Circuit (administrative division) facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Circuit |
|||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
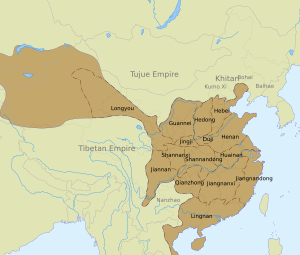
The inspection circuits of the Tang dynasty in 742
|
|||||||||||
| Dao (mainly Tang dynasty) | |||||||||||
| Chinese | 道 | ||||||||||
| Literal meaning | way, path, circuit | ||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| Lu (Song and Jin dynasties) | |||||||||||
| Chinese | 路 | ||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| Korean name | |||||||||||
| Hangul | 도 | ||||||||||
| Hanja | 道 | ||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| Japanese name | |||||||||||
| Kanji | 道 | ||||||||||
| Kana | どう | ||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
A circuit (called dào or lù in Chinese) was a special type of administrative division used in the past in China. It was also a historical and modern administrative unit in Japan. In Korea, a similar term (do) is used for their main administrative divisions, which are usually called provinces because they are very important.
Contents
Circuits in China
| "Circuit" | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Period | Chinese | Pinyin | Level |
| Han | Chinese: 道 | dào | 3rd |
| Tang, Liao | 1st | ||
| Song, Jin | Chinese: 路 | lù | |
| Yuan | Chinese: 道 | dào | 2nd |
| Qing, ROC (12-28) | |||
| ROC (32-49) | Chinese: 行政督察區 | xíngzhèng dūchá qū | |
Early Circuits: Han Dynasty
Circuits first appeared in China during the Han dynasty. At this time, they were a lower-level administrative division. You could compare them to a county today.
These early circuits were mostly used in areas far from the main parts of the empire. These were often places where non-Han Chinese people lived. They were also used in areas that were hard to reach due to geography. The system stopped being used after the Western Jin dynasty ended.
Revival and Change: Tang to Yuan Dynasties
The idea of circuits was brought back in 627 during the Tang dynasty. Emperor Taizong of Tang made circuits the highest administrative division. He divided China into ten circuits. At first, these were just geographical areas, not meant for direct administration.
Later, Emperor Xuanzong of Tang added five more circuits. Over time, these circuits became very powerful regional forces. They even caused the country to break apart during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period.
During the Song dynasty and Jin dynasties, circuits were renamed lu. Both dao and lu mean "road" or "path."
The dao circuits were used again during the Yuan dynasty. However, they were no longer the top division. The Yuan dynasty created provinces as the highest level. This meant circuits became the second-highest level. They stayed at this level for several centuries.
Later Circuits: Qing and Republic of China
Under the Qing dynasty, circuits were managed by an official called a circuit intendant or tao-tai. The circuit intendant in Shanghai was especially important and powerful.
During the Republic of China era, circuits still existed. They were high-level divisions, but not the very top. An example is the Qiongya Circuit, which is now Hainan province.
In 1928, after China was reunified, all circuits were replaced or simply removed. But in 1932, "administrative circuits" were brought back. They continued to exist until 1949.
After the People's Republic of China was founded in 1949, these administrative circuits changed names. They became zhuanqu and later diqu (which means "prefecture").
Circuits in Japan
Gokishichidō: Ancient Japanese Circuits
During Japan's Asuka period (538–710), the country adopted a system from China. Japan was organized into five provinces and seven circuits. This system was known as the Gokishichidō (which means "5 provinces, 7 circuits").
Even though these units stopped being used as administrative structures after the Muromachi period (1336–1573), they remained important geographical areas until the 1800s.
The seven circuits covered the main islands of Honshū, Shikoku, and Kyūshū:
- Tōkaidō ("East Sea Circuit"): This circuit had 15 provinces.
- Nankaidō ("South Sea Circuit"): This circuit had 6 provinces.
- Saikaidō ("West Sea Circuit"): This circuit had 8 provinces.
- Hokurikudō ("North Land Circuit"): This circuit had 7 provinces.
- San'indō ("Shaded-side Circuit"): This circuit had 8 provinces.
- San'yōdō ("Sunny-side Circuit"): This circuit had 8 provinces.
- Tōsandō ("East Mountain Circuit"): This circuit had 13 provinces.
Hokkaido: A Modern Circuit
In the mid-1800s, the northern island of Ezo was settled. It was then renamed Hokkaidō, which means "North Sea Circuit."
Today, Hokkaido is the only prefecture in Japan that still uses the dō (circuit) suffix in its name.
Circuits in Korea
Since the late 900s, the do (which means "province") has been the main administrative division in Korea. These "provinces" are similar to the circuits in China and Japan.
You can learn more about them by looking at the Eight Provinces of Korea, Provinces of Korea, Subdivisions of South Korea, and Administrative divisions of North Korea.
See also
 In Spanish: Circuito (división administrativa) para niños
In Spanish: Circuito (división administrativa) para niños
 | Aurelia Browder |
 | Nannie Helen Burroughs |
 | Michelle Alexander |