Chemical symbol facts for kids
Chemical symbols are like short nicknames for things in chemistry. They are mostly used for chemical elements, which are the basic building blocks of everything. But they can also stand for groups of atoms or even whole chemical compounds. Most element symbols are one or two letters from the Latin alphabet. The first letter is always a capital letter.
Contents
Why Do We Use Chemical Symbols?
Using symbols makes it much easier to write about chemistry! Imagine having to write "hydrogen" or "oxygen" every time. With symbols like H for hydrogen and O for oxygen, writing chemical formulas like H2O (water) becomes super quick and clear.
A Look Back: How Symbols Started
The first chemical symbols came from old Latin and Greek words. For example:
- Pb is the symbol for lead. It comes from the Latin word plumbum.
- Hg is for mercury. This comes from the Greek word hydrargyrum.
- He is for helium. This name is newer because helium wasn't known in ancient times.
- W is for tungsten. This symbol comes from the German word Wolfram.
Sometimes, when a new element is made in a lab, it gets a temporary three-letter symbol. For example, before element 108 was officially named hassium (Hs), its temporary symbol was "Uno" from its temporary name unniloctium.
Adding Details to Symbols
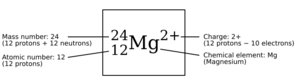
You might see extra numbers or letters added to a chemical symbol. These are like secret codes that tell you more about the element! They can be written as small numbers or letters above or below the main symbol.
- Top-left number: This tells you the mass number (how many protons and neutrons are in that specific version of the element, called an isotope). For example, 14N means a nitrogen atom with a mass number of 14.
- Bottom-left number: This shows the atomic number (how many protons are in the atom). For example, 64Gd is gadolinium, which always has 64 protons. This number is usually left out because the element symbol already tells you the atomic number.
- Top-right number/symbol: This shows if an atom has an electric charge (like Ca2+ for a calcium ion with a +2 charge).
- Bottom-right number: This tells you how many atoms of that element are in a molecule. For example, N2 means two nitrogen atoms are joined together. If there's only one atom, like in O for oxygen, the number 1 is usually not written.
Some groups of atoms that often appear together in molecules also have their own symbols, like Ph for the phenyl group or Me for the methyl group.
Symbols for Chemical Elements
Here is a list of some common chemical elements and what their symbols mean. The full periodic table has all the elements!
| Z | Symbol | Name | Origin of name |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | H | Hydrogen | From Greek words meaning 'water-forming' |
| 2 | He | Helium | From the Greek word for 'sun' |
| 3 | Li | Lithium | From the Greek word for 'stone' |
| 4 | Be | Beryllium | Named after the mineral beryl |
| 5 | B | Boron | From the mineral borax |
| 6 | C | Carbon | From the Latin word for 'coal' |
| 7 | N | Nitrogen | From Greek words meaning 'niter-forming' |
| 8 | O | Oxygen | From Greek words meaning 'acid-forming' |
| 9 | F | Fluorine | From the Latin word meaning 'to flow' |
| 10 | Ne | Neon | From the Greek word for 'new' |
| 11 | Na | Sodium | From the English word 'soda' (symbol from Latin natrium) |
| 12 | Mg | Magnesium | Named after Magnesia, a region in Greece |
...and many more elements are listed in the full periodic table!
Old and Temporary Symbols
Over time, some chemical symbols and names have changed. This happened as scientists learned more about elements. For example, the element argon used to have the symbol A, but now it's Ar. Also, new elements that are just discovered or made in a lab often get temporary symbols until they are officially named.
Scientists also used to have "systematic" names and symbols for very new, heavy elements. These names were based on the element's atomic number. For example, element 118 was temporarily called ununoctium (symbol Uuo) before it was officially named oganesson (Og).
Special Symbols for Isotopes
Most elements have different versions called isotopes. These isotopes have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Some very important isotopes have their own special symbols:
- D for deuterium (a heavier version of hydrogen, also called "heavy hydrogen").
- T for tritium (an even heavier version of hydrogen).
You might see "d" used in chemistry to show that a molecule contains deuterium instead of regular hydrogen. For example, C6D6 is a type of benzene made with deuterium.
Other Chemical Symbols You Might See
Besides element symbols, chemists use other abbreviations:
General Symbols
- A: Can mean an acid or a negatively charged ion (anion).
- E: Can mean any element or an electrophile (something that likes electrons).
- L: Stands for any ligand (a molecule or ion that binds to a central metal atom).
- M: Represents any metal.
- R: In organic chemistry, this often means any unspecified group of atoms that isn't important for what's being discussed.
- X: Usually means any halogen element (like fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine).
Organic Chemistry Symbols
Organic chemistry is the study of compounds that contain carbon. Here are some common symbols used there:
 In Spanish: Símbolo químico para niños
In Spanish: Símbolo químico para niños
See also
Images for kids