Fjord facts for kids
A fjord (pronounced "fee-ord") is a long, narrow arm of the sea that stretches far inland. It has very steep sides, often like cliffs, and was created by a giant glacier moving slowly over the land.
Contents
Formation and Characteristics
How Fjords Are Made
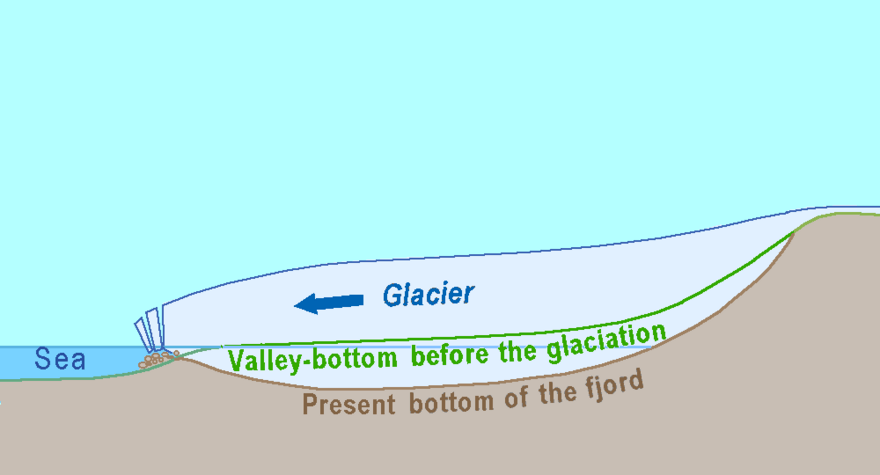
Fjords are formed when a huge glacier carves out a deep, U-shaped valley. This happens because the glacier's immense weight and movement grind away the rock beneath it. When the glacier melts and retreats, the sea fills up this deep valley, creating the narrow, steep-sided inlet we call a fjord.
Fjords are found in places where glaciers once reached below the current sea level. The sea fills the valley floor after the glacier has moved away. This creates a narrow, steep-sided inlet that can be very deep, sometimes over 1300 meters (about 4,265 feet) deep!
At the entrance of a fjord, there's often a shallow area. This is because the glacier pushed a lot of rock and dirt (called glacial debris) to the valley's end. This debris forms a natural barrier underwater. This shallow entrance, along with the protection from the valley's high sides, makes fjords excellent natural harbors. Many fishing boats use fjords as their home base. In some areas, fjords are also used for fish farming and building ships.
Amazing Underwater Life

Did you know that some of the world's largest coral reefs have been found at the bottom of Norwegian fjords? These reefs are found all along Norway's coast. The amazing marine life on these reefs is a big reason why Norway has such great fishing grounds.
These reefs are home to thousands of different creatures. You can find plankton, corals, anemones, fish, and even several types of sharks. Most of these creatures are specially adapted to live under the high pressure of deep water and in total darkness.
New Zealand's fjords also have deep-sea corals. However, a layer of dark freshwater on the surface allows these corals to grow in shallower water than usual. In Milford Sound, there's an underwater observatory. This lets tourists see these corals without needing to dive into the cold water.
Locations Around the World
Fjords can be found in many parts of the world, especially in places that were once covered by large glaciers. You can find them along the coasts of:
- Norway
- Iceland
- Greenland
- The west coast of Scotland
- The southwest corner of New Zealand
- The west coast of Newfoundland (Canada)
- British Columbia (Canada) down to Puget Sound (USA)
- The south and west coasts of Alaska (USA)
- Southern Chile
- The coast of the Baltic Sea in Germany
- Parts of Antarctica, especially the Antarctic Peninsula
- Various Arctic and Sub-antarctic islands
Longest and Deepest Fjords
The longest fjords in the world include:
- Scoresby Sund in Greenland—350 km (217 miles) long
- Sognefjord in Norway—204 km (127 miles) long
- Independence Fjord in Greenland—200 km (124 miles) long
- Matochkin Shar, Novaya Zemlya, Russia—125 km (78 miles) long
Some of the deepest fjords are:
- Skelton Inlet in Antarctica—1,933 m (6,342 ft) deep
- Sognefjord in Norway—1,308 m (4,291 ft) deep
- Messier Channel in Tortel, Chile—1,358 m (4,455 ft) deep
- Baker Channel in Tortel, Chile—1,251 m (4,104 ft) deep
Freshwater Fjords
Sometimes, a river flows into a lake or the sea. When this happens, the water slows down and drops the dirt and sand it was carrying. This sediment builds up at the river's mouth, forming a delta.
Some lakes in Norway are called "fjords" even though they are freshwater. These lakes formed in long valleys carved by glaciers. When the ice melted, it sometimes stayed in one place for a long time. This created landforms called "ice front deltas." These deltas are narrow strips of land between the lake and the saltwater fjord. They are great sources of sand and gravel for building houses and roads.
Some of these lakes were salty after the ice age. But later, they became cut off from the ocean as the land slowly rose (a process called post-glacial rebound). Some saltwater fish got trapped in these lakes. Over time, they slowly adapted to live in freshwater, like the arctic char.
Great Lakes Fjords
The North American Great Lakes also have a special type of freshwater fjord. For example, Baie Fine is located on the northwestern coast of Georgian Bay in Lake Huron, Ontario. It is one of the largest freshwater fjords in the world. Huron Bay is another example, found on the southern shore of Lake Superior in Michigan.
Images for kids
-
Sørfjorden (Hardanger) with Sandvinvatnet and Odda valley can be clearly seen as continuation of the fjord. Odda sits on the isthmus. Folgefonna on the right hand.
-
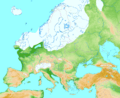
Distribution of ice (white) in Europe during the last glacial period
-
Fjord à Christiania, by Claude Monet (1895).
-
Holandsfjorden with Svartisen glacier in Nordland.
-
Eyjafjörður in north Iceland, Akureyri can be seen to the far right
-
Killary Harbour, western Ireland
-
New Zealand's Milford Sound
-
Glacier in a fjord at Kenai Fjords National Park, Alaska
-
The entrance to Larsen Harbour, a sub-embayment of Drygalski Fjord in South Georgia Island
-
The calving end of Inostrantsev Glacier at Inostrantsev Fjord, Novaya Zemlya.
See also
 In Spanish: Fiordo para niños
In Spanish: Fiordo para niños