Outline of Colorado prehistory facts for kids
This article is about the amazing history of the first people who lived in Colorado long ago, before Europeans arrived in 1776. These early people were Native Americans. They lived in different ways, some were hunter-gatherers who moved around, while others lived in villages or special homes called pueblos.
Ancient Times in Colorado: Periods and Peoples
Paleo-Indian Period: The First Hunters
The Paleo-Indian period was when the very first people came to the Americas. This was during the last Ice Age, many thousands of years ago. Scientists believe these big-game hunters crossed a land and ice bridge from Asia into North America. This bridge, called Beringia, existed between 45,000 and 12,000 BCE. They followed large herbivores like mammoths far into Alaska.
- Pre-Clovis People
These were Paleo-Indian hunters who lived before the famous Clovis points were used. For example, at Lamb Spring in Littleton, mammoth bones from 14,140 to 12,140 years ago show hunting with stone tools different from Clovis points. Other sites like Dutton and Selby in eastern Colorado also show this early period.
- Clovis Culture
This is the oldest group of Paleo-Indians known for using special stone tools called Clovis points. These were the first fluted (grooved) projectile points in North America. Sites like Dent and the Drake Clovis Cache in Colorado are examples. The Dent Site was important because it proved that humans hunted mammoths.
- Folsom Tradition
As giant animals like mammoths disappeared, people changed their hunting methods. They started hunting smaller animals using smaller Folsom projectile points. The Lindenmeier Site, dated around 10,600 to 10,720 years ago, and the Jones-Miller Bison Kill Site are examples of Folsom sites.
- Plano Cultures
These cultures came after Folsom.
-
- Cody Complex
This Plano culture used unfluted (not grooved) projectile points and other tools. They lived from about 9,000 to 7,000 BCE. The Olsen-Chubbuck Bison Kill Site, Jurgens Site, and Lamb Spring are examples of Cody complex sites.
-
- Hell Gap Complex
This Plano culture existed from about 10,060 to 9,600 years ago. They are known for their long, unfluted Hell Gap points. The Jones-Miller Bison Kill Site is the only Hell Gap site found in Colorado.
- Other Paleo-Indian Sites
Other places where evidence of Paleo-Indians has been found include Canyons of the Ancients National Monument, Picture Canyon, and Roxborough State Park Archaeological District.
Archaic Period: Adapting to Change
The Archaic period saw people hunting smaller animals like deer, antelope, and rabbits. They also gathered wild plants. These groups moved with the seasons to find the best hunting and gathering spots. Later in this period, around 200-500 A.D., people started growing maize (corn) and making pottery to store food.
- Archaic–Early Basketmaker Era
This period, from 7000 to 1500 BC, involved ancestors of the Ancient Pueblo People. They used baskets to collect and store wild seeds, nuts, and fruits. They hunted with spears, atlatls (spear-throwers), and darts, living in simple homes.
- Mount Albion Complex
This early Archaic culture (4050 to 3050 BC) is known for its unique Mount Albion corner-notched projectile points. Sites like LoDaisKa Site, Magic Mountain Site, and Franktown Cave show evidence of this culture.
- Oshara Tradition
The Oshara Tradition was an Archaic culture from 5,440 B.C. to A.D. 460. It is thought to be an early stage of the Basketmaker culture of the Ancient Pueblo People.
Post-Archaic Period: New Ways of Life
- Later Hunter-Gatherers
- Apishapa Culture
This culture existed from A.D. 1000-1400 in southeastern Colorado. Over 68 Apishapa sites have been found. Some sites include Franktown Cave and Picture Canyon.
-
- Dismal River Culture
This culture, dating from 1650-1750 A.D., was different from other groups on the western plains. Some Colorado sites include Cedar Point Village and Franktown Cave.
-
- Panhandle Culture
Found in the southern High Plains (about AD 1200-1400), this culture built single or multi-room stone structures. They also traded with Southwestern Ancestral Pueblo peoples.
-
- Plains Woodland or Ceramic Period
Around AD 0, people on the Plains started making pottery (cord-wrapped), settling in areas, and using smaller projectile points for hunting with bows and arrows. Sites include Colorado Millennial Site, Franktown Cave, and Magic Mountain Site.
-
- Sopris Phase
This culture (about AD 1000-1250) was found in southeastern Colorado. Even though they were influenced by pueblo people, they mostly remained hunter-gatherers. See Trinchera Cave Archeological District.
- Puebloan People
- Ancestral Pueblo Peoples
These were ancient Native American cultures living in the Four Corners area (where Colorado, Utah, Arizona, and New Mexico meet).
-
-
- Basketmaker Culture
-
This culture (about 1500 BC to AD 500) is named for the many baskets found at their sites. They were followed by the Pueblo I Era. Basketmaker sites include Canyons of the Ancients National Monument and Hovenweep National Monument.
-
-
- Pueblo Culture
-
Starting around AD 500, people began living in pueblo structures. They improved their architecture, art, and ways to save water. Many Pueblo sites are in southwestern Colorado, like Mesa Verde National Park and Canyon of the Ancients.
- Tipi Ring Period
This later period is marked by circles of stones called tipi rings, which show where nomadic hunters set up their Tipis. This period continued into more recent times. Picture Canyon has evidence of both Apishapa and Tipi ring periods.
Daily Life in Prehistoric Colorado
Art
- Rock Art
These are carvings or paintings made on natural stone, like petroglyphs (carvings) and pictographs (paintings). You can find examples at Cañon Pintado, Mesa Verde National Park, and Picture Canyon.
- Solar Calendars
Some ancient people created calendars using the sun's position to track seasons, like the summer and winter equinox. Examples are found at Hovenweep National Monument and Picture Canyon.
Clothing and Personal Items
- Blankets
People wove blankets from turkey feathers, yucca fibers, and rabbit fur. Animal hides were also used for warmth.
- Cradleboards
These were special carriers for babies, made from yucca, twigs, and rabbit fur.
- Hairstyles
Based on ancient burials, Basketmaker men sometimes had fancy hairstyles. Women likely kept their hair short.
- Jewelry
Both men and women wore necklaces, bracelets, and pendants made from shells, stone, bone, and dried berries. Shells from the Pacific coast were obtained through trade.
- Sandals
Footwear was made from woven yucca fibers or strips of leaves.
Food and Diet
- Cultivation
Ancient Pueblo People and some hunter-gatherers grew maize (corn), squash, and beans. Growing crops meant they had to stay in one place for planting and harvesting.
- Paleolithic Diet
Hunter-gatherers ate a diet based on wild plants and animals they found seasonally.
Homes and Shelters
- Adobe Dwellings
Some homes were built from Adobe, a material made from sand, clay, water, and plant fibers like straw.
- Crude Lean-tos
These were simple shelters made of poles covered with brush or animal hides, with a single-sloping roof.
- Rock Shelters
People often lived in cave-like openings in cliffs. They sometimes built walls to protect themselves from the weather.
- Pit-houses
These homes were built partly underground and covered with poles, brush, earth, or hides.
- Tipis
Cone-shaped shelters made of wooden poles covered with animal skins, used by nomadic hunters.
- Wikiups
These were shelters made from downed branches, forming a tight top and a circular base. They were covered with smaller branches and grasses, with one opening. Wikiups were not portable and were used seasonally.
Tools
Ancient people made many tools from stone, such as knives and other tools for pounding, scraping, and cutting.
- For Food
- Baskets
Used for gathering, storing, and even cooking food (when lined with pitch).
-
- Digging Sticks
Used to plant seeds.
-
- Manos and Metates
A mano is a stone used to grind food, like corn, by hand on a larger stone called a Metate.
-
- Pottery
Ceramic pots made from clay and fired to make them strong, used for cooking and storage.
-
- Storage Pits
Underground pits, often lined with stone, used to protect extra food from weather and animals.
- For Hunting
- Atlatl
A spear-thrower used to hunt game.
-
- Bow and Arrow
A weapon used to hunt game, which was a big improvement over the atlatl.
-
- Nets and Snares
Used to trap small animals.
-
- Projectile Points
Stone points crafted for spears, darts, arrows, or knives.
-
- Spears
Long pole weapons with a pointed head.
- Other Tools
- Bone Awls
Simple tools made from bone, used for sewing or making holes in animal skins for clothing.
-
- Fire
Native Americans used fire for many purposes, including cooking, warmth, and shaping tools.
-
- Rope
Woven from yucca fibers.
-
- Scrapers
Stone tools used for working with hides or wood.
-
- Yucca
A very useful plant that provided food, materials for clothing and sandals, soap, and more.
Origins of Today's Tribes
The Ute people arrived in Colorado by the 1600s and lived in much of the state. Later, the Comanches came from the south in the 1700s, followed by the Arapaho and Cheyenne from the plains. These last three groups were the largest Native American tribes in Colorado when settlers first arrived. Here are some of the language groups and ancestors of today's Native American tribes:
- Algonquian Languages
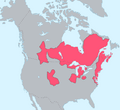
These groups lived across North America, from the Rocky Mountains to the East Coast. The Plains Algonquians included the Arapaho, Cheyenne, and Blackfoot people.
-
- Arapaho
They lived on the eastern plains of Colorado and Wyoming. They were close allies with the Cheyenne. They spent winters in the Rocky Mountain foothills and hunted buffalo on the plains.
-
- Cheyenne
They lived on the plains east of the Rocky Mountains with the Arapaho.
- Southern Athabaskan Languages
This group includes the Apachean and Navajo Nations. They moved from Alaska and northwestern Canada to the Great Plains, including Colorado, before settling in the Southwestern United States.
-
- Apache
- Dismal River Culture
- Apache
The Apache presence in Colorado began with the Dismal River cultures.
-
-
- Jicarilla Apache
-
By A.D. 1525, the Jicarilla Apache lived in northern New Mexico and southern Colorado, also ranging through Texas, Oklahoma, and Kansas. See Cedar Point Village and Picture Canyon.
- Caddoan Languages
These groups lived on the Great Plains of the central United States.
-
- Pawnee
They ranged through the Great Plains and hunted bison on the plains of eastern Colorado.
- Tanoan Languages
This family includes Pueblo languages and the Kiowa, who are ancestors to the Pueblo people.
-
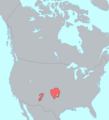
- Kiowa
They lived or ranged in the southwestern plains near the Arkansas River in southeastern Colorado.
- Uto-Aztecan Languages
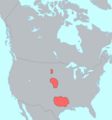
- Comanche
They were located in southeastern Colorado, south of the Arkansas River.
-
- Shoshone
Eastern Shoshone tribes lived in northern Colorado and Wyoming.
-
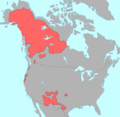
- Ute
The Ute moved from Utah and the Great Basin before the 1600s. They lived in most of Colorado and were prehistoric hunters in western Colorado. They are the only native people with reservations in Colorado today: the Southern Ute Indian Reservation and the Ute Mountain Ute Tribe Reservation.
Important Archaeologists
- Cynthia Irwin-Williams
Known for her work at sites like LoDaisKa Site and Magic Mountain Site, and her studies on the Oshara Tradition.
- Paul Sidney Martin
Excavated many ancient pueblo sites, including Lowry Pueblo.
- Waldo Rudolph Wedel
Notable for his work at Lamb Spring and on the Dismal River culture.
- Joe Ben Wheat
His most famous excavation site is the Joe Ben Wheat Site Complex. He also worked at the Jurgens Site and Olsen-Chubbuck Bison Kill Site.
Images for kids