Knoppix facts for kids
Quick facts for kids KNOPPIX |
|
|---|---|
 |
|

KNOPPIX 8.6
|
|
| Developer | Klaus Knopper |
| OS family | Linux (Unix-like) |
| Working state | Current |
| Source model | Open source |
| Initial release | 30 September 2000 |
| Latest release | 9.1 / 25 January 2021 |
| Repository |
|
| Available in | German and English |
| Update method | LTS |
| Package manager | APT (frontend); dpkg (maintenance) |
| Kernel type | Monolithic (Linux) |
| Userland | GNU |
| Default user interface |
LXDE |
| License | Free software licenses (mainly GPL) |
KNOPPIX (pronounced KNOP-iks) is a special type of operating system based on Debian Linux. What makes it unique is that it's designed to run directly from a CD, DVD, or USB flash drive. This means you don't have to install it on your computer's hard drive! It was one of the very first "live" operating systems, appearing shortly after Yggdrasil Linux.
KNOPPIX was created by a Linux expert named Klaus Knopper, and it's named after him. When you start a program in KNOPPIX, the system loads it from the CD, DVD, or USB and then quickly unpacks it into your computer's RAM. This unpacking happens so fast that you don't even notice it!
Even though KNOPPIX is mostly used as a "Live CD" (or DVD/USB), you can also install it on your computer's hard disk if you want, just like a regular operating system. If your computer can start up from a USB device, you can use KNOPPIX from a USB flash drive or memory card.
There are two main versions of KNOPPIX: a smaller one that fits on a CD (about 700 megabytes) and a larger "Maxi" edition that fits on a DVD (about 4.7 gigabytes). The CD version wasn't updated for a while, but with version 9.1, new CD images are being released again. Both the CD and DVD versions come in English and German.
KNOPPIX mostly uses software that is free and open source. This means anyone can use, change, and share the software. However, it also includes some proprietary software (software you can't freely change or share), as long as it meets certain rules.
One cool use for Knoppix is to easily copy files from hard drives that have operating systems that aren't working. It's also great if you want to try out Linux software quickly and safely, without having to install a whole new operating system on your computer.
Contents
What's Inside KNOPPIX?
The CD version of KNOPPIX comes with over 1,000 software programs, and the DVD version has more than 2,600! The DVD can hold up to nine gigabytes of programs because they are stored in a compressed (squeezed) form. Some of the programs you'll find include:
- LXDE: This is a lightweight and easy-to-use desktop environment. It has been the main desktop since Knoppix version 6.0.
- MPlayer: A program for playing videos and music, including MP3 and Ogg Vorbis audio files.
- Internet access tools: Programs to help you connect to the internet, like the KPPP dialer and tools for ISDN.
- Iceweasel: A web browser that is based on Mozilla Firefox.
- Icedove: An email program that is based on Mozilla Thunderbird.
- GIMP: A powerful program for editing images, similar to Photoshop.
- Tools for data rescue: These can help you get back files from damaged drives.
- System repair tools: Programs to fix problems with your computer.
- Network tools: Software for checking and managing computer networks.
- LibreOffice: A complete office suite with programs for writing documents, making spreadsheets, and creating presentations.
- Terminal server: A tool for connecting to other computers.
What Your Computer Needs to Run KNOPPIX
To run KNOPPIX, your computer needs to meet some basic requirements:
* At least 32 MB for text-only mode (no graphics). * For graphics mode with just the LXDE desktop, you need 512 MB. * To use the web browser and other programs, 1 GB is needed. * 2 GB is recommended for the best experience.
- Bootable Drive:
* A DVD-ROM drive for current versions. * For older versions (7.2 and earlier), a CD-ROM drive or a floppy disk drive with a standard CD-ROM drive.
- Graphics Card: A standard SVGA-compatible graphics card.
- Mouse: A serial, PS/2, or IMPS/2-compatible USB mouse.
Saving Your Work and Settings
Before Knoppix version 3.8.2, anything you created or any settings you changed would disappear when you turned off the computer. You had to save your documents to a hard drive, over a network, or to a removable media like a USB flash drive.
Later, Knoppix added a "persistent home directory" feature. This allowed you to save your documents and settings to a hard drive or USB drive. Knoppix would then automatically find and use these saved changes every time you started it. It used a special file called knoppix.img to store your changes. This meant you could work on your files and settings as if they were always there.
Newer versions (from 3.8.1 onwards) used a feature called "union mount" (first UnionFS, then Aufs). This allowed Knoppix to combine the original files from the read-only CD/DVD with your changes saved on a separate writable drive (like a USB stick or hard drive). This made it seem like you were updating the software on the CD/DVD itself! So, you could install new programs or update existing ones using tools like APT. To keep your changes, the storage device with your saved data needed to be connected when you started Knoppix. You could even tell Knoppix exactly where to find your saved data using a special command when it starts up, like: `home=/dev/hda1/knoppix.img`
This feature meant you could carry your Knoppix CD and a USB drive, and have your own personalized computer environment, programs, and data available on almost any computer that could run Knoppix! This special saving method was available up to Knoppix 5.1.1 (CD) or 5.3.1 (DVD). Now, many portable operating systems run directly from external storage.
Starting KNOPPIX with Special Options
When you use Knoppix as a Live CD/DVD/USB, you can use "boot options" (also called "cheatcodes"). These are special commands you type when Knoppix is starting up. They help you change default settings or fix problems if Knoppix has trouble recognizing your computer's hardware. For example, you might want to start Knoppix in a simple text mode, or without support for certain types of hard drives.
If you don't type any cheat codes, Knoppix will start with its usual settings. To set the language to French instead of the default, you would type: `knoppix lang=fr`
Knoppix is based on 32-bit Debian Linux. However, recent DVD versions (like 7.6 and newer) also include a 64-bit kernel. This means it can automatically start in 64-bit mode on 64-bit computers. You can also manually choose the 64-bit kernel by typing `knoppix64` when booting. The `knoppix` command will start the 32-bit kernel. If you have more than 4GB of RAM, you need the 64-bit kernel to use all of it.
The DVD version of Knoppix can also be copied onto a USB flash drive using a tool called flash-knoppix. Running Knoppix from a USB drive is much faster (about 5 times faster!) than running it from a CD or DVD. Also, Knoppix has experimental support for UEFI (a newer way computers start up) when running from a USB drive, but not from a DVD.
Why KNOPPIX Became Popular
Knoppix was one of the first "Live CD" Linux versions to become widely known. Several things made it popular:
- Pioneer Live CD: It was one of the first Live CDs available and is often called the "original" Debian-based Live CD.
- Easy Hardware Detection: Knoppix is very good at automatically figuring out what hardware your computer has. This means most systems can start Knoppix without you needing to set anything up.
- Automatic Network Connection: It can usually connect to most types of networks on its own.
- Useful Tools: It includes many helpful tools for fixing computer problems and troubleshooting.
Knoppix works on a lot of different computers, but not all of them. Sometimes, its automatic hardware detection might not work perfectly, or the drivers it uses might not be the best. Older computers (made before 1998) or motherboards with very old BIOS (before 2002) might have trouble. But sometimes, you can fix these issues by typing special codes when Knoppix starts.
If a computer doesn't have enough RAM to run the full desktop environment (like KDE), older Knoppix versions (before 6.0) would start a very simple desktop called Tab Window Manager (twm). This simple desktop usually only showed a single window for typing commands.
Knoppix Versions Over Time
| Version | Release date | CD | DVD |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.4 | 2000-09-30 | Yes | No |
| 1.6 | 2001-04-26 | Yes | No |
| 2.1 | 2002-03-14 | Yes | No |
| 2.2 | 2002-05-14 | Yes | No |
| 3.1 | 2002-10-01 | Yes | No |
| 3.2 | 2003-06-16 | Yes | No |
| 3.3 | 2003-09-22 | Yes | No |
| 3.4 | 2004-05-17 | Yes | No |
| 3.5 LinuxTag version | 2004-06 | No | Yes |
| 3.6 | 2004-08-16 | Yes | No |
| 3.7 | 2004-12-09 | Yes | No |
| 3.8 CeBIT version | 2005-02-28 | Yes | No |
| 3.8.1 | 2005-04-08 | Yes | No |
| 3.8.2 | 2005-05-12 | Yes | No |
| 3.9 | 2005-06-01 | Yes | No |
| 4.0 LinuxTag version | 2005-06-22 | No | Yes |
| 4.0 updated | 2005-08-16 | No | Yes |
| 4.0.2 | 2005-09-23 | Yes | Yes |
| 5.0 CeBIT version | 2006-02-25 | No | Yes |
| 5.0.1 | 2006-06-02 | Yes | Yes |
| 5.1.0 | 2006-12-30 | Yes | Yes |
| 5.1.1 | 2007-01-04 | Yes | Yes |
| 5.2 CeBIT version | 2007-03 | No | Yes |
| 5.3 CeBIT version | 2008-02-12 | No | Yes |
| 5.3.1 | 2008-03-26 | No | Yes |
| ADRIANE | |||
| 6.0.0 | 2009-01-28 | Yes | No |
| 6.0.1 | 2009-02-08 | Yes | No |
| 6.1 CeBIT version | 2009-02-25 | Yes | Yes |
| 6.2 / ADRIANE 1.2 | 2009-11-18 | Yes | Yes |
| 6.2.1 | 2010-01-31 | Yes | Yes |
| 6.3 CeBIT version | 2010-03-02 | No | Yes |
| 6.4.3 | 2010-12-20 | Yes | Yes |
| 6.4.4 | 2011-02-01 | Yes | Yes |
| 6.5 CeBIT version | 2011-03 | No | Yes |
| 6.7.0 | 2011-08-03 | Yes | Yes |
| 6.7.1 | 2011-09-16 | Yes | Yes |
| 7.0.1 | 2012-05-24 | No | Yes |
| 7.0.2 | 2012-05-30 | No | Yes |
| 7.0.3 | 2012-07-01 | Yes | Yes |
| 7.0.4 | 2012-08-20 | Yes | Yes |
| 7.0.5 | 2012-12-21 | Yes | Yes |
| 7.2.0 | 2013-06-24 | Yes | Yes |
| 7.4.0 | 2014-08-07 | No | Yes |
| 7.4.1 | 2014-09-15 | No | Yes |
| 7.4.2 | 2014-09-28 | No | Yes |
| 7.5 CeBIT version | 2015-03-16 | No | Yes |
| 7.6.0 | 2015-11-21 | No | Yes |
| 7.6.1 | 2016-01-16 | No | Yes |
| 7.7.0 CeBIT version | 2016-03-14 | No | Yes |
| 7.7.1 | 2016-10-27 | No | Yes |
| 8.0.0 CeBIT version | 2017-03-24 | No | Yes |
| 8.1.0 | 2017-09-27 | No | Yes |
| 8.2.0 | 2018-05-16 | No | Yes |
| 8.3.0 (DELUG-DVD) | 2018-06-07 | No | Yes |
| 8.5.0 Linux-Magazin / Linux-User edition | 2019-03-14 | No | Yes |
| 8.6.0 | 2019-08-08 | No | Yes |
| 8.6.1 | 2019-11-22 | No | Yes |
| 9.0 (DELUG-DVD) | 2020-03-05 | No | Yes |
| 9.1 | 2021-01-25 | Yes | Yes |
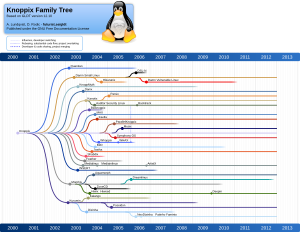
The table to the right shows the history of major Knoppix releases.
Knoppix 4.x–5.x
From 2008, Knoppix versions 4 through 5.1.1 were split into a large DVD "maxi" edition (with over 9 GB of software) and a smaller CD "light" edition. Both were developed at the same time.
These CD editions included different graphical environments, like the simple TWM window manager and KDE 3, which was a full desktop environment used by default in Knoppix 5.3.1 and earlier. These older 5.x versions are no longer being developed.
Knoppix 6.x
KNOPPIX 6.0.1 / ADRIANE 1.1 was a CD-only version that was completely rebuilt from scratch. LXDE became the main desktop environment, and the software collection was made much smaller to fit easily on a CD.
The KNOPPIX 6.2.1 release came in both CD and DVD versions. Knoppix 6.7.1 was the last CD version that had very stable drivers for touchpads.
Knoppix 7.x
From June 2013 until March 2019, Knoppix 7.2 was the newest CD edition. By 2018, the software in this version became quite old. Version 7.2 is also known for having some issues with touchpads.
Version 7.2 is still the most common CD version of Knoppix that people use.
Knoppix 8.x
The KNOPPIX 8.0.0 edition was first shown at a big tech fair called CeBIT in 2017.
KNOPPIX 8.1.0 was the first version in the 8.x series that was made available to the public in September 2017. Version 8.0.0 offered a "dual boot" option, letting you choose between three different desktops: LXDE (the default), KDE, or GNOME.
Versions 8.2.0 and newer (like 8.2.x, but not 8.5.x) can be found on Knoppix download sites.
Knoppix 8.5 was a special DVD version that you couldn't download. It was only given out with physical copies of Linux-Magazin or LinuxUser magazines. This version no longer included a system component called Systemd, which was replaced by elogind. It also had fixes for security problems like Spectre and Meltdown.
Knoppix 8.6 and newer versions are DVD editions that you can download from Knoppix websites.
Other Versions Based on KNOPPIX
KNOPPIX has been used as a starting point for many other Linux versions. These are called "derivatives."
Adriane Knoppix
Adriane Knoppix is a special version made for people who are blind or have low vision. It can be used completely without needing to see the screen. It was released in 2007 as a Live CD. Adriane Knoppix is named after Adriane Knopper, the wife of Klaus Knopper (who created Knoppix). Adriane has a visual impairment and helped Klaus develop this software. The name ADRIANE also stands for "Audio Desktop Reference Implementation And Networking Environment."
Adriane Knoppix is helpful not just for blind people, but also for beginners who are new to computers. It uses a screen reader called SUSE Blinux, which can read text aloud using a speech engine.
Other Knoppix-Based Projects
Here are some other Linux versions that started from Knoppix:
- Kali Linux: This is a popular version now based on Debian. It's used for digital forensics (finding clues on computers) and penetration testing (checking computer security). It was a rewrite of BackTrack, which was based on Knoppix.
- Kanotix: Another live version now based on Debian.
- KnoppMyth: This version makes it super easy to install Linux and MythTV (a program for recording TV).
- Musix GNU+Linux: Made especially for musicians.
- Poseidon Linux: A well-known version designed for scientists.
- KnoppiXMAME: Created for playing MAME video games.
- PelicanHPC: Used for connecting many computers together to work as one (clustering).
- TechUSB: An automated computer system made by RepairTech, Inc.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Knoppix para niños
In Spanish: Knoppix para niños