Weymouth, Dorset facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Weymouth |
|
|---|---|
| Town and civil parish | |
 Weymouth harbour and bay |
|
 Coat of arms of Weymouth, granted 1592 |
|
| Population | 53,416 (2021) |
| OS grid reference | SY6779 |
| • London | 121 miles (195 km) ENE |
| Civil parish |
|
| Unitary authority |
|
| Ceremonial county | |
| Region | |
| Country | England |
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom |
| Post town | WEYMOUTH |
| Postcode district | DT3, DT4 |
| Dialling code | 01305 |
| Police | Dorset |
| Fire | Dorset |
| Ambulance | South Western |
| EU Parliament | South West England |
| UK Parliament |
|
Weymouth is a lively seaside town in Dorset, England. It sits on a calm bay where the River Wey meets the sea. Weymouth is about 7 miles (11 km) south of Dorchester, the county town. In 2021, over 53,000 people lived here. It is the third biggest town in Dorset, after Bournemouth and Poole.
Weymouth has a long history, going back to the 1100s. It played a part in big events like the Black Death and the settling of the Americas. The town also became famous for its special Georgian architecture. During World War II, it was a key place for soldiers leaving for the Normandy Landings. Today, Weymouth is a popular holiday spot. Its economy relies a lot on visitors. People love its harbour and its location on the Jurassic Coast. This coast is a World Heritage Site known for its amazing rocks and landforms. Weymouth Harbour is now home to fishing boats and pleasure boats. Nearby Portland Harbour hosted the sailing events for the 2012 Olympic Games and 2012 Paralympic Games.
Contents
- History of Weymouth: A Journey Through Time
- Geography: Nature and Coastline
- People of Weymouth: Who Lives Here?
- Economy: How Weymouth Makes a Living
- Culture and Community: Fun Things to Do
- Transport: Getting Around Weymouth
- Education: Schools and Colleges
- Sport and Recreation: Fun and Games
- Media: News and Entertainment
- Notable People: Famous Faces from Weymouth
- Images for kids
- See also
History of Weymouth: A Journey Through Time
Weymouth started as a small settlement near its harbour in the 1100s. It grew into a busy seaport by 1252. A nearby area called Melcombe Regis grew separately. These two towns were often rivals for trade.
Black Death and Town Unity
In June 1348, the terrible Black Death arrived in England. Many historians believe it first came ashore at Melcombe Regis. Later, in 1571, Weymouth and Melcombe Regis joined together. This created one larger town, which became known as Weymouth. Over time, other villages like Wyke Regis and Preston also became part of Weymouth.
Castles and Early Settlers

King Henry VIII built two castles in the 1530s to protect the coast. These were Sandsfoot Castle and Portland Castle. Sadly, parts of Sandsfoot Castle have fallen into the sea. In 1635, about 100 people from Weymouth sailed to America. They helped start a new town called Weymouth in Massachusetts. Other people from Weymouth also helped settle places like Weymouth, Nova Scotia and Salem, Massachusetts. You can find memorials to these brave settlers by Weymouth Harbour.
Famous Architects and Royal Visits
Sir Christopher Wren, a famous architect, was a Member of Parliament for Weymouth in 1702. He was in charge of the stone quarries on nearby Portland. He used Portland stone to build the famous St Paul's Cathedral in London. Another famous artist, Sir James Thornhill, was born in Weymouth. He also helped decorate St Paul's Cathedral.
Weymouth became one of the first modern tourist spots. This happened after King George III started visiting for his summer holidays. He came to Weymouth 14 times between 1789 and 1805. He even went swimming in the sea using a special bathing machine. A painted statue of King George III stands on the seafront today. There is also a huge white horse carved into the chalk hills nearby, representing the King.
Weymouth's seafront has many beautiful buildings. These are called Georgian terraces. They were built between 1770 and 1855. Today, they are apartments, shops, and hotels. The seafront also has the colourful Jubilee Clock. It was put up in 1887 to celebrate 50 years of Queen Victoria's reign.
Harbour Life and World Wars
Weymouth Harbour is very important to the town. It separates the main town centre (Melcombe Regis) from the southern harbourside (Weymouth). Bridges have connected these two parts since the 1700s. The current Town Bridge, built in 1930, can lift up to let boats pass. The Royal National Lifeboat Institution has had a lifeboat stationed in Weymouth since 1869.
During World War I, many soldiers from Australia and New Zealand came to Weymouth to recover from injuries. In World War II, German planes bombed Weymouth and Portland. Over 500,000 troops left from Weymouth to fight in the Battle of Normandy. The famous Bouncing bomb was even tested nearby. You can learn more about the area's history at the Timewalk museum.
Geography: Nature and Coastline
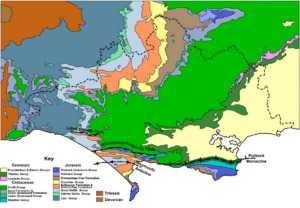
Weymouth is on the south coast of England, about 121 miles (195 km) southwest of London. The town is built on soft sand and clay. These soft rocks are protected by Chesil Beach and the strong limestone Isle of Portland. Portland is about 2 miles (3 km) south of Wyke Regis. The island causes a special "double low tide" in Weymouth Bay.
Lakes and Nature Reserves
Weymouth has two lakes that are RSPB nature reserves. Radipole Lake is in the town centre. Lodmoor is between the town centre and Preston. Radipole Lake is the largest reserve. It is home to many fish, migratory birds, and over 200 types of plants. Both Radipole Lake and Weymouth Beach are very close to the main town centre. There are 11 special nature sites in the area.
Jurassic Coast and Coastal Paths
Weymouth is a gateway to the Jurassic Coast. This UNESCO World Heritage Site stretches for 96 miles (155 km) along the coast. It is famous for its amazing geology and landforms. The South West Coast Path also passes through Weymouth. This is the longest national trail in the UK, at 630 miles (1014 km).
Weymouth is the biggest town in its area. It is larger than Dorchester, which is just to the north. This makes Weymouth a hub for people living nearby. The land around Weymouth is very low. This means some areas could flood during big storms. To prevent this, a sea wall was built around Weymouth Harbour. Also, the beach has been made wider with pebbles to protect the land.
Weymouth's Climate: Sunny and Mild
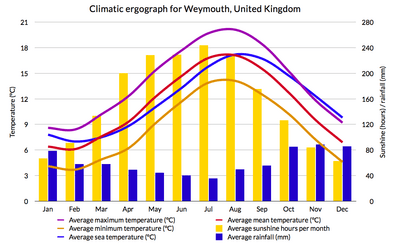
Weymouth has a mild climate because it's on the southwest coast of England. The average temperature is around 11.2°C (52.2°F). August is the warmest month, and February is the coolest. Weymouth gets more sunshine than most of the UK. It averages over 1800 hours of sunshine each year. December is the cloudiest month, and July is the sunniest and driest. Weymouth also gets less rain than the UK average, especially in summer.
It rarely snows or freezes in Weymouth. This is because of the mild sea and lakes around the town. The growing season for plants lasts for more than 310 days a year. This means plants can grow for most of the year.
People of Weymouth: Who Lives Here?
In 2021, Weymouth had a population of 53,416 people. This makes it the largest town in rural Dorset. The town is quite spread out, with about 2,868 people living in each square kilometre.
The number of people living in Weymouth has grown steadily since the 1970s. There are more people aged 60-84 here than the average for England. Most people in Weymouth are White British (95.2%). The most common religion is Christianity (61.0%). The next largest group (29.3%) say they have no religion.
Economy: How Weymouth Makes a Living
Tourism is very important to Weymouth. It provides jobs for 17% of the local workers. In 2019, visitors spent over £200 million in the area. People come to see Weymouth's beaches, lakes, museums, and aquarium. There are many hotels, guest houses, and camping sites for visitors.
In 2019, there were over 2,100 businesses in Weymouth. Most of these were small businesses with fewer than nine employees. The biggest types of businesses were shops, retail, and repair services. Construction and food services were also very important. Two of the largest employers are FGP systems (aerospace parts) and New Look (clothing).
Weymouth Harbour: A Busy Port
Weymouth Harbour used to be a major port for ferries and trade. While ferry services stopped in 2015, the harbour is still busy. It has a working fishing fleet. In 2004, Weymouth's fishing fleet caught the most fish by weight in England. Local boats offer fun trips like fishing, diving, and cruises along the Jurassic Coast.

The main shopping area is in Melcombe Regis. It has two streets just for walking, and a new shopping area near the harbour. There are also shops and restaurants at Hope Square and Brewers Quay. These areas are connected to the town centre by the Town Bridge.
Town Improvements and Awards
Weymouth has been improved a lot, especially before the 2012 Summer Olympics. The seafront was updated with a new public square and a restored statue of King George III. New cafes, a beach rescue centre, and a sand art pavilion were also built. The town has won awards for its beach. In 2023, The Times and Sunday Times named Weymouth Beach the best in the UK. TripAdvisor also gave it an award in 2024.
Culture and Community: Fun Things to Do

Weymouth hosts over 200 events each year. These include firework festivals, dragon boat racing, and beach volleyball. The annual carnival in August is also very popular. Weymouth is the only port in the world to have hosted the start of The Tall Ships' Races three times. The 1994 race brought 300,000 people to watch.
The Pavilion Theatre
The Pavilion Theatre was built in 1960. It is on a piece of land between the harbour and the seafront. The Pavilion hosts shows, events, and performances by local groups. It is now run by a non-profit group.
Museums and Gardens
Weymouth has two museums. Weymouth Museum is in an old brewery building. It shows items from Roman, Tudor, and Georgian times. Nothe Fort was a military fort from 1872 to 1956. Now it is a museum about its own history and coastal defence.
Next to Nothe Fort are Nothe Gardens. These are beautiful informal gardens with trees and shrubs. They are great for ball games, picnics, and nature walks. Other nice gardens in town include Radipole Park and Greenhill Gardens.
Weymouth's Sea Life centre is a zoo and adventure park. It has over 1,000 sea and water animals, like sharks, turtles, and penguins. The centre also helps protect marine environments around the world.
Transport: Getting Around Weymouth

Weymouth railway station is the end of train lines from London Waterloo and Bristol. Until 1987, trains used to run right through the streets of Weymouth! This was the Weymouth Harbour Tramway. It took passengers to the Quay station to catch ferries. This line officially closed in 2016.
Buses and Roads
Local buses run from Weymouth to Isle of Portland, Dorchester, and other nearby villages. There is also a special bus route, X53, that connects Weymouth to towns along the Jurassic Coast.
The A354 road connects Weymouth to Dorchester. Other main roads link Weymouth to places like Wareham and Bridport. A new relief road was built in 2011 to help traffic flow better. During its construction, a burial pit with 51 Viking skeletons was found!
Walking and Cycling
Route 26 of the National Cycle Network goes through Weymouth. The South West Coast Path and the Hardy Way also pass through the town. These are great for walking and exploring the area.
Education: Schools and Colleges
Weymouth has 14 primary schools and three secondary schools. The secondary schools are All Saints Church of England Academy, Budmouth Academy, and Wey Valley Academy. These schools have become academies.
Budmouth Academy also has a sixth form centre for older students. They study for A-Levels and other courses. Weymouth College is a further education college. It has about 3,000 students from the local area and other countries. The college offers many different courses, from apprenticeships to university-level studies.
There are also three special schools in Weymouth for children of all ages. In 2011, most adults in Weymouth (77.5%) had qualifications.
Sport and Recreation: Fun and Games
Weymouth's sandy beach is perfect for swimming and sunbathing. It also hosts many sports events throughout the year. These include beach motocross, handball championships, and the beach volleyball classic. The international kite festival in May attracts thousands of people.
Weymouth has two sports centres. One is shared by the college and the community. The other, Redlands community sports hub, has pitches for football and cricket. It is home to Weymouth Cricket Club.
Football and Sailing
The local football team is Weymouth F.C., also known as 'the Terras'. They play in the National League South. Their home ground is the Bob Lucas Stadium.
The Weymouth and Portland National Sailing Academy is a world-class sailing centre. It is located on the shores of Portland Harbour. This academy hosted the sailing events for the 2012 Olympic and Paralympic Games. The waters around Weymouth and Portland are known as some of the best in Europe for sailing. Many local, national, and international sailing events are held here.
Water Sports and Activities
Weymouth Bay is also great for other water sports. The strong winds are perfect for windsurfing and kitesurfing. The calm waters in Portland Harbour are used for fishing, diving to shipwrecks, snorkelling, canoeing, and jet skiing.
Media: News and Entertainment
Local news for Weymouth comes from BBC South West and ITV West Country. The local newspaper is the Dorset Echo. You can also listen to local radio stations like BBC Radio Solent and Greatest Hits Radio South. There is also a community radio station called AIR Radio.
Notable People: Famous Faces from Weymouth
Many famous writers have connections to Weymouth. Thomas Hardy worked in Weymouth before he became a famous author. Parts of his novels, like Under the Greenwood Tree and The Trumpet-Major, were written here or feature the town. He even renamed Weymouth "Budmouth" in some of his books.
John Cowper Powys's novel Weymouth Sands is set in the town. He felt very at home in Weymouth. His ashes were scattered in the waters around Chesil Bank.
Other notable people include Sir Christopher Wren, the architect, and Sir James Thornhill, the artist. Both were Members of Parliament for Weymouth. Thomas Fowell Buxton, a social reformer who fought to end slavery, was also Weymouth's MP. The main road to Portland is named after him.
Images for kids
-
US soldiers marched through Weymouth to board landing ships for the 1944 invasion of France.
See also
 In Spanish: Weymouth para niños
In Spanish: Weymouth para niños