Suffolk County, Massachusetts facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Suffolk County
|
||
|---|---|---|

Suffolk County Courthouse
|
||
|
||
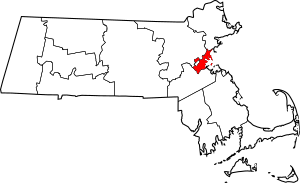
Location within the U.S. state of Massachusetts
|
||
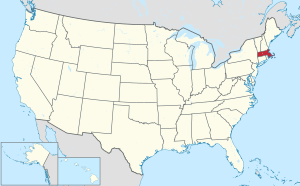 Massachusetts's location within the U.S. |
||
| Country | ||
| State | ||
| Founded | May 10, 1643 | |
| Named for | Suffolk | |
| Seat | Boston | |
| Largest city | Boston | |
| Area | ||
| • Total | 120 sq mi (300 km2) | |
| • Land | 58.15 sq mi (150.6 km2) | |
| • Water | 62 sq mi (160 km2) 52%% | |
| Population
(2020)
|
||
| • Total | 797,936 |
|
| • Density | 13,698/sq mi (5,289/km2) | |
| Time zone | UTC−5 (Eastern) | |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) | |
| Congressional districts | 5th, 7th, 8th | |
Suffolk County is located in the state of Massachusetts, in the United States. It's home to the important city of Boston, which is the state capital. In 2020, about 797,936 people lived here. This makes it the fourth-most populated county in Massachusetts.
Suffolk County includes the cities of Boston, Chelsea, and Revere. It also includes the town of Winthrop. Even though the county government stopped in 1999, Suffolk County is still an important area. It helps organize state government services and is used for counting people and other statistics. It's also a key part of the larger Boston area.
Contents
History of Suffolk County
Suffolk County was created a long time ago, on May 10, 1643. This happened when the leaders of the Massachusetts Bay Colony decided to divide the area into four main parts, called "shires."
When it was first formed, Suffolk County included Boston and several other towns. These towns were Roxbury, Dorchester, Dedham, Braintree, Weymouth, and Hingham. The county was named after Suffolk, a place in England. The name "Suffolk" means "southern folk."
Over the years, the borders of Suffolk County changed. In 1731, some western parts of the county, like Mendon and Uxbridge, became part of Worcester County. Later, in 1793, most of the original Suffolk County split off. These areas became Norfolk County. Only Boston, Chelsea, Hingham, and Hull stayed in Suffolk County.
In 1803, Hingham and Hull also left Suffolk County. They joined Plymouth County instead. Revere became its own town in 1846, separating from Chelsea. Winthrop became a town in 1852, separating from Revere.
In the late 1800s and early 1900s, Boston grew bigger. It added several nearby cities and towns. These included Hyde Park, Roxbury, West Roxbury, and Dorchester from Norfolk County. It also added Charlestown and Brighton from Middlesex County. This made Suffolk County larger again.
In the early 1900s, the City of Boston started taking over many of the county's jobs. The Boston City Council began acting like the county's main group. The City Treasurer also took on the role of County Treasurer. The county government was officially ended in 1999.
Geography of Suffolk County
Suffolk County covers a total area of about 120 square miles (310 square kilometers). About 58 square miles (150 square kilometers) of this is land. The rest, about 62 square miles (160 square kilometers), is water. This means more than half of the county's total area is water! It is the second-smallest county in Massachusetts by land area. It is the smallest by total area.
Neighboring Counties
Suffolk County shares borders with these other counties:
- Essex County (to the north)
- Norfolk County (to the south)
- Middlesex County (to the west)
Even though it doesn't touch land, Suffolk County also shares a water border with Plymouth County. This border is in the middle of Massachusetts Bay.
Special Protected Areas
Some important protected areas are found in Suffolk County:
- Boston African American National Historic Site
- Boston Harbor Islands National Recreation Area (part of it)
- Boston National Historical Park
Main Roads and Highways
Many major roads and highways pass through Suffolk County. These include:
 I‑90 / Mass Pike (Massachusetts Turnpike)
I‑90 / Mass Pike (Massachusetts Turnpike) I‑93
I‑93 US 1
US 1 US 20
US 20 Route 1A
Route 1A Route 9
Route 9 Route 16
Route 16 Route 28
Route 28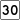 Route 30
Route 30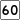 Route 60
Route 60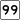 Route 99
Route 99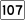 Route 107
Route 107 Route 145
Route 145 Route 203
Route 203
People of Suffolk County
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1790 | 44,865 | — | |
| 1800 | 28,015 | −37.6% | |
| 1810 | 34,381 | 22.7% | |
| 1820 | 43,940 | 27.8% | |
| 1830 | 62,163 | 41.5% | |
| 1840 | 95,773 | 54.1% | |
| 1850 | 144,517 | 50.9% | |
| 1860 | 192,700 | 33.3% | |
| 1870 | 270,802 | 40.5% | |
| 1880 | 387,927 | 43.3% | |
| 1890 | 484,780 | 25.0% | |
| 1900 | 611,417 | 26.1% | |
| 1910 | 731,388 | 19.6% | |
| 1920 | 835,522 | 14.2% | |
| 1930 | 879,536 | 5.3% | |
| 1940 | 863,248 | −1.9% | |
| 1950 | 896,615 | 3.9% | |
| 1960 | 791,329 | −11.7% | |
| 1970 | 735,190 | −7.1% | |
| 1980 | 650,142 | −11.6% | |
| 1990 | 663,906 | 2.1% | |
| 2000 | 689,807 | 3.9% | |
| 2010 | 722,023 | 4.7% | |
| 2020 | 797,936 | 10.5% | |
| 2023 (est.) | 768,425 | 6.4% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census 1790-1960 1900-1990 1990-2000 2010-2020 |
|||
In 2020, Suffolk County had 797,936 people. The average age of people living here was about 31.5 years old.
Different Backgrounds
Suffolk County is a diverse place with people from many different backgrounds. Here's a look at the main groups in 2017:
| Race | Percentage of Suffolk County population |
Percentage of Massachusetts population |
Percentage of United States population |
County-to-State Difference |
County-to-USA Difference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| White | 61.7% | 81.3% | 76.6% | –19.6% | –14.9% |
| White (Non-Hispanic) | 45.4% | 72.1% | 60.7% | –26.7% | –15.3% |
| Black | 24.9% | 8.8% | 13.4% | +16.1% | +11.5% |
| Hispanic | 22.9% | 11.9% | 18.1% | +11.0% | +4.8% |
| Asian | 9.1% | 6.9% | 5.8% | +2.2% | +3.3% |
| Native Americans/Hawaiians | 0.9% | 0.6% | 1.5% | +0.3% | –0.6% |
| Two or more races | 3.4% | 2.4% | 2.7% | +1.0% | +0.7% |
Family Backgrounds (Ancestry)
Many people in Suffolk County have roots from different parts of the world. Based on a survey from 2012-2016, some of the largest ancestry groups are:
- Irish
- Italian
- West Indian
- Puerto Rican
- English
- German
- Chinese
- Sub-Saharan African
- Haitian
Cities and Towns in Suffolk County
Suffolk County is made up of four main communities:
Education in Suffolk County
Each city and town in Suffolk County has its own public school system. These include:
- Boston Public Schools
- Chelsea Public Schools
- Revere Public Schools
- Winthrop Public Schools
There are also many colleges and universities in Suffolk County. Some of these are:
- Benjamin Franklin Institute of Technology
- Berklee College of Music
- Boston Architectural College
- Boston College (eastern side)
- Boston University
- Bunker Hill Community College (with a campus in Chelsea)
- Cambridge College
- Emerson College
- Emmanuel College
- Fisher College
- Parts of Harvard University, like its Business and Medical Schools
- Massachusetts College of Art and Design
- Massachusetts College of Pharmacy and Health Sciences
- MGH Institute of Health Professions
- New England College of Optometry
- New England Conservatory
- New England Law Boston
- North Bennet Street School
- Northeastern University
- Roxbury Community College
- Saint John's Seminary
- Sattler College
- Simmons University
- Suffolk University
- Tufts University School of Medicine
- University of Massachusetts Boston
- Urban College of Boston
- Wentworth Institute of Technology
The county also has several public library systems:
- Boston Public Library
- Chelsea Public Library
- Revere Public Library
- Winthrop Public Library and Museum
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Condado de Suffolk (Massachusetts) para niños
In Spanish: Condado de Suffolk (Massachusetts) para niños
 | Kyle Baker |
 | Joseph Yoakum |
 | Laura Wheeler Waring |
 | Henry Ossawa Tanner |




