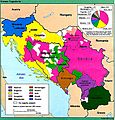
Yugoslavia facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Yugoslavia
Југославија
Jugoslavija |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1918–1941 1945–1992 1941–1945: Government-in-exile |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Anthem: "Himna Kraljevine Jugoslavije" (1919–1941)
"Hej, Slaveni" (1945–1992) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
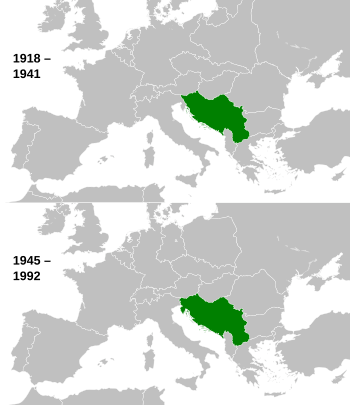
Yugoslavia during Interwar period and the Cold War
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Capital and largest city
|
Belgrade 44°49′N 20°27′E / 44.817°N 20.450°E |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Official languages | Serbo-Croatian Macedonian Slovene |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Demonym(s) | Yugoslav | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy (1918–1941) Socialist republic (1945–1990) Federal republic (1990–1992) Details
Unitary constitutional monarchy
(1918–1929, 1931–1939) Unitary absolute monarchy under a royal dictatorship (1929–1931) Federal constitutional monarchy (1939–1941) Government-in-exile (1941–1945) Provisional socialist government presiding over liberated territories (1943–1945) Federal Marxist–Leninist one-party authoritarian dictatorship (1945–1948) Federal Titoist one-party benevolent dictatorship (1948–1980) Federal Titoist one-party socialist republic (1980–1990) Federal parliamentary constitutional republic (1990–1992) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Historical era | 20th century | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
• Creation
|
1 December 1918 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 April 1941 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 24 October 1945 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 29 November 1945 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 27 April 1992 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Currency | Yugoslav dinar | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Calling code | 38 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Internet TLD | .yu | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Today part of | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
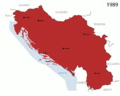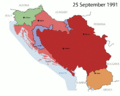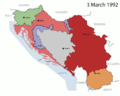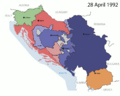
Yugoslavia was a country in Europe, mostly in Balkan Peninsula, its meaning South Slavs deriving from Slavs who came from area what is now Poland in 7th century. It existed in three forms during 1918–2006.
From 1918 until 1928 it was called the Kingdom of the Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes. From 1928 until World War II it was the Kingdom of Yugoslavia. After WWII it was renamed to the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia with six republics, 2 autonomous provinces: Bosnia-Herzegovina, Croatia, North Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia and Slovenia and two autonomous provinces in Serbia: Vojvodina in the north, and Kosovo, next to Albania.
In 1991, came the independence of Slovenia, Croatia, in 1992, North Macedonia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, causing the end of the country. Serbia and Montenegro, were the last two republics in the Socialist Yugoslavia. In 1992, they formed a new Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (FRY) which fell in 2006
Contents
Kingdom of Yugoslavia (1918-1945)
In 1903 the Serbian king was murdered and replaced with Peter I. After this Serbia became more nationalist. Tensions with Austria-Hungary heightened when it conquered Bosnia in 1908. During this period Serbia managed to extend its borders and capture Kosovo and North Macedonia from the Ottoman Empire. Many Serbian nationalists wanted to create a unified state for the Slavs of the Balkans. Covert gangs attempted to assassinate Austro-Hungarian officials, like the Bosnian governor. In June 1914 a Bosnian Serb called Gavrilo Princip killed Austrian Archduke Franz Ferdinand in Sarajevo, Bosnia. This event eventually led to the outbreak of the Great War (World War One).
Yugoslavia came into existence in 1918 after World War I. Most of its northern territories were given to it from Austria-Hungary when it collapsed during the war. Southern territories were taken by Serbia from the Ottoman Empire during the Balkan Wars (1912-13). The reigning king in Serbia became the king of all Yugoslavia.
For ten years it was known as the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes. It began using the name 'Yugoslavia' in 1929. The name 'Yugoslavia' is Serbo-Croatian for 'Land of the Southern Slavs'. The Kingdom was invaded by axis powers in 1941 and quickly fell during World War II. A Federal Democratic Republic was declared in 1943 with the King's approval, but the monarchy was abolished shortly after.
Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (1945-1992)
A People's republic was created in 1945 by a newly established communist government. It was ruled by Josip Tito from then until 1980. The country renamed itself SFR Yugoslavia in 1963. It was made up of six individual Socialist Republics: SR Croatia, SR Bosnia and Herzegovina, SR Macedonia, SR Montenegro, SR Serbia and SR Slovenia. The SFR Yugoslavia was different to other socialist states of the Cold War, deciding to keep itself out of it. Yugoslavia was the only socialist state to have open borders and allowed Yugoslavs and tourists to freely move around the country. Yugoslavia also kept warm relations with the West. It was also an enemy of the Soviet Union after the Tito-Stalin split as Stalin considered him a traitor. In 1968 the Soviet Union invaded socialist Czechoslovakia to stop its leader from making the country more free. Tito told the Czechoslovak leader that he was willing to fly to Prague to help him face the Soviets if he wanted.
The Yugoslav republics began turning against one another in the 1970s and 1980s. Josip Tito ruled Yugoslavia with an iron fist and crushed any nationalist movements that wanted to see the country break up. His government forced the six republics to stay part of Yugoslavia. When he died in 1980, the new leaders were less strict and let nationalist feelings to grow in the republics of Yugoslavia. The breakup was caused by many things like nationalism, economic difficulty and ethnic problems. The Socialist state was dissolved in 1992 during the Yugoslav wars. Serbia and Montenegro stayed together as FR Yugoslavia.
Federal Republic of Yugoslavia/Serbia & Montenegro (1992-2006)
After the dissolution of the SFR Yugoslavia only Serbia and Montenegro were willing to remain in union. They renamed themselves the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia in 1992. The country was led by the controversial statesman Slobodan Milosevic from 1996 until 2000. He was widely accused of having his opposition assassinated in 2000. Yugoslavia applied for UN membership in October 2000 and was granted the following month. For most of its existence the country was involved with what was called the Yugoslav Wars. There was much ethnic violence including mass genocide in Bosnia and Herzegovina (1995) and ethnic cleansing in Kosovo (1998). It was the worst acts of war seen in Europe since World War II. The country was bombed by NATO forces in 1999 during the Kosovo war. In the late 1990s separatism was growing in Yugoslavia and the country dropped the name Yugoslavia in favour of a state union in 2003. Serbia and Montenegro became independent states in 2006, formally ending the last remaining parts of Yugoslavia
Now, Yugoslavia has been split up and made into these countries:
- Slovenia
- Croatia
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Montenegro
- Serbia
- North Macedonia
- Kosovo (recognized by some countries only, not UN recognized)
Images for kids
-
Marshal Josip Broz Tito
See also
 In Spanish: Yugoslavia para niños
In Spanish: Yugoslavia para niños