Unit of measurement facts for kids
Measurement is how we use numbers to describe things we see or feel. We measure how big, warm, or heavy things are, and many other features too. This helps us compare them to each other.
Units of Measurement are like standard tools for comparing things. They make sure the numbers we use mean the same thing to everyone. For example, the metre is a standard unit for measuring length. It helps us understand distances.
If something is 2 metres long, it means it's twice as long as the standard metre. Today, most units belong to one of three main systems. The older ones are the British imperial system and the US customary system. They use the foot for length, the pound for weight, and the second for time. In these systems, the number of smaller units that make up bigger units can change. For example, there are 12 inches in a foot, but 16 ounces in a pound.
The newer system is the metric system, also called the SI system. This system usually uses 10 of a smaller unit to make a bigger one. It uses the metre for length, the kilogram for weight, and the second for time, just like the other systems.
Contents
What Are Numbers and Units?
When you measure something, you get a number and a unit. The number only makes sense when you also know the unit of measurement.
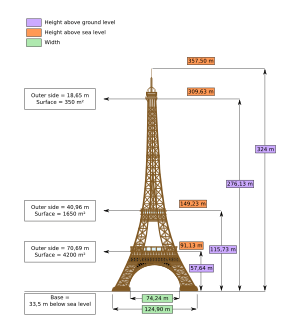
For example, the Eiffel Tower in Paris, France, is 324 meters tall. Here, the "property" being measured is the tower's height or distance from top to bottom. The number is 324. This number needs the unit "meters" to make sense. Without the unit, "324" doesn't tell us much about the tower's height.
Why Do We Need Measurement Standards?
Standards are special objects or rules that help us measure things using fixed units. A metre stick is a good example of a standard. When you measure something with a metre stick, you can easily compare that measurement to anything else measured with another metre stick. This makes measuring much easier and helps us make clear comparisons.
How Do Unit Sizes Vary?
Units of measurement come in different sizes. We use small units to measure small things and big units to measure big things.
In Science, medicine, and engineering, smaller units help measure tiny things with great accuracy. It's also easier to measure large things using larger units. For example, the width of a galaxy needs a very large unit, while the mass of an atom needs a very small, special unit.
Different Systems of Measurement
Many different standards and units are used around the world.
The Metric System (SI)
The metric system is used in most parts of the world. It's also known as the International System of Units, or SI.
Units in the metric system include:
- Length: Based on the metre.
- The kilometre (km) is 1000 metres.
- The centimetre (cm) and millimetre (mm) are smaller. A millimetre is 1/1000th of a metre.
- Volume: The litre is used for measuring liquids.
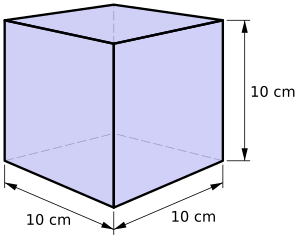
- A millilitre (ml) is the amount of liquid that fills a cube 1 centimetre on each side.
- One litre of liquid fills a cube that is 10 cm on each side.
- Mass: The kilogram is the main unit.
British Imperial Units
Imperial units were set up in the United Kingdom in 1825. They were used in countries that were part of the British Empire. Even though many of these countries, including the UK, now officially use the SI system, some older imperial units are still used.
US Customary Units
US customary units are the official units in the United States. They are similar to British imperial units and come from units used in the UK before American Independence. However, some units are different. For example, a US pint is smaller than an imperial pint. This means US gallons are also smaller than imperial gallons. The metric system has been legal in the US since 1866, but units like the gallon, inch, and pound are still very common.
Here are some imperial and US units:
- Length: inch (in), foot (ft), yard (yd), and mile.
- 1 foot = 12 inches
- 1 yard = 3 feet = 36 inches
- 1 mile = 1760 yards = 5280 feet
- Imperial Volume: imperial fluid ounce (fl oz), imperial pint (pt), and imperial gallon (gal).
- 1 imperial pint = 20 imperial fluid ounces
- 1 imperial gallon = 8 imperial pints
- US Volume: US fluid ounces (fl oz), US cup (cp), US pint (pt), US quart (qt), and US gallon (gal).
- 1 US cup = 8 US fluid ounces
- 1 US pint = 2 US cups = 16 US fluid ounces
- 1 US quart = 2 US pints
- 1 US gallon = 4 US quarts = 8 US pints
- Weight and Mass: Measured in ounces (oz) and pounds (lb). The stone (st) is used in imperial only.
- 1 pound = 16 ounces
- 1 stone = 14 pounds
Remember, ounces for weight and volume are different. Even for water, the number of ounces by weight is not the same as the number of fluid ounces.
Converting Between Systems
It's helpful to know how to change measurements from one system to another.
- Metric to US
- 1 meter = 1.09 yards = 39.37 inches.
- 1 liter = 33.3 fluid ounces = 1.76 pints = 0.26 US gallons.
- 1 kilogram = 35.32 ounces = 2.2 pounds.
- US to Metric
- Length
- 1 inch = 2.54 centimetres
- 1 foot = 30.48 centimetres
- 1 yard = 0.914 metres
- 1 mile = 1.61 kilometres
- Volume
- 1 fluid ounce = 29.6 millilitres
- 1 pint = 473.1 millilitres
- 1 gallon = 3.79 litres
- 1 cup = 16 ounces
- Mass
- 1 ounce = 28.35 grams
- 1 pound = 0.45 kilograms
Other Important Units
Measuring Time
The basic unit of time is the second. Larger units include the minute (60 seconds) and hour (60 minutes or 3600 seconds). A day is usually 24 hours. Sometimes, a "leap second" is added to correct for tiny differences in the Earth's rotation. A week (7 days) and month are also standard units of time.
Measuring Money
A unit of measurement for money is called a unit of account. This is usually the currency a country uses. For example, the United States uses dollars. Each dollar is 100 cents. The United Kingdom uses pounds. Each pound is 100 pennies or pence. Many countries in Europe use the Euro, which is also divided into 100 cents.
Images for kids
-
Units of measurement, Palazzo della Ragione, Padua
-
An example of metrication in 1860 when Tuscany became part of modern Italy (ex. one "libbra" = 339.54 grams)
-
The former Weights and Measures office in Seven Sisters, London
See also
 In Spanish: Unidad de medida para niños
In Spanish: Unidad de medida para niños