Lakeland, Florida facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Lakeland, Florida
|
||
|---|---|---|

Downtown Lakeland
|
||
|
||
| Nickname(s):
Swan City
|
||
Location in Polk County and the state of Florida
|
||
| Country | United States | |
| State | Florida | |
| County | Polk | |
| Settled | c. 1870s | |
| Incorporated | January 1, 1885 | |
| Government | ||
| • Type | Commission-Manager | |
| Area | ||
| • City | 75.30 sq mi (195.02 km2) | |
| • Land | 66.29 sq mi (171.69 km2) | |
| • Water | 9.01 sq mi (23.34 km2) 10.9% | |
| Elevation | 203 ft (62 m) | |
| Population
(2020)
|
||
| • City | 112,641 | |
| • Density | 1,699.27/sq mi (656.09/km2) | |
| • Urban | 277,915 (US: 147th) | |
| • Urban density | 1,904.4/sq mi (735.3/km2) | |
| • Metro | 725,046 (US: 80th) | |
| Demonym(s) | Lakelander | |
| Time zone | UTC−5 (EST) | |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) | |
| ZIP Codes |
33801–33815
|
|
| Area code(s) | 863 | |
| FIPS code | 12-38250 | |
| GNIS feature ID | 2404873 | |
| Website | www.lakelandgov.net | |
Lakeland is a city in Polk County, Florida, United States. It's located along I-4, east of Tampa and west of Orlando. With a population of over 112,000 people (as of 2020), it's the largest city in Polk County.
Lakeland is famous for its many lakes, especially Lake Morton downtown. It's often called "Swan City" because of its large population of swans. These beautiful birds are descendants of two mute swans given to Lakeland by Queen Elizabeth II in 1957. The city is also home to several colleges and universities. You'll find Lakeland Linder International Airport here, along with the main office of Publix, a big supermarket chain.
European-American settlers first arrived in Lakeland in the 1870s. The city grew quickly in the 1880s when the railroad came through. People came for farming, citrus, cattle, and the phosphate industry.
Contents
History of Lakeland
Early Days
Long ago, in the 1700s, Native American groups called "Seminoles" lived in this area. In 1823, the U.S. government and the tribes signed a treaty. This agreement created a special area for them in central Florida, which included what is now Polk County. Later, the government tried to move the Seminoles further west. This led to a war from 1835 to 1842. After the war, most Seminoles were moved, but some stayed in southern Florida.
Becoming a City
Florida became a state in 1845. Polk County was created in 1861. Lakeland started to grow in the 1870s. The railroad arrived in 1884, helping the town develop. Lakeland officially became a city on January 1, 1885.
The city was founded by Abraham Munn from Kentucky. He bought land in 1882 and planned out the town in 1884. Lakeland got its name because of the many lakes nearby.
In 1898, the Spanish–American War began. Lakeland became an important place for the military. Over 9,000 troops stayed in the small town. The 10th Cavalry Regiment, known as Buffalo Soldiers, camped near Lake Wire.
Growth in the 1900s
The "Florida boom" in the 1920s brought many new buildings to Lakeland. Some of these are now famous historic places. These include the Terrace Hotel and the Polk Theatre. The city also has several historic areas with large buildings from the 1920s and 1940s.
After the boom ended, the city took time to recover. A big help was when the Detroit Tigers baseball team started training here in 1934. The Tigers still train at Lakeland's Joker Marchant Stadium. They also own the local baseball team, the Lakeland Flying Tigers.
In the 1930s, the Works Progress Administration built the Lakeland Municipal Airport.
Frank Lloyd Wright's "Child of the Sun"
In 1938, Florida Southern College invited famous architect Frank Lloyd Wright to design buildings for their campus. Wright worked on the project for over 20 years. He designed 30 buildings, and 12 were completed.
Wright called his project Child of the Sun. He said his buildings were "out of the ground, into the light." This campus has the largest collection of Frank Lloyd Wright buildings in the world. About 30,000 people visit it every year. In 2012, the campus became a National Historic Landmark.
Lakeland in World War II
During World War II, the Lakeland School of Aeronautics helped train pilots. It was part of a national program for the war effort. Between 1940 and 1945, over 8,000 Army Air Corps students trained there. They learned to fly on biplanes.
From 1941 to 1942, 1,327 British Royal Air Force students also trained in Lakeland. The school closed in 1945. The airport later became the "Tiger Town" baseball complex for the Detroit Tigers.
Geography and Lakes
Lakeland covers about 67 square miles. Most of this is land, but about 10% is water. The city is in the Central Florida Highlands. This area has flat land mixed with gentle hills.
Lakeland's Many Lakes
A main feature of Lakeland is its many lakes. There are 38 named lakes, plus other unnamed water bodies. The biggest lake is Lake Parker, which is 2,550 acres in size. The lakes are a big part of Lakeland's culture. People often use them to describe locations, like "I live near Lake Beulah." Other important lakes include Lake Hollingsworth, Lake Morton, and Lake Mirror.
The Swans of Lakeland
The swans are a very famous sight on Lakeland's downtown lakes. The first swans appeared around 1923. But by 1954, all the swans were gone. A Lakeland resident missed them and wrote to Queen Elizabeth II. The royal family allowed two of their swans to be sent to Lakeland. The swans you see on the lakes today are descendants of one of those royal swans.
In 2006, Scott Lake almost completely drained due to sinkholes. It later refilled partially.
Lakeland's Climate
Lakeland has a humid subtropical climate. This means summers are hot and humid. High temperatures are often around 90°F or more. Afternoon thunderstorms are common in summer. Winters are drier and warm, with sunny skies. High temperatures are usually in the mid-70s. Temperatures sometimes drop below freezing a couple of times a year.
| Climate data for Lakeland, Florida, 1991–2020 normals, extremes 1948–present | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °F (°C) | 91 (33) |
90 (32) |
92 (33) |
96 (36) |
103 (39) |
105 (41) |
102 (39) |
100 (38) |
98 (37) |
96 (36) |
93 (34) |
89 (32) |
105 (41) |
| Mean maximum °F (°C) | 83.1 (28.4) |
85.2 (29.6) |
87.9 (31.1) |
91.5 (33.1) |
95.2 (35.1) |
96.2 (35.7) |
96.3 (35.7) |
96.0 (35.6) |
94.3 (34.6) |
91.4 (33.0) |
87.2 (30.7) |
83.8 (28.8) |
97.3 (36.3) |
| Mean daily maximum °F (°C) | 73.7 (23.2) |
76.7 (24.8) |
80.2 (26.8) |
85.1 (29.5) |
89.5 (31.9) |
91.3 (32.9) |
92.1 (33.4) |
92.2 (33.4) |
90.3 (32.4) |
85.9 (29.9) |
79.8 (26.6) |
75.6 (24.2) |
84.4 (29.1) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 62.2 (16.8) |
65.0 (18.3) |
68.3 (20.2) |
73.2 (22.9) |
78.2 (25.7) |
81.8 (27.7) |
83.2 (28.4) |
83.3 (28.5) |
81.7 (27.6) |
76.4 (24.7) |
69.2 (20.7) |
64.8 (18.2) |
73.9 (23.3) |
| Mean daily minimum °F (°C) | 50.6 (10.3) |
53.3 (11.8) |
56.5 (13.6) |
61.4 (16.3) |
66.9 (19.4) |
72.3 (22.4) |
74.2 (23.4) |
74.4 (23.6) |
73.1 (22.8) |
66.9 (19.4) |
58.6 (14.8) |
53.9 (12.2) |
63.5 (17.5) |
| Mean minimum °F (°C) | 31.2 (−0.4) |
34.7 (1.5) |
39.7 (4.3) |
47.9 (8.8) |
57.2 (14.0) |
66.8 (19.3) |
69.9 (21.1) |
70.3 (21.3) |
66.6 (19.2) |
51.7 (10.9) |
42.0 (5.6) |
35.5 (1.9) |
29.3 (−1.5) |
| Record low °F (°C) | 20 (−7) |
24 (−4) |
25 (−4) |
35 (2) |
47 (8) |
56 (13) |
64 (18) |
63 (17) |
61 (16) |
38 (3) |
28 (−2) |
20 (−7) |
20 (−7) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 2.99 (76) |
2.33 (59) |
3.06 (78) |
2.82 (72) |
3.80 (97) |
8.69 (221) |
8.85 (225) |
9.08 (231) |
7.62 (194) |
3.04 (77) |
1.93 (49) |
2.61 (66) |
56.82 (1,443) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in) | 6.9 | 6.4 | 5.4 | 5.4 | 7.8 | 16.5 | 19.0 | 18.7 | 14.9 | 7.5 | 5.1 | 7.1 | 120.7 |
| Source: NOAA | |||||||||||||
People of Lakeland
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1890 | 552 | — | |
| 1900 | 1,180 | 113.8% | |
| 1910 | 3,719 | 215.2% | |
| 1920 | 7,062 | 89.9% | |
| 1930 | 18,554 | 162.7% | |
| 1940 | 22,068 | 18.9% | |
| 1950 | 30,851 | 39.8% | |
| 1960 | 41,350 | 34.0% | |
| 1970 | 42,803 | 3.5% | |
| 1980 | 47,406 | 10.8% | |
| 1990 | 70,576 | 48.9% | |
| 2000 | 78,452 | 11.2% | |
| 2010 | 97,422 | 24.2% | |
| 2020 | 112,641 | 15.6% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census | |||
In 2020, Lakeland had 112,641 people. There were 41,750 households and 24,433 families living in the city.
Most people in Lakeland speak English at home (91%). About 6.4% of the population speaks Spanish.
Religions in Lakeland
The first Jewish settlers arrived in Lakeland in 1913. The first synagogue, Temple Emanuel, opened in 1932.
Lakeland also has a Swaminarayan Hindu Temple, which opened in 2005. The first and only mosque in the county, now called the Islamic Center of Lakeland, was built in 1994.
Christianity is the largest religious group in Lakeland. In 2013, there were about 300 churches in the city.
Lakeland's Economy

Lakeland is the biggest city on Interstate 4 between Orlando and Tampa. Important industries here include citrus, cattle, and phosphate mining. In recent years, tourism, medicine, insurance, transportation, and music have also become very important.
Citrus farming started with the early settlers in the 1850s. After some cold weather damaged farms north of Polk County, this area became a major place for growing citrus in Florida. Even though it's not the biggest industry anymore, citrus still plays a large part in Lakeland's economy.
Phosphate mining is still important, even though most mining now happens further south. The Bone Valley area once produced a quarter of the U.S. phosphate supply.
Lakeland's biggest employer is Publix Super Markets. Publix is one of the largest grocery chains in the United States. It has over 1,200 stores across the southern U.S. Publix employs over 6,500 people in the Lakeland area.
Lakeland is also a major transportation center. Companies like FedEx and Amazon have large operations here. Other big employers include GEICO and Lakeland Regional Health.
Culture and History
The Lakeland History Room is a special archive at the Lakeland Public Library. It was started in 1987. It keeps the city's historical items, like documents, photos, maps, and old postcards. You can find over 7,000 images of Lakeland's history there.
In 2019, the city decided to create the first History and Culture Center. It opened in September 2022 at the Lakeland Public Library. This center shares the story of Lakeland's past.
Historic Places
Lakeland has several historic districts. These are areas with many old and important buildings.
- Beacon Hill-Alta Vista Residential District
- Dixieland Historic District
- East Lake Morton Residential District
- Munn Park Historic District
- South Lake Morton Historic District
Famous Buildings and Locations
Many interesting places are in Lakeland:
- Florida Southern College
- Lakeland Center
- Polk Museum of Art
- Polk Theatre
- Southeastern University (Florida)
- Florida Polytechnic University
- Silvermoon Drive-in
- Bonnet Springs
Libraries in Lakeland
- Lakeland Public Library
- Larry R. Jackson Branch Library
- eLibrary South Lakeland
Sports in Lakeland
Lakeland is home to several sports teams and venues.
| Club | Sport | Founded | Current league | Stadium |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lakeland Flying Tigers | Baseball | 1963 | Florida State League | Publix Field at Joker Marchant Stadium |
| Florida Complex League Tigers | Baseball | 1995 | Florida Complex League | Publix Field at Joker Marchant Stadium |
| Lakeland Magic | Basketball | 2017-2023 | NBA G League | RP Funding Center |
| Florida Southern Mocs | Multi-sport | 1883 | NCAA DII | George W. Jenkins Field House Henley Field Moccasin Field |
| Southeastern Fire | Multi-sport | 2014 | NAIA | Victory Field The Furnace Ted A. Broer Stadium |
| Caledonia SC | Soccer | 2022 | USL League Two | |
| Lakeland Tropics | Soccer | 2017 | UPSL | Bryant Stadium |
| Lakeland United FC | Soccer | 2022 | UPSL | |
| Florida Tropics SC | Indoor soccer | 2016 | Major Arena Soccer League | RP Funding Center |
| Lakeland Renegades | Rugby league | 2019 | USA Rugby League | All Saints' Academy |
| Lakeland NightShade | eSports | 2019 | Florida eSports League |
Sports Stadiums
Joker Marchant Stadium, north of downtown, is where the Detroit Tigers baseball team has their spring training. It's also home to the Lakeland Flying Tigers and the GCL Tigers, which are minor league baseball teams.
The RP Funding Center hosts two indoor sports teams. The Lakeland Magic is a basketball team in the NBA G League. They are connected to the Orlando Magic. The Florida Tropics SC is an indoor soccer team.
Education in Lakeland
The schools in Lakeland are managed by the Polk County School Board. There are 28 elementary schools, seven middle schools, and five high schools. There are also three special magnet high schools.
High Schools
- George W. Jenkins High School
- Kathleen High School
- Lake Gibson High School
- Lakeland Senior High School
- Tenoroc High School
Magnet High Schools
- Central Florida Aerospace Academy
- Lois Cowles Harrison Center for the Visual and Performing Arts
- Polk State College Lakeland Collegiate High School
Middle Schools
- Kathleen Middle School
- Lake Gibson Middle School
- Crystal Lake Middle school
- Sleepy Hill Middle School
- Lakeland Highlands Middle School
- Southwest Middle School
Magnet Middle Schools
- Lawton Chiles Middle School
- Rochelle School of the Arts (also an elementary school)
Colleges and Universities
Lakeland has many options for higher education:
- Florida Polytechnic University
- Florida Southern College
- Florida Technical College
- Keiser University
- Webster University
- Polk State College
- Southeastern University
Southeastern University is the largest university in the area. Florida Southern College is known for having the world's largest collection of buildings designed by Frank Lloyd Wright.
In 2008, the University of South Florida's Lakeland campus became Florida Polytechnic University. This university focuses on STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Math) programs.
Media and News
Lakeland is part of the Tampa Bay television market. You can watch most TV stations from Tampa Bay here. WMOR-TV, an independent TV station, is licensed to Lakeland.
Lakeland also has its own radio market. Some local radio stations include:
- WLKF 1430 AM
- WONN 1230 AM
- WPCV 97.5 FM
For news, Lakeland has The Ledger, a local newspaper. The Lakelander is a local magazine. LkldNow is a nonprofit online news organization that covers Lakeland news.
Transportation
Lakeland is an important transportation center because it's the largest city on I-4 between Tampa and Orlando.
Major Roads
 I-4: This is the main interstate that connects Tampa, Lakeland, Orlando, and Daytona Beach.
I-4: This is the main interstate that connects Tampa, Lakeland, Orlando, and Daytona Beach. SR 570 (Polk Parkway): This is a toll road that goes around Lakeland. It helps you get from one part of town to another and connect to I-4.
SR 570 (Polk Parkway): This is a toll road that goes around Lakeland. It helps you get from one part of town to another and connect to I-4.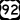 US 92: This road used to be the main route to Tampa and Orlando before I-4 was built.
US 92: This road used to be the main route to Tampa and Orlando before I-4 was built.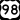 US 98: This road goes south to Bartow and north to Dade City.
US 98: This road goes south to Bartow and north to Dade City.
Bike Paths
Lakeland has many paved bike paths. The Lake-To-Lakes Trail goes through downtown and past several lakes. The University Trail connects Polk State College to Florida Polytechnic University. The Fort Fraser Trail runs along US Highway 98.
Public Transportation
- Lakeland Amtrak Station: For train travel.
- Lakeland Linder International Airport: The local airport, which became international in 2018.
- Lakeland Greyhound Terminal: For bus travel.
- Citrus Connection: Provides local bus service within the city.
Utilities and Power
Lakeland Water Utilities manages water and wastewater for the area. The city's water comes mainly from wells that draw from the Floridan aquifer.
Lakeland Electric is a public power company that provides electricity to the city. Lakeland was one of the first cities in Florida to have electric lighting in 1891. Citizens bought the private power plant in 1904, creating Lakeland Electric.
Power Plants
Lakeland Electric gets its power from two plants: C.D. McIntosh Power Plant and Larsen Memorial. The last coal unit at C.D. McIntosh Power Plant stopped operating in January 2024.
Famous People from Lakeland
- Nat Adderley, jazz musician
- Lindsey Alley, actress
- Bobby Braddock, music producer
- Frances Langford, singer and actress
- Neva Jane Langley, Miss America 1953
- Ray Lewis, NFL football player
- Maurkice Pouncey, NFL football player
- Mike Pouncey, former NFL football player
- Boog Powell, former MLB baseball player
- Andrew Reynolds, professional skateboarder
- Chris Sale, MLB baseball player
- Justin Verlander, MLB baseball player
- Lawton Chiles, former Senator and Governor of Florida
- George W. Jenkins, founder of Publix Super Markets
Sister Cities
Lakeland has "sister city" relationships with cities around the world. These partnerships help people from different countries learn about each other.
 Bălți, Moldova (since 1997)
Bălți, Moldova (since 1997) Chongming County, Shanghai, China (since 2007)
Chongming County, Shanghai, China (since 2007) Imabari, Ehime, Japan (since 1995)
Imabari, Ehime, Japan (since 1995) Portmore, Jamaica (since 2009)
Portmore, Jamaica (since 2009) Richmond Hill, Ontario, Canada (since 1990)
Richmond Hill, Ontario, Canada (since 1990)
Lakeland also has "regional friendships" with:
 Rîbnița, Moldova
Rîbnița, Moldova Jiaxing, China
Jiaxing, China
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Lakeland (Florida) para niños
In Spanish: Lakeland (Florida) para niños
 | James Van Der Zee |
 | Alma Thomas |
 | Ellis Wilson |
 | Margaret Taylor-Burroughs |














