Holmes County, Mississippi facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Holmes County
|
|
|---|---|
 |
|
Location within the U.S. state of Mississippi
|
|
 Mississippi's location within the U.S. |
|
| Country | |
| State | |
| Founded | 1833 |
| Named for | David Holmes |
| Seat | Lexington |
| Largest city | Durant |
| Area | |
| • Total | 765 sq mi (1,980 km2) |
| • Land | 757 sq mi (1,960 km2) |
| • Water | 7.9 sq mi (20 km2) 1.0% |
| Population
(2020)
|
|
| • Total | 17,000 |
| • Density | 22.2/sq mi (8.58/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−6 (Central) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−5 (CDT) |
| Congressional district | 2nd |
Holmes County is a county in the state of Mississippi. Its western border is the Yazoo River, and its eastern border is the Big Black River. The western part of the county is in an area called the Yazoo-Mississippi Delta.
In 2020, about 17,000 people lived here. The main town and county seat is Lexington. The county is named after David Holmes. He was a governor of Mississippi and later a U.S. Senator. Another important person from Holmes County was Edmond Favor Noel. He was a lawyer and served as Mississippi's governor from 1908 to 1912.
For a long time, the main crop grown in Holmes County was cotton. Before the Civil War, enslaved African Americans did most of the farm work. After the war, many formerly enslaved people, called freedmen, bought land in the Delta. They cleared trees to earn money for the land. However, many lost their land later due to money problems. They often became tenant farmers or sharecroppers, meaning they farmed land owned by others.
From the 1940s to the 1970s, many people left Holmes County. This was because farming became more mechanized, meaning machines did more of the work. Also, many African Americans moved to cities in the West and Midwest for jobs. This movement is known as the Great Migration.
In the 1940s, some African Americans got land again through New Deal programs. By 1960, about 800 independent Black farmers owned half of the land in Holmes County. These farmers were very important in the Civil Rights Movement during the 1960s. In 1967, many Black candidates ran for local offices. These were the first African Americans to run for office in the county since the Reconstruction period after the Civil War.
Robert G. Clark, Jr., a teacher from Holmes County, made history in 1967. He was the first Black person elected to the state government in Mississippi in the 20th century. He served in the state legislature until 2003 and was even chosen as Speaker of the state House three times.
Contents
History of Holmes County
Holmes County's history is closely tied to its rivers. The Yazoo River forms its western border, and the Big Black River is on its eastern side. The county was developed for large cotton farms, called plantations, before the American Civil War. Most of these farms were built along the rivers for easy transport. Because of the plantation economy, most people in the county before the Civil War were enslaved African Americans.
After the Civil War, many freedmen and white settlers moved to the Mississippi Delta area. They cleared land and sold timber to buy their own farms. By the early 1900s, many landowners in the Delta were Black. However, new laws in 1890 made it very hard for Black people to vote. This loss of political power, along with money problems, caused many Black landowners to lose their farms. They often had to become sharecroppers or tenant farmers.
Around the late 1870s, the first Chinese immigrants came to the Delta. More arrived between 1900 and 1930, including some in Holmes County. They worked hard, often becoming shopkeepers in small towns. They created a unique place for themselves "between black and white" communities. Many Chinese Americans later moved to bigger cities.
During the New Deal in the 1930s and 1940s, the government helped Black people buy land. They offered low-interest loans. Many Black people in Holmes County became landowners through this program. These independent farmers were strong supporters of the Civil Rights Movement in the 1960s.
The population of Holmes County dropped a lot from 1940 to 1970. Thousands of African Americans left during the Great Migration. For example, from 1950 to 1960, about 6,000 Black people left the county. Even with this decline, in 1960, Holmes County was still 72% Black. It also had more independent Black farmers than any other county in Mississippi. These farmers were key in starting the Civil Rights Movement.
In 1954, some white people formed the White Citizens Council. They wanted to stop schools from integrating (mixing Black and white students). They tried to hurt businesses of Black people and white people who supported civil rights. One target was Hazel Brannon Smith, a local newspaper publisher. She won a Pulitzer Prize in 1964 for her writings about the Civil Rights Movement.
The Freedom Democratic Party (FDP) was formed in 1964. It worked to help Black people register to vote and learn about elections. Even after the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the Voting Rights Act of 1965 were passed, it was hard to make changes locally. White officials often resisted Black voter registration. In 1965, a federal official was sent to the county, and 2,000 Black voters registered in just two months.
The FDP also helped Black farmers get elected to local farming boards. In 1965, six Black farmers were elected to the county board. This gave them a say in how local farming programs were run.
In 1966, many communities focused on setting up the new federal Head Start program for young children. The FDP also worked to end unfair hiring and discrimination in other areas. By November 1967, almost 6,000 new Black voters were registered in the county.
In 1967, eight of the ten candidates who ran for local and state offices were Black farmers and landowners. Robert G. Clark and Robert Smith, both teachers, also ran for office. Clark won a seat in the Mississippi House of Representatives. He was the first and only Black person elected to the state legislature in 1967. He was re-elected many times and became Speaker of the House.
Since the mid-1900s, many white people have also left the county. Large farming businesses have bought up land, and there are fewer independent farmers. By 2010, the total population was less than half of what it was in 1940. Holmes County still faces challenges with poverty and healthcare access today.
Geography and Nature
Holmes County covers about 765 square miles. Most of this area is land, with about 7.9 square miles of water.
Main Roads in Holmes County
 Interstate 55
Interstate 55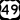 U.S. Route 49
U.S. Route 49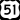 U.S. Route 51
U.S. Route 51 Mississippi Highway 12
Mississippi Highway 12 Mississippi Highway 14
Mississippi Highway 14 Mississippi Highway 17
Mississippi Highway 17 Mississippi Highway 19
Mississippi Highway 19
Neighboring Counties
- Carroll County (north)
- Attala County (east)
- Yazoo County (south)
- Humphreys County (west)
- Leflore County (northwest)
Protected Natural Areas
- Hillside National Wildlife Refuge (part)
- Mathews Brake National Wildlife Refuge (part)
- Morgan Brake National Wildlife Refuge
- Theodore Roosevelt National Wildlife Refuge (part)
Population Changes
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1840 | 9,452 | — | |
| 1850 | 13,928 | 47.4% | |
| 1860 | 17,791 | 27.7% | |
| 1870 | 19,370 | 8.9% | |
| 1880 | 27,164 | 40.2% | |
| 1890 | 30,970 | 14.0% | |
| 1900 | 36,828 | 18.9% | |
| 1910 | 39,088 | 6.1% | |
| 1920 | 34,513 | −11.7% | |
| 1930 | 38,534 | 11.7% | |
| 1940 | 39,710 | 3.1% | |
| 1950 | 33,301 | −16.1% | |
| 1960 | 27,096 | −18.6% | |
| 1970 | 23,120 | −14.7% | |
| 1980 | 22,970 | −0.6% | |
| 1990 | 21,604 | −5.9% | |
| 2000 | 21,609 | 0.0% | |
| 2010 | 19,198 | −11.2% | |
| 2020 | 17,000 | −11.4% | |
| 2023 (est.) | 15,777 | −17.8% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census 1790-1960 1900-1990 1990-2000 2010-2013 |
|||
From 1940 to 1970, the number of people living in Holmes County went down a lot. Many African Americans left the state during the Great Migration. White people also left because there were fewer job opportunities in the rural county.
2020 Population Data
| Race | Number of People | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| White | 2,359 | 13.88% |
| Black or African American | 14,194 | 83.49% |
| Native American | 36 | 0.21% |
| Asian | 20 | 0.12% |
| Pacific Islander | 3 | 0.01% |
| Other/Mixed | 279 | 1.64% |
| Hispanic or Latino | 112 | 0.66% |
In 2020, there were 17,000 people living in Holmes County.
2010 Population Data
In 2010, there were 19,198 people in the county. This was less than half the number of people in 1940.
- 83.4% were Black or African American
- 15.6% were White
- 0.2% were Asian
- 0.1% were Native American
- 0.1% were of some other race
- 0.6% were of two or more races
- 0.7% were Hispanic or Latino (of any race)
Education in Holmes County
Colleges
- Holmes Community College (in Goodman)
Schools for Younger Students
During the time of segregation, when schools for Black students received less money, a private school for Black students was started in Lexington in 1918. It was called Saints Academy. Arenia Mallory became the principal in 1926. She made the school bigger and better, offering classes for grades 1-12. She raised money from outside the state and made the school famous for its strong academics. The academy continued until 2006.
When public schools started to integrate in the late 1960s, some white parents in Holmes County sent their children to new private schools. These were called "segregation academies" because they were created to avoid integration.
- Public Schools
- Holmes County Consolidated School District
- The Durant School District joined this larger district in 2018.
- Holmes County Consolidated School District
- Private Schools
- Central Holmes Christian School (in Lexington) - This school was also started as a segregation academy.
- Old Dominion Christian School
- Pillow Academy in Leflore County also has some students from Holmes County. It was also founded as a segregation academy.
- East Holmes Academy - This school closed in 2006.
Local News
The county newspaper is the Holmes County Herald. It started in 1959. It was created by the local chapter of the White Citizens Council. This group was against school integration and the Civil Rights Movement. They wanted to compete with The Lexington Advertiser, a newspaper owned by Hazel Brannon Smith. She was known for her fair reporting and support for civil rights. The Council tried to hurt her business.
The Herald would publish the names of African Americans who were involved in civil rights actions. This was done to put pressure on them. For example, in 1963, it published the names of 14 Black people who tried to register to vote. This made it easier for people to face problems like losing their jobs or homes. The Herald was bought by a new owner in 1970.
Communities in Holmes County
Cities
Towns
Other Communities
Famous People from Holmes County
- Homer Casteel: A politician who served as lieutenant governor from 1920 to 1924.
- Robert G. Clark, Jr.: A teacher and politician. He was the first African American elected to the Mississippi state legislature since Reconstruction in 1967. He served many terms and was Speaker of the state House three times.
- Steven Fonti: An animator and storyboard artist, born in Holmes County.
- Perry Wilbon Howard: A lawyer and politician who held a high position in the U.S. Department of Justice. He was the highest-ranking African American in government during his time.
- Arenia Mallory: A principal and president of Saints Academy. She built it into a well-known private school for Black children during segregation.
- Edmond Favor Noel: Governor of Mississippi from 1908 to 1912. He worked to improve education in the state.
- Hazel Brannon Smith: A newspaper publisher and journalist. She won a Pulitzer Prize in 1964 for her writings supporting civil rights.
Images for kids
Error: no page names specified (help). In Spanish: Condado de Holmes (Misisipi) para niños
In Spanish: Condado de Holmes (Misisipi) para niños


