columbia, and Eugene, Oregon. Freight trains also use the rail lines in Centralia, which can sometimes affect Amtrak schedules.
Public Transportation
Bus service in Centralia is provided by Lewis County Transit. Buses from Centralia go to places like Olympia, Chehalis, and Kelso.
Automotive
Centralia is located right next to I-5, almost exactly halfway between Portland and Seattle. Its main exit is at mile marker 82. U.S. Route 12 also passes through Centralia, sharing the road with I-5 for a bit. Washington State Route 507 starts in Centralia and goes north through towns like Tenino and Yelm.
Utilities
Communications
Telephone services in Centralia began in 1891. The first customer was a pair of lawyers. By 1910, over 500 customers had telephone lines. By the mid-1960s, over 12,000 customers in Centralia and Chehalis had phone service.
Water
As of 2023, Centralia Public Works received money to find lead pipes in the city's water system. The city has found very few lead connections since the late 1970s.
Centralia built a new wastewater treatment facility starting in 2001. This facility, which cost almost $27 million, replaced an older plant. As of 2024, the facility can process up to 10.5 million US gallons (40 million liters) of wastewater per day.
Notable People
- Charlie Albright, a pianist
- Calvin Armstrong, an American football player
- Bob Coluccio, a baseball player
- Merce Cunningham, a modern dancer
- Noah Gundersen, a singer
- Sandy Marth Hill, a TV journalist
- Soren Johnson, a video game designer
- James Kelsey, a sculptor
- Craig McCaw, an entrepreneur
- Angela Meade, an opera singer
- Lyle Overbay, a former Major League Baseball player
- Brock Peterson, a former Major League Baseball player
- Detlef Schrempf, an NBA player
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Centralia (Washington) para niños
In Spanish: Centralia (Washington) para niños
 | Ernest Everett Just |
 | Mary Jackson |
 | Emmett Chappelle |
 | Marie Maynard Daly |