Hydrogen bromide facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Hydrogen bromide |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| IUPAC name | Hydrogen bromide |
|
Preferred IUPAC name
Bromane
|
|
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | |
| PubChem | |
| EC number | 233-113-0 |
| KEGG | C13645 |
| MeSH | |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:47266 |
| RTECS number | MW3850000 |
| SMILES | Br |
| Beilstein Reference | 3587158 |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | |
| Molar mass | 0 g mol-1 |
| Appearance | Colorless gas |
| Odor | Acrid |
| Density | 3.307 g/L (25 °C) |
| Melting point | |
| Boiling point | |
| 221 g/100 mL (0 °C) 204 g/100 mL (15 °C) 193 g/100 mL (20 °C) 130 g/100 mL (100 °C) |
|
| Solubility | Soluble in alcohol, organic solvents |
| Vapor pressure | 2.308 MPa (at 21 °C) |
| Acidity (pKa) | −8.8 (±0.8); ~−9 |
| Basicity (pKb) | ~23 |
| Conjugate acid | Bromonium |
| Conjugate base | Bromide |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.325 |
| Structure | |
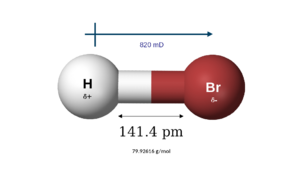
| Molecular shape | Linear |
| Dipole moment | 820 mD |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std enthalpy of formation ΔfH |
−36.45...−36.13 kJ/mol |
| Standard molar entropy S |
198.696–198.704 J/(K·mol) |
| Specific heat capacity, C | 350.7 mJ/(K·g) |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Highly corrosive |
| NFPA 704 |
|
| U.S. Permissible exposure limit (PEL) |
TWA 3 ppm (10 mg/m3) |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) | |
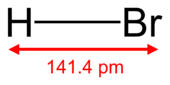
Hydrogen bromide is a chemical compound made of hydrogen and bromine atoms. Its chemical formula is HBr. It's a type of compound called a hydrogen halide.
At room temperature, hydrogen bromide is a colorless gas. It has a very strong, sharp smell. When this gas dissolves in water, it creates a strong acid called hydrobromic acid. This acid is often used in chemistry to make other compounds that contain bromine.
Contents
What is Hydrogen Bromide Used For?
Hydrogen bromide and hydrobromic acid are very useful in making other chemicals. They are often used to create compounds that contain bromine.
For example, they can be used to change certain types of carbon-based molecules, like those found in alkenes, into new substances that include bromine. These new bromine-containing compounds are important building blocks for making many different products.
Hydrogen bromide can also react with other inorganic compounds. It helps create different types of metal bromides, like vanadium(III) bromide.
How is Hydrogen Bromide Made?
Making it for Industry
Large amounts of hydrogen bromide are made by mixing hydrogen gas and bromine gas. This reaction needs high temperatures, usually between 200 and 400 degrees Celsius.
Sometimes, special materials like platinum are used to help the reaction happen faster. These materials are called catalysts.
Making it in the Lab
Scientists can also make hydrogen bromide in smaller amounts for experiments. One way is to mix certain bromine-containing salts, like sodium bromide, with a strong acid such as phosphoric acid.
Another method involves reacting bromine with water and other simple chemicals. These lab methods help scientists study hydrogen bromide and its reactions.
Safety First!
Hydrogen bromide is a very strong and dangerous chemical. It is highly corrosive, which means it can cause severe burns to skin and eyes.
If someone breathes in hydrogen bromide gas, it can seriously harm their lungs and respiratory system. Because of these dangers, hydrogen bromide must always be handled with extreme care by trained professionals, using special safety equipment.
See also
 In Spanish: Ácido bromhídrico para niños
In Spanish: Ácido bromhídrico para niños
 | Leon Lynch |
 | Milton P. Webster |
 | Ferdinand Smith |