Printing facts for kids


Printing is a way to put words and pictures onto paper. It uses machines to make many copies. Think of how Books and newspapers are made – that's printing! Usually, special ink is used to create the images and text. This ink is put onto paper using large machines called printing presses.
Printing is one of the most important inventions in history. It changed how people share writing and information. Before printing, everything had to be copied by hand, which was very slow. Printing made it possible to make many copies quickly. This meant more people could read and learn.
Contents
The Story of Printing: How it All Started
Writing began a very long time ago, over 5,000 years ago! People started writing after they settled down in one place. Before paper was invented, people wrote on many different things. They used clay tablets, papyrus (a plant like paper), wood, slate, and parchment (prepared animal skins). The invention of paper in China was a big step forward for writing.
Early Printing in Asia
The first known printing happened in the 8th century in China and Korea. People carved whole pages onto flat wooden blocks. They put carbon-based ink on these blocks. Then, they pressed the blocks onto sheets of paper to make copies.
Later, in the 11th century, China and Korea started using separate characters. These were made by wood carving or casting metal. However, this method wasn't very successful there. The Chinese and Korean languages have thousands of characters. So, using separate pieces for each character was still very difficult. It wasn't much faster than copying by hand.
Printing Comes to Europe
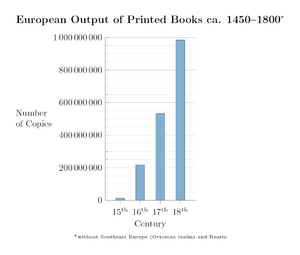
Printing was invented again in Europe in the 15th century. Things moved slowly until Johannes Gutenberg made some important improvements. He developed a better way to use movable metal type. He also created a special ink and a new kind of printing press.
Because European languages use an alphabet (a smaller set of letters), printing with movable type was much easier. It was also much cheaper than copying by hand. This meant many more copies of books could be made. This "information revolution" helped Europe grow and become a powerful part of the world.
Printing Pictures and Photos
Besides printing words, people also found ways to print pictures. For a long time, artists carved pictures onto wood blocks or engraved them onto copper plates. Around the 1800s, many new inventions arrived. These included lithography, a way to print using a flat stone or metal plate. Later, methods were invented to print photographs.
Printing in the Modern Age
The 19th century brought even more changes during the Industrial Revolution. New machines made printing much faster. Paper became cheaper, and machines could automatically stitch and bind books. What used to be done by a few people by hand was now done by large companies using huge machines. This made books and newspapers much cheaper. As a result, many more people could afford to read them.
How Printing Changed Society
The invention of printing had a huge impact on the world. It helped knowledge spread much faster. Before printing, only a small group of people, like scribes and monks, controlled books. They were the ones who copied texts by hand. Printing put books and information into the hands of many more people.
Many of the first printed books were in Latin or Greek. But soon, almost all books were printed in the "vernacular". This means they were printed in the language that ordinary people spoke. The Bible was one of the first books printed. It was also one of the first to be translated into everyday languages. This happened even though some powerful groups didn't want it to.
Printing also gave a big boost to science. New scientific ideas could be shared quickly through printed books and papers. Some experts even believe that printing changed the way people think!
Related topics
Images for kids
-
From top to bottom, left to right: cylinder seal of a scene, block used for woodblock printing, movable type, printing press, lithograph press, offset press used for modern lithographic printing, linotype machine for hot metal typesetting, digital printer, 3D printer in action.
-
The intricate frontispiece of the Diamond Sutra from Tang-dynasty China, 868 AD (British Library)
-
The earliest known woodcut, 1423, Buxheim, with hand-colouring
-
Miehle press printing Le Samedi journal. Montreal, 1939.
See also
 In Spanish: Impresión para niños
In Spanish: Impresión para niños