Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA)
|
|
|---|---|
|
Anthem: "People of Africa"
|
|
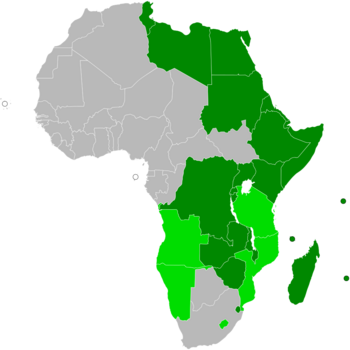
Map of Africa indicating COMESA membership.
Current members Former members |
|
| Secretariat | |
| Official languages | |
| Type | Trade bloc |
| Membership | 21 member states |
| Leaders | |
|
• Secretary General
|
Chileshe Mpundu Kapwepwe |
| Establishment | Agreement |
|
• Signed
|
5 November 1993 |
|
• Ratified
|
8 December 1994 |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
12,000,000 km2 (4,600,000 sq mi) |
| Population | |
|
• Estimate
|
Over 640 million |
| GDP (PPP) | estimate |
|
• Total
|
$1.0 trillion |
The Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA) is a group of twenty-one countries in Africa. These countries stretch from Tunisia in the north all the way to Eswatini in the south. COMESA was created in December 1994. It took over from an older group called the Preferential Trade Area, which had been around since 1981.
COMESA helps its member countries work together. Nine of these countries created a free trade area in 2000. This means they removed special taxes on goods traded between them. More countries joined this free trade area later, making it easier for businesses to trade across the region.
COMESA is an important part of the bigger African Economic Community. This community aims to bring all African countries closer through trade and cooperation.
In 2008, COMESA agreed to make its free trade zone even bigger. This new zone would include members from two other African trade groups: the East African Community (EAC) and the Southern Africa Development Community (SADC). COMESA is also thinking about a common visa. This would make it easier for tourists to visit many member countries with just one travel document.
Contents
Who are the Member Countries?
COMESA has 21 member countries. They work together to improve trade and economic growth.
Current Members
Here are the countries that are currently part of COMESA:
- Djibouti (joined 1981)
- Eritrea (joined 1994)
- Ethiopia (joined 1981)
- Somalia (joined 1981, then 2018 for COMESA)
- Egypt (joined 1999)
- Libya (joined 2005)
- Sudan (joined 1981)
- Tunisia (joined 2018)
- Comoros (joined 1981)
- Madagascar (joined 1981)
- Mauritius (joined 1981)
- Seychelles (joined 2001)
- Burundi (joined 1981)
- Kenya (joined 1981)
- Malawi (joined 1981)
- Rwanda (joined 1981)
- Uganda (joined 1981)
- Eswatini (joined 1981)
- Zambia (joined 1981)
- Zimbabwe (joined 1981)
- Democratic Republic of the Congo (joined 1981)
Former Members
Some countries have left COMESA over the years:
- Lesotho (left 1997)
- Mozambique (left 1997)
- Tanzania (left 2000)
- Namibia (left 2004)
- Angola (left 2007)
How COMESA Works
COMESA has different groups that make decisions and help it run smoothly.
The Authority
This is the most important group. It is made up of the leaders (Presidents or Prime Ministers) of all the member countries. They meet once a year to set the main goals and plans for COMESA. The leader of the country hosting the meeting becomes the Chairman for that year. Decisions are usually made by everyone agreeing.
The Council of Ministers
This group helps carry out the decisions made by the Authority. It is made up of ministers from each member country.
The COMESA Court of Justice
This court helps solve disagreements related to COMESA's rules. Its decisions are very important and must be followed by member countries. People or businesses can also bring cases to this court if they believe a COMESA rule or a country's action goes against the treaty. The court also handles issues between COMESA and its employees.
The Court has two parts:
- The Court of First Instance: This is where cases are heard for the first time.
- The Appellate Division: This part reviews decisions from the Court of First Instance if someone wants to appeal.
Even though the Court is important, it sometimes faces challenges. For example, it might not have enough money to hear all its cases quickly. This can lead to a backlog of cases, especially as trade disputes in the region grow.
Other Important Groups
- Committee of Governors of Central Banks: This group helps manage money matters and financial stability in the region.
- The Secretariat: This is like the main office of COMESA. It manages the day-to-day work and helps organize meetings.
There are also other groups that give advice and recommendations to the main decision-making bodies.
COMESA's Other Institutions
COMESA has also created special institutions to help with development and trade:
- The PTA Bank: This bank helps fund trade and development projects in Eastern and Southern Africa. It is located in Bujumbura, Burundi.
- The COMESA Clearing House: This helps make payments easier between businesses in different member countries. It is in Harare, Zimbabwe.
- The COMESA Association of Commercial Banks: This group brings together banks from the region to work on common goals. It is also in Harare, Zimbabwe.
- The COMESA Leather Institute: This institute helps develop the leather industry in the region. It is in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.
- The COMESA Re-Insurance Company (ZEP-RE): This company helps provide insurance for large projects and risks. It is located in Nairobi, Kenya.
- The Regional Investment Agency: This agency helps attract new investments into the COMESA region. It is in Cairo, Egypt.
- COMTEL Project: This project aims to build better telephone and internet connections across the region.
How COMESA Compares to Other Groups
COMESA is one of several groups in Africa that work on economic cooperation. It is part of the larger goal to create a single economic community across the whole continent. Other similar groups include the East African Community (EAC) and the Southern African Development Community (SADC). These groups often work together on bigger projects, like the expanded free trade zone.
See also
- Rules of Origin
- Market access
- Free-trade area
- Tariffs
- Trade bloc
- East African Community (EAC)
- Economic Community of Central African States (ECCAS)
- Southern African Development Community (SADC)
- Southern African Customs Union (SACU)
- Southern African Confederation of Agricultural Unions (SACAU)
- Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS)
- Arab Maghreb Union (UMA)
- Intergovernmental Authority on Development (IGAD)
- Greater Arab Free Trade Area (GAFTA)
- Yellow card system, the COMESA motor insurance scheme.
 | DeHart Hubbard |
 | Wilma Rudolph |
 | Jesse Owens |
 | Jackie Joyner-Kersee |
 | Major Taylor |

