Yom Kippur War facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Yom Kippur War/October War |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Cold War and Arab–Israeli conflict | |||||||||
 Egyptian forces crossing the Suez Canal on October 7 |
|||||||||
|
|||||||||
The Yom Kippur War (also known as the Ramadan War or the October War) was a big conflict between Israel and a group of Arab countries. The main countries fighting against Israel were Egypt and Syria. This war happened from October 6 to October 24, 1973.
The war started on a special Jewish holiday called Yom Kippur. It also happened during the Muslim month of Ramadan. Egypt and Syria launched a surprise attack on Israel. They wanted to get back land that Israel had taken from them in 1967. This land included the Sinai Peninsula from Egypt and the Golan Heights from Syria.
Egypt's leader, Anwar Sadat, wanted to use the war to start peace talks. Syria wanted to win back all of the Golan Heights by fighting.
Contents
How the War Started
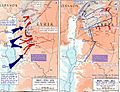
The Surprise Attack
When the war began, Egypt and Syria had some big early successes. Israel was very surprised by the attack. For a short time, it looked like Israel might lose.
Israel tried to fight back, but their first attempts did not work well against Egypt and Syria.
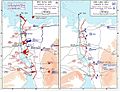
Fighting on the Syrian Front
Later, the Israeli army pushed the Syrian forces back. They even moved further into Syria, getting very close to Damascus, the capital city. The Iraqi army then joined the fight to help Syria. This stopped the Israeli army from going any further.
America Helps Israel
Why Israel Needed Help
On the Egyptian side, Israel's fight against Syria helped Egypt. It allowed the Egyptian army to move deeper into the Sinai. Israel became very worried about losing the war. They asked the United States of America for help.
At first, America did not want to send aid. But Israel made it clear they needed help urgently. This convinced President Richard Nixon to send supplies.
Operation Nickel Grass
America started Operation Nickel Grass. This operation sent a lot of military equipment and ammunition to Israel by airplane. This help was very important for Israel to keep fighting.
Henry Kissinger, who was a top US official at the time, later said that America saved Israel during the war. However, this statement was later questioned.
Fighting in the Sinai
Crossing the Suez Canal
Many people in the Western world thought Israel would win quickly because of its strong military. But on October 6, the Egyptian army crossed the Suez Canal. They broke through Israel's defenses on the other side.
For several days, Israel tried to push the Egyptians back across the canal, but they could not.
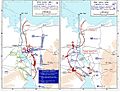
Egypt's Attack and Israeli Counterattack
Syria asked Egypt to attack Israel again to ease the pressure on them. On October 14, Egypt attacked, trying to move even further into the Sinai. Israel stopped this attack. Egypt lost about 250 tanks in this battle.
After this, the Israelis attacked again. They fought hard and managed to cross the Suez Canal themselves. They crossed between two large Egyptian armies. They then moved both north and south. They went south until they reached the city of Suez. They also trapped a large Egyptian force on the eastern side of the canal.
The Israelis tried to capture Suez but were defeated. They also failed to advance much further north. They got to an area about 101 kilometers from Cairo, the capital of Egypt.
The War Ends
The Ceasefire Agreement
The United Nations passed a resolution asking all countries to stop fighting. This was called a 'ceasefire'. Both the Arab countries and Israel agreed to it.
However, the ceasefire did not last. The Israeli army kept moving south towards Suez. Because of this, the Soviet leader, Leonid Brezhnev, told the US president that if the US did not send troops, he would send Soviet troops.
A Close Call for Superpowers
This was seen as a serious threat. The United States put its military on high alert, even for nuclear weapons. This created a lot of tension between the United States and the Soviet Union. It was the closest these two superpowers had come to a nuclear war since the Cuban Missile Crisis in the 1960s.
Because of this high tension, Israel agreed to a ceasefire, and the war finally ended.
After the War
Peace Talks and Agreements
The war officially ended on October 26, 1973. After the fighting stopped, Egypt and Israel started talking. They agreed to move their forces apart. This agreement led to Israel pulling back behind the Suez Canal. The Egyptian forces stayed in the Sinai near the canal. There was a large space between the two armies.
Israel also had talks with Syria. They agreed to leave some of the places they had captured in Syria. However, they stayed in the Golan Heights.
Egypt and Israel continued their talks. In 1979, they signed the Egypt–Israel Peace Treaty. This treaty brought peace between Israel and Egypt. Israel returned the entire Sinai Peninsula to Egypt. This peace treaty is still in effect today.
Who Won the War?
Many people believe there was no clear military winner in the war. It was more like a "stalemate," where neither side completely won or lost on the battlefield. However, the war was seen as a big political victory for the Arab countries, especially for Egypt. Syrians, on the other hand, often see the war as a defeat rather than a victory.
Images for kids
-
Egyptian President Anwar Sadat
-
Wreckage of an Israeli A-4 Skyhawk on display in Egypt's war museum.
-
An Israeli Mirage III shot down by an Egyptian MiG-21
-
An Egyptian MiG-17 shot down during the dogfight over Sharm el-Sheikh.
-
An Israeli M60 Patton tank destroyed in the Sinai.
-
President Hafez al-Assad (right) with soldiers, 1973
-
The aftermath of an Israeli airstrike on the Syrian General Staff headquarters in Damascus
-
Plaque commemorating the supply of 8 East German Air Force MiG-21s to Syria during the war, on display at the Flugplatzmuseum Cottbus
-
Egyptian President Anwar Sadat and Israeli Prime Minister Menachem Begin acknowledge applause during a joint session of Congress in Washington, D.C., during which President Jimmy Carter announced the results of the Camp David Accords, September 18, 1978.
See also
 In Spanish: Guerra de Yom Kipur para niños
In Spanish: Guerra de Yom Kipur para niños