ExxonMobil facts for kids

Floating cube at ExxonMobil headquarters in Spring, Texas
|
|
|
Formerly
|
|
|---|---|
| Public | |
| Traded as | |
| ISIN | [https://isin.toolforge.org/?language=en&isin=US30231G1022 US30231G1022] |
| Industry | Energy |
| Predecessors |
|
| Founded | August 5, 1882 |
| Founders |
|
| Headquarters | Spring, Texas, U.S. |
|
Area served
|
Worldwide |
|
Key people
|
Darren Woods (chairman & CEO) |
| Products |
|
| Brands |
|
| Revenue | |
|
Operating income
|
|
| Total assets | |
| Total equity | |
|
Number of employees
|
60,900 (2024) |
| Parent | Standard Oil (1882–1911) |
| Subsidiaries |
|
Exxon Mobil Corporation is a huge American company that works with oil and gas. Its main office is in Spring, Texas, near Houston. It was formed in 1999 when two big companies, Exxon and Mobil, joined together. These companies were once part of John D. Rockefeller's original Standard Oil company.
ExxonMobil is involved in every step of the oil and gas business. This includes finding oil, drilling for it, and turning it into products like gasoline and plastics. It is one of the largest energy companies in the world that is owned by investors, not governments.
Like many large companies, ExxonMobil has faced challenges and criticisms. These often relate to environmental events, such as oil spills. One of the most well-known was the 1989 Exxon Valdez oil spill in Alaska. The company is working on new ways to produce energy and reduce its environmental impact.
Contents
A Look at ExxonMobil's History
ExxonMobil's story began a long time ago with the Vacuum Oil Company, started in 1866. This company later became part of Standard Oil. After Standard Oil was broken up in 1911, its New Jersey branch, known as Jersey Standard, grew very large.
Jersey Standard bought Humble Oil in the 1930s and became a major player in the global oil industry. To make all its brands like Esso, Enco, and Humble Oil easier to recognize, the company changed its name to Exxon in 1972.
In 1998, Exxon and Mobil decided to merge. This big deal was completed on November 30, 1999. They merged to better compete in the global market and deal with changing oil prices. The new company was named ExxonMobil, combining both famous names.
How ExxonMobil Operates Globally
ExxonMobil is one of the biggest non-government energy companies. It produces about 3% of the world's oil and 2% of the world's total energy. The company has many different parts that work together. These parts are usually grouped into three main areas.
- Upstream: This involves finding and drilling for oil and natural gas.
- Product Solutions: This part turns crude oil into useful products like gasoline and chemicals.
- Low Carbon Solutions: This newer division focuses on cleaner energy and reducing carbon emissions.
Finding and Producing Oil (Upstream)
The upstream division is where ExxonMobil gets most of its money, about 70%. In 2021, ExxonMobil had about 30 billion barrels of oil and oil equivalents. They also had 38.1 billion cubic feet of natural gas.
In the United States, ExxonMobil drills for oil and gas in places like the Permian Basin and the Gulf of Mexico. Their natural gas activities are handled by their company, XTO Energy. They also have joint projects, like Aera Energy LLC in California with Shell Oil.
ExxonMobil also has operations in many other countries. These include Canada, Argentina, Germany, Norway, and the United Kingdom. In Africa, they work in Angola, Chad, Equatorial Guinea, and Nigeria. In Asia, they have operations in Azerbaijan, Indonesia, Iraq, Kazakhstan, and Malaysia.
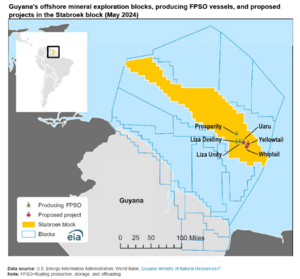
In March 2024, ExxonMobil found oil in the Stabroek block off the coast of Guyana. They plan to have six large floating production vessels there by the end of 2027.
Operations in Australia and Papua New Guinea
In Australia, ExxonMobil has large offshore areas for oil and gas. They also run the Longford Gas Conditioning Plant. In Papua New Guinea, they are involved in the PNG Gas project.
Making Products (Product Solutions)
ExxonMobil created its Product Solutions division in 2022. This part of the company combines their previous efforts in refining oil and making chemicals.

Gas Stations and Retail Products
ExxonMobil sells its products around the world using the brands Exxon, Mobil, and Esso. In the United States, Mobil is the main brand for gas stations in California, Florida, New York, and the Midwest. Exxon is used in most other parts of the U.S., especially in Texas and the Southeast.
Outside the U.S., Esso and Mobil are the main brands. Esso operates in 14 countries, and Mobil in 29. Since 2008, Mobil has been the only brand for the company's lubricants. ExxonMobil also has a rewards program where customers can earn points at their gas stations.
Chemical Products
ExxonMobil Chemical makes many different chemical products. These include basic chemicals like olefins and aromatics, which are used to make plastics. They also produce polyethylene and polypropylene, which are common plastics.
The company also makes special products like elastomers (used in rubber) and solvents. They are the largest producer of butyl rubber, which is used in tires and other products. ExxonMobil also has a joint company called Infineum with Shell plc, which makes additives for lubricants and fuels.
Sponsoring Sports
Mobil 1, a type of synthetic motor oil, is a big sponsor in racing. It has been the official motor oil of NASCAR since 2003. ExxonMobil also partners with teams like Oracle Red Bull Racing in Formula One.
Oil Refineries
ExxonMobil runs 21 oil refineries around the world. A refinery is a factory that turns crude oil into useful products like gasoline, diesel, and jet fuel. Their largest refinery is the ExxonMobil Beaumont Refinery in Texas. Another large one is the Baytown Refinery, also in Texas.
In 2017, a court ordered Exxon to pay money for breaking clean air rules at its Baytown facilities. This decision was confirmed in 2024. ExxonMobil has been expanding its refining capacity, including a large expansion at its Beaumont refinery in early 2023.
Working Towards a Low Carbon Future
ExxonMobil officially created its Low Carbon Solutions division in 2022. This part of the company focuses on finding cleaner energy solutions. It is led by Dan Ammann, who used to be the president of General Motors.
This division aims to reduce emissions in industries that are hard to make cleaner. These include heavy industry, transportation, and power generation. They plan to use cleaner fuels, hydrogen, and carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies.
Low Carbon Solutions also researches new energy technologies. These include algae biofuels and biodiesel made from farm waste. They are also looking into new ways to make plastic that produce less carbon dioxide. The company believes this low-carbon business could become as valuable as its oil and gas operations in the future.
Capturing Carbon and Storing It
ExxonMobil has announced it will invest $15 billion in a "lower carbon future." They say they are a world leader in carbon capture and storage (CCS). CCS is a process that captures carbon dioxide emissions from industrial sources and stores them underground.
The company also plans to make its own operations carbon neutral by 2050. This means they aim to balance the carbon they release with the carbon they remove. In 2022, ExxonMobil bought a biofuel company called Biojet AS. In July 2023, Exxon bought Denbury Resources to help with its low-carbon efforts. In July 2024, ExxonMobil and CF Industries agreed to capture and store 500,000 tonnes of CO2 per year starting in 2028.
New Low-Carbon Energy Projects
Exxon is working on several low-carbon energy projects. They are doing research in areas like algae biofuels and biodiesel from agricultural waste. They are also exploring new ways to make plastic that create less carbon dioxide.
Mining for Lithium
In November 2023, ExxonMobil started drilling for lithium in Arkansas, USA. Lithium is a key material for making lithium-ion batteries, which power electric vehicles. In June 2024, they signed an agreement to supply lithium to SK for these batteries.
Company Information
| Company | Revenue (USD) | Profit (USD) | Brands |
|---|---|---|---|
| ExxonMobil | $286 billion | $23 billion | Mobil Esso Imperial Oil |
| Shell plc | $273 billion | $20 billion | Jiffy Lube Pennzoil |
| TotalEnergies | $185 billion | $16 billion | Elf Aquitaine SunPower |
| BP | $164 billion | $7.6 billion | Amoco Aral AG |
| Chevron | $163 billion | $16 billion | Texaco Caltex Havoline |
| Marathon | $141 billion | $10 billion | ARCO |
| Phillips 66 | $115 billion | $1.3 billion | 76 Conoco JET |
| Valero | $108 billion | $0.9 billion | N/A |
| Eni | $77 billion | $5.8 billion | N/A |
| ConocoPhillips | $48.3 billion | $8.1 billion | N/A |
Business Performance
ExxonMobil is one of the largest companies in the world by revenue. For the year 2023, ExxonMobil reported a net income of US$36.0 billion.
Main Offices
ExxonMobil's main headquarters are in Spring, Texas. This location is a suburb of Houston. The company decided to bring all its Houston operations together into this new campus. The new complex has many office buildings, a wellness center, and laboratories. It is designed to hold almost 10,000 employees.
Company Leaders
The current chairman of the board and CEO of ExxonMobil Corp. is Darren W. Woods. He became chairman and CEO on January 1, 2017. Before that, he was the president of ExxonMobil.
As of August 2025, the board members include:
- Michael J. Angelakis
- Angela Braly
- Maria S. Dreyfus
- John D. Harris II
- Kaisa H. Hietala
- Joseph L. Hooley (lead independent director)
- Steven A. Kandarian
- Alexander A. Karsner
- Lawrence W. Kellner
- Dina Powell McCormick
- Jeffrey W. Ubben
- Darren W. Woods
The main executives at ExxonMobil are:
- Darren Woods, chairman and CEO
- Neil Chapman, Senior Vice President
- Kathryn Mikells, CFO and Senior Vice President
- Jack Williams, Senior Vice President
- James Spellings, General Tax Counsel and Vice President
Images for kids
-
Former ExxonMobil offices in Downtown Houston were vacated in early 2015.
See also
 In Spanish: ExxonMobil para niños
In Spanish: ExxonMobil para niños
 | Delilah Pierce |
 | Gordon Parks |
 | Augusta Savage |
 | Charles Ethan Porter |