Organ (biology) facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Organ |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
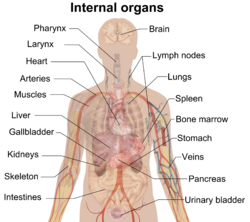
| Many of the internal organs inside the human body | |
| System | Organ systems |
In living things with many cells, an organ is a group of different tissues working together. These tissues form a special part of the body that does a specific job. Think of it like a team where each player (tissue) has a role, and together they achieve a goal (the organ's function).
Organs are found between tissues and organ systems in the way living things are organized. Tissues are made of the same type of cells that work together. Different types of tissues then combine to form an organ. For example, your intestines have both epithelial tissue (which lines surfaces) and smooth muscle tissue (which helps move food). When two or more organs work together for a bigger job, they form an organ system, also called a body system.
An organ has two main types of tissue. The first is the parenchyma, which is the tissue that does the organ's main job. For example, in a gland, the parenchyma makes the hormones. The second type is the stroma, which is the support tissue. The stroma includes nerves that send signals, blood vessels that bring oxygen and food, and connective tissue that holds everything in place. Most organs in animals and plants have these two types of tissues.
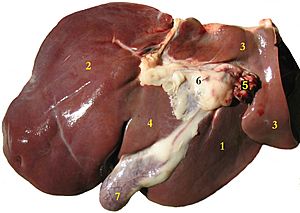
In the study of the body, viscera (say: VISS-er-uh) is a fancy word for the internal organs. These are the organs found inside your belly, chest, and pelvis. For example, in your belly, you have solid organs like the liver, pancreas, spleen, kidneys, and adrenal glands. You also have hollow organs like the stomach, intestines, gallbladder, bladder, and rectum. In your chest, your heart is a hollow, muscular organ.
Scientists have identified about 79 different organs in the human body. The exact number can change a bit depending on how you define an "organ."
Animals
Most animals, including humans, have many different organ systems. These systems are studied in human anatomy, which is the study of the body's structure. Often, these systems work closely together. For instance, your nervous system and endocrine system both use a part of the brain called the hypothalamus. Because they are so connected, they are sometimes studied together as the neuroendocrine system. The same is true for the musculoskeletal system, which combines the muscles and bones.
Here are some of the main organ systems in animals:
- Cardiovascular system: This system pumps and moves blood around your body and to your lungs. It includes the heart, blood, and blood vessels.
- Digestive system: This system breaks down food and processes it. It includes your salivary glands, esophagus, stomach, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, intestines, colon, and rectum.
- Endocrine system: This system uses hormones to send messages throughout your body. Hormones are made by endocrine glands like the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, pineal body, thyroid, parathyroids, and adrenal glands.
- Excretory system: This system helps balance fluids and remove waste from your body. It includes your kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra.
- Immune system: This system protects your body from sickness and disease. It works with the Lymphatic system, which moves lymph (a clear fluid) around the body. Parts of this system include leukocytes (white blood cells), tonsils, adenoids, thymus, and spleen.
- Integumentary system: This is your body's outer covering. In mammals, it includes skin, hair, and nails. In other animals, it can include scales (fish, reptiles, birds) or feathers (birds).
- Muscular system: This system helps you move using your muscles.
- Nervous system: This system gathers, sends, and processes information. It includes your brain, spinal cord, and nerves.
- Respiratory system: This system is used for breathing. It includes your pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs, and diaphragm.
- Skeletal system: This system provides support and protection for your body. It includes your bones, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons.
Plants

The study of plant organs is called plant morphology. Plants have two main types of organs: vegetative and reproductive.
Vegetative organs are essential for the plant's survival and growth. These include:
- Roots: They anchor the plant and absorb water and nutrients from the soil.
- Stems: They support the plant, transport water and nutrients, and hold the leaves and flowers.
- Leaves: They are the main sites for photosynthesis, where plants make their own food using sunlight.
Reproductive organs are important for plants to make new plants. These organs can be different depending on the type of plant:
- In flowering plants, the reproductive organs are the flowers, seeds, and fruit.
- In conifers (like pine trees), the reproductive structures are found in cones.
- Other plants, like mosses, have different reproductive organs.
All the parts of a plant above the ground (like stems, leaves, and flowers) are often grouped together as the "shoot system." The roots make up the "root system." While animals have many organ systems, plants have fewer, but each is vital for life and reproduction.
Organ Transplants
Since the 1900s, doctors have learned a lot about organs and started performing organ transplants. This is when a failing organ in one person is replaced with a healthy organ from another person, called a donor. Organ transplants can be very complex and sometimes require special medicines to stop the body from rejecting the new organ.
There is a lot of interest around the world in growing organs in a laboratory or creating artificial organs. This could help people who need transplants in the future.
History of Organs
The word "organ" has been around since the 1100s. Back then, it meant any musical instrument. Later, in the late 1300s, it started to mean a part of the body that does a specific job.
Ancient Roman priests, called haruspices, used to examine the internal organs (viscera) of animals. They believed they could predict the future by looking at the shape or size of these organs. This practice is still important in some tribal societies today.
Long ago, some alchemists (early scientists who tried to turn metals into gold) believed that each of the seven main internal organs was connected to one of the seven classical planets:
| Planet | Organ |
| Sun | Heart |
| Moon | Brain |
| Mercury | Lungs |
| Venus | Kidneys |
| Mars | Gall bladder |
| Jupiter | Liver |
| Saturn | Spleen |
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Órgano (biología) para niños
In Spanish: Órgano (biología) para niños
- Organoid
- Organ-on-a-chip