Kumamoto facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Kumamoto
熊本市
|
|||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kumamoto City | |||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
| Nickname(s):
The Heart of Kyushu
|
|||||||||||||
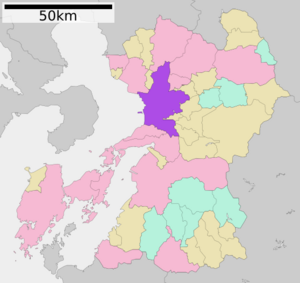
Location of Kumamoto in Kumamoto Prefecture
|
|||||||||||||
| Country | Japan | ||||||||||||
| Region | Kyushu | ||||||||||||
| Prefecture | Kumamoto Prefecture | ||||||||||||
| First official recorded | 558 AD | ||||||||||||
| City Settled | April 1, 1889 | ||||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||||
| • Total | 390.32 km2 (150.70 sq mi) | ||||||||||||
| Population
(June 1, 2019)
|
|||||||||||||
| • Total | 738,907 | ||||||||||||
| • Density | 1,893.080/km2 (4,903.05/sq mi) | ||||||||||||
| Time zone | UTC+09:00 (JST) | ||||||||||||
| Climate | Cfa | ||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
Kumamoto (熊本市, Kumamoto-shi) is an important city in Japan. It is the capital city of Kumamoto Prefecture. You can find it on the island of Kyushu.
As of June 2019, about 738,907 people live in Kumamoto. The city covers an area of 390.32 square kilometers. This means about 1,893 people live in each square kilometer. The larger area around Kumamoto had a population of 1,461,000 in 2000. Kumamoto became a special "designated city" on April 1, 2012. This means it has more local powers.
Contents
History of Kumamoto
Early Times
Building Kumamoto Castle
In 1588, a powerful lord named Katō Kiyomasa became the ruler of half of the Higo region. He was a friend of the famous leader Toyotomi Hideyoshi. Kiyomasa built the amazing Kumamoto Castle. This castle was known for its clever defenses. People thought it was impossible to capture. Kiyomasa was one of the best castle builders in Japanese history.
Edo Period Changes
Kiyomasa passed away in 1611. His son, Tadahiro, took over. But in 1632, another powerful leader, Tokugawa Iemitsu, replaced Tadahiro with the Hosokawa clan. Hosokawa Tadatoshi became the third lord of Kumamoto. He was a supporter of the famous artist and swordsman Miyamoto Musashi.
Modern History
City Founded
The city of Kumamoto as we know it today was officially started on April 1, 1889.
World War II and Peace
Near the end of World War II, on July 1, 1945, Kumamoto was bombed. About 20% of the city was destroyed.
After the war, a Japanese Buddhist monk named Nichidatsu Fujii wanted to promote peace. He decided to build a Peace Pagoda on top of Mount Hanaoka in Kumamoto. It was finished in 1954. This was the very first of over 80 Peace Pagodas built by Fujii and his followers around the world. They were built to remember those lost in wars and to encourage peace.
Recent Changes and Events
Over the years, several smaller towns joined Kumamoto city. This made the city bigger.
- On February 1, 1991, Akita, Kawachi, Tenmei, and Hokubu joined.
- On October 6, 2008, Tomiai joined.
- On March 23, 2010, Jōnan and Ueki joined.
In April 2016, a series of strong earthquakes hit the area. One big earthquake happened on April 16, 2016.
Geography and Climate
Climate of Kumamoto
Kumamoto has a humid subtropical climate. This means it has hot, humid summers and cool winters. It rains a lot throughout the year, especially in June and July.
The average yearly temperature in Kumamoto is about 17.2 degrees Celsius (63 degrees Fahrenheit). The average yearly rainfall is about 2007.0 millimeters (79 inches). August is usually the hottest month, with temperatures around 28.4 degrees Celsius (83 degrees Fahrenheit). January is the coldest, with temperatures around 6.0 degrees Celsius (43 degrees Fahrenheit).
The hottest temperature ever recorded in Kumamoto was 38.8 degrees Celsius (101.8 degrees Fahrenheit) on July 17, 1994. The coldest was -9.2 degrees Celsius (15.4 degrees Fahrenheit) on February 11, 1929.
| Climate data for Kumamoto (1991−2020 normals, extremes 1890−present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 22.5 (72.5) |
26.4 (79.5) |
27.4 (81.3) |
30.7 (87.3) |
34.4 (93.9) |
36.1 (97.0) |
38.8 (101.8) |
38.8 (101.8) |
37.0 (98.6) |
33.7 (92.7) |
28.9 (84.0) |
24.6 (76.3) |
38.8 (101.8) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 10.7 (51.3) |
12.4 (54.3) |
16.1 (61.0) |
21.4 (70.5) |
26.0 (78.8) |
28.1 (82.6) |
31.8 (89.2) |
33.3 (91.9) |
30.1 (86.2) |
25.0 (77.0) |
18.8 (65.8) |
12.9 (55.2) |
22.2 (72.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 6.0 (42.8) |
7.4 (45.3) |
10.9 (51.6) |
15.8 (60.4) |
20.5 (68.9) |
23.7 (74.7) |
27.5 (81.5) |
28.4 (83.1) |
25.2 (77.4) |
19.6 (67.3) |
13.5 (56.3) |
8.0 (46.4) |
17.2 (63.0) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 1.6 (34.9) |
2.6 (36.7) |
5.9 (42.6) |
10.6 (51.1) |
15.6 (60.1) |
20.2 (68.4) |
24.2 (75.6) |
24.8 (76.6) |
21.2 (70.2) |
14.9 (58.8) |
8.8 (47.8) |
3.4 (38.1) |
12.8 (55.0) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −9.2 (15.4) |
−9.2 (15.4) |
−6.9 (19.6) |
−2.5 (27.5) |
1.3 (34.3) |
7.1 (44.8) |
14.3 (57.7) |
15.3 (59.5) |
6.7 (44.1) |
0.5 (32.9) |
−3.8 (25.2) |
−7.9 (17.8) |
−9.2 (15.4) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 57.2 (2.25) |
83.2 (3.28) |
124.8 (4.91) |
144.9 (5.70) |
160.9 (6.33) |
448.5 (17.66) |
386.8 (15.23) |
195.4 (7.69) |
172.6 (6.80) |
87.1 (3.43) |
84.4 (3.32) |
61.2 (2.41) |
2,007 (79.02) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 1 (0.4) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
0 (0) |
1 (0.4) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.5 mm) | 8.1 | 9.0 | 11.4 | 10.7 | 10.4 | 15.2 | 13.3 | 11.3 | 10.4 | 7.2 | 8.3 | 8.3 | 123.5 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 70 | 67 | 66 | 65 | 67 | 76 | 76 | 72 | 71 | 69 | 72 | 71 | 70 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 133.0 | 141.1 | 169.6 | 184.0 | 194.3 | 130.8 | 176.7 | 206.0 | 176.4 | 187.1 | 153.7 | 143.4 | 1,996.1 |
| Source: Japan Meteorological Agency | |||||||||||||
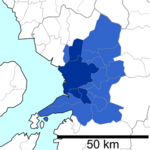
City Wards
Since April 1, 2012, Kumamoto has five main areas called wards (ku):
| Wards of Kumamoto | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Place Name | Map of Kumamoto | |||
| Rōmaji | Kanji | Color | ||
| 1 | Kita-ku | 北区 | Blue | |
| 2 | Nishi-ku | 西区 | Yellow | |
| 3 | Chuo-ku | 中央区 (administrative center) |
Purple | |
| 4 | Higashi-ku | 東区 | Red | |
| 5 | Minami-ku | 南区 | Green | |
Neighboring Towns and Cities
Kumamoto is surrounded by several other towns and cities in Kumamoto Prefecture. These include:
- Uki
- Kikuchi
- Tamana
- Uto
- Yamaga
- Kōshi
- Mashiki
- Kōsa
- Kashima
- Kikuyō
- Mifune
- Gyokuto
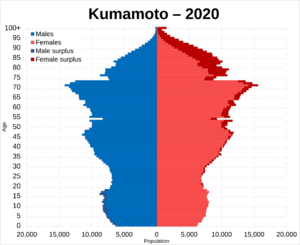
Population Changes
According to Japanese census data, Kumamoto had 738,865 people in 2020. The city has been counting its population since 1920.
| Historical population | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kumamoto population statistics | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Getting Around Kumamoto
The Kumamoto City Transportation Bureau helps people get around the city.
Air Travel
Kumamoto Airport
Kumamoto Airport is located nearby in Mashiki. It connects Kumamoto to other parts of Japan.
Train Travel
High-Speed Rail: Shinkansen
On March 12, 2011, the Kyushu Shinkansen (high-speed bullet train) line was finished. This train connects Kumamoto directly to Tokyo through Fukuoka's Hakata station. It makes travel very fast!
- Kyushu Railway Company (JR Kyushu)
- Kyushu Shinkansen: Kumamoto Station -
Local Train Lines
The JR Kumamoto station is a major hub. It connects to Japan's large train network.
- Kyushu Railway Company (JR Kyushu)
- Kagoshima Main Line: Tabaruzaka - Ueki - Nishizato - Sōjōdaigakumae - Kami-Kumamoto - Kumamoto - Nishi-Kumamoto - Kawashiri - Tomiai -
- Hōhi Main Line: Kumamoto - Heisei - Minami-Kumamoto - Shin-Suizenji - Suizenji - Tōkai-Gakuen-mae - Tatsutaguchi - Musashizuka - Hikarinomori -
- Kumamoto Electric Railway
- Kikuchi Line: Kami-Kumamoto - Kankanzaka - Ikeda Station - Uchigoshi - Tsuboigawa-kōen - Kita-Kumamoto - Kamei - Hakenomiya - Horikawa -
- Fujisaki Line: Kita-Kumamoto - Kurokamimachi - Fujisakigū-mae -
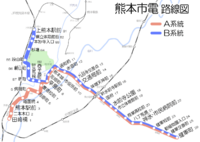
Trams in the City
Trams run to some areas close to the city center.
- Kumamoto City Transportation Bureau
Bus Services
The Kotsu Centre is a big bus station. You can catch buses there to go to local places or other cities.
Taxis
Several taxi companies operate in Kumamoto. Taxis are the only public transport available 24 hours a day.
Roads and Highways
Expressways
 Kyushu Expressway
Kyushu Expressway
National Routes
 Japan National Route 3
Japan National Route 3 Japan National Route 57
Japan National Route 57 Japan National Route 208
Japan National Route 208 Japan National Route 218
Japan National Route 218 Japan National Route 219
Japan National Route 219 Japan National Route 266
Japan National Route 266 Japan National Route 387
Japan National Route 387 Japan National Route 443
Japan National Route 443 Japan National Route 445
Japan National Route 445 Japan National Route 501
Japan National Route 501
Sea Travel
Port of Kumamoto
The Port of Kumamoto is a busy seaport.
Ferry Services
You can take ferries from Kumamoto to other places:
- Kyusyu Shosen: Kumamoto - Shimabara
- Kumamoto-Ferry: Kumamoto - Shimabara
- Korean Marine Transport: Kumamoto - Busan (in South Korea)
Education in Kumamoto
Kumamoto has several universities where students can continue their studies:
- Kumamoto University
- Prefectural University of Kumamoto
- Kumamoto Gakuen University
- Sojo University
- Kyūshū Lutheran College
- Shokei College
- Shokei Gakuin University
- Tokai University
Famous Places in Kumamoto
Kumamoto Castle
The most famous landmark in Kumamoto is Kumamoto Castle. It's a very large and strong Japanese castle. The main tower (called a donjon) was rebuilt in the 1970s using concrete. But many other original wooden buildings from the castle still stand.
The castle was attacked during a historical event called the Satsuma Rebellion. It was burned down after a long fight. During this time, people started eating basashi (raw horse meat). This food is still popular in Kumamoto today and is considered a special treat.
Inside the castle grounds, you can find the Hosokawa Gyobu-tei. This was once the home of the Higo daimyō (a powerful feudal lord). It's a beautiful traditional wooden house with a lovely Japanese garden.
Places of Worship
The first of many peace pagodas around the world was built by Japanese Buddhist monk Nichidatsu Fujii on Mount Hanaoka. It was started in 1947 and opened in 1954.
Kumamoto is also home to Takahashi Inari Shrine and Fujisaki Hachimangū. These are important religious sites.
Suizenji Garden Area
Kumamoto has a beautiful formal garden called Suizen-ji Jōju-en. It's next to Suizenji Temple, about 3 kilometers southeast of Kumamoto Castle. The Suizenji Park area also has the Suizenji Municipal Stadium. The city's football team, Roasso Kumamoto, used to play there. Now they use the bigger KKWing Stadium.
Other Interesting Sites
The famous swordsman Miyamoto Musashi spent the last years of his life in Kumamoto. His tomb and the cave where he lived (called Reigandō, or "spirit rock cave") are nearby. He wrote his famous book, Go Rin No Sho (The Book of Five Rings), while living there.
The downtown area has a lively shopping district. It has two main shopping arcades, Shimotori and Kamitori. These arcades stretch for several city blocks. You'll find large department stores, smaller shops, restaurants, and bars there. Many local festivals are held in or near these arcades.
For art and performances, you can visit the Kumamoto Prefectural Museum of Art and the Kumamoto Prefectural Theater.
Culture and Sports
Sports Teams
Kumamoto is home to several sports teams:
- The Hinokuni Salamanders play in the Kyusyu Asia League.
- Roasso Kumamoto is the local football club, playing in the J.League.
- The Kumamoto Volters play in the B.League.
- Forest Leaves Kumamoto plays in the Volleyball V.League (V2).
Sporting Events
The Kumamoto Castle Marathon is an annual running event in Kumamoto City. It started in 2012 to celebrate Kumamoto becoming a special "designated city." The city has also hosted big international handball events, like the 1997 World Men's Handball Championship and the 2019 World Women's Handball Championship.
Sister Cities
Kumamoto has special partnerships with these cities around the world:
 Billings, Montana, United States
Billings, Montana, United States Bristol, England, United Kingdom
Bristol, England, United Kingdom Guilin, Guangxi, People's Republic of China
Guilin, Guangxi, People's Republic of China Heidelberg, Baden-Württemberg, Germany (since 1992)
Heidelberg, Baden-Württemberg, Germany (since 1992) Helena, Montana, United States
Helena, Montana, United States San Antonio, Texas, United States (since 1987)
San Antonio, Texas, United States (since 1987) Ulsan, South Korea (since 2010)
Ulsan, South Korea (since 2010) Kaohsiung, Taiwan (since 2017)
Kaohsiung, Taiwan (since 2017)
Notable People from Kumamoto
Many interesting people have connections to Kumamoto:
- Aimer, a pop singer and lyricist.
- Yuki Fukushima, a Japanese badminton player.
- Lafcadio Hearn, a writer who lived in Kumamoto for three years starting in 1891.
- Higonoumi Naoya, a sumo wrestler.
- Sayaka Hirota, a Japanese badminton player.
- Sayuri Ishikawa, an enka singer.
- Yuta Iwasada, a Japanese baseball player.
- Masahiko Kimura, a judoka (judo expert).
- Kobato Miku, a lyricist, guitarist, and singer from the rock band BAND-MAID.
- Noriko Kubo, a Japanese female fencer.
- Rie Kugimiya, a voice actress.
- Yuri Masuda, a vocalist from the group m.o.v.e.
- Musashi Miyamoto, the famous swordsman, lived and passed away in Kumamoto in 1645.
- Chisato Moritaka, a pop singer and lyricist.
- Eiichiro Oda, a manga artist, known for One Piece.
- Akari Ogata, a judoka.
- Yōko Shimada, an actress.
- Go Shiozaki, a Japanese professional wrestler.
- Shōdai Naoya, a sumo wrestler.
- Soseki Natsume, a writer who lived in Kumamoto from 1896-1900.
- Tochihikari Masayuki, a sumo wrestler.
- Momoko Ueda, a professional golfer.
- Sean Michael Wilson, a Scottish manga writer who has lived in Kumamoto since 2004.
- Kaji Yajima, an educator and peace activist.
- Yokoi Shōnan, a scholar and political reformer.
- Seiki Yoshioka, a Japanese professional wrestler.
- Isao Yukisada, a film director.
Images for kids
-
Mon of Miyamoto Musashi, born in Ōhara-chō province of Mimasaka.
See also
 In Spanish: Kumamoto para niños
In Spanish: Kumamoto para niños