Altiplano facts for kids
The Altiplano is a huge, high plain in west-central South America. It's also called the Andean Plateau. The name "Altiplano" means "high plain" in Spanish. Another name, "Collao," comes from the Quechua and Aymara languages, meaning "place of the Qulla people."
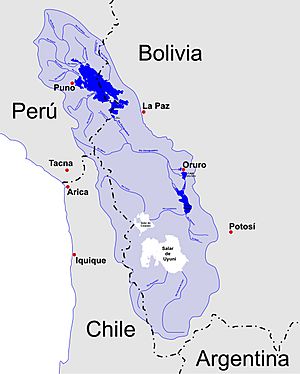
This high plain is the largest of its kind on Earth, except for the Tibetan Plateau. It sits in the middle of the wide Andes mountains. Most of the Altiplano is in Bolivia. Parts of it also reach into Peru and Chile.
Many cities are found on the Altiplano. These include El Alto, La Paz, Oruro, and Puno. The northern part of the Altiplano gets more rain. The southwestern part is very dry. This dry area has many salares, which are huge salt flats.
Lake Titicaca, the biggest lake in South America, is on the border between Bolivia and Peru. There used to be another large lake, Lake Poopó, in Bolivia. But it completely dried up by 2015. Scientists are not sure if it can ever be restored.
Many ancient cultures lived in the Altiplano before Europeans arrived. These included the Chiripa, Tiawanaku, and the Inca Empire. Spain took control of the region in the 1500s.
Today, people in the Altiplano work in mining. They also herd animals like llamas and vicuñas. Cities offer many services. The area also draws visitors from around the world.
Contents
What is the Geography of the Altiplano?

The Altiplano is a large area in the central Andes mountains. It has no rivers flowing out to the ocean. This means it's an inland drainage area. It covers parts of northern Chile, western Bolivia, southern Peru, and northwest Argentina.
The average height of the Altiplano is about 3,750 meters (12,300 feet). This is a bit lower than the Tibetan Plateau. Unlike Tibet, the Altiplano has many active volcanoes to its west. Some of these huge volcanoes include Ampato (6,288 m), Tutupaca (5,816 m), Parinacota (6,348 m), and Licancabur (5,916 m). To the northeast, there are also high mountains like Illampu (6,368 m) and Illimani (6,438 m).
To the southwest of the Altiplano is the Atacama Desert. This is one of the driest places on Earth. To the east, you'll find the wet Amazon rainforest.
The air on the Altiplano has less oxygen because of its high elevation. This is called hypoxic air. The people who live here, like the Qulla, Uros, Quechua, and Aymara, have adapted to these conditions.
How Did the Altiplano Form?
Scientists have different ideas about how the Altiplano formed. They want to know why this large, flat area is so high up within the Andes mountain range. Here are some of their ideas:
- Some think there were weak spots in the Earth's crust before the mountains formed. These weaknesses might have caused the mountains to rise on the east and west, leaving space for the Altiplano basin in the middle.
- Others believe that hot rock from deep inside the Earth helped lift the plateau.
- The climate might have played a role. It affected where erosion happened and where sediment was deposited. This could have influenced how the tectonic plates moved and pushed up the land.
- The climate also caused water to stay in the region, forming inland lakes. This might have stopped the land from deforming in the center, pushing the mountain building to the sides.
- Another idea is that heavy rock from under the Altiplano moved away. This made the region "float" higher, like a boat rising in water.
During the Pleistocene Ice Age, large parts of the Altiplano were covered by huge ancient lakes. Today, Lake Titicaca is a remnant of these lakes. Lake Poopó was another, but it dried up. The vast dry salt flats like Salar de Uyuni and Salar de Coipasa are what's left after these ancient lakes disappeared.
What is the Climate Like on the Altiplano?

The term Altiplano is sometimes used to describe a type of climate zone. This climate is colder than the tierra fría (cold land) but not as cold as the tierra helada (frozen land). The tierra helada usually starts at about 4,500 meters (15,000 feet). Other names for this climate type include puna and páramos.
Generally, the Altiplano climate is cool and can be humid, semi-dry, or even very dry. The average yearly temperatures range from about 3°C (37°F) near the western mountains to 12°C (54°F) near Lake Titicaca. The total yearly rainfall varies a lot. It can be less than 200 mm (8 inches) in the southwest. Near Lake Titicaca, it can be more than 800 mm (31 inches).
The temperature changes a lot between day and night. Daytime temperatures can be from 12°C to 24°C (54°F to 75°F). But at night, they can drop to -20°C to 10°C (-4°F to 50°F).
The coldest temperatures happen in the southwestern Altiplano during June and July, which are winter months there. The rainy season is mainly from December to March. The rest of the year is usually very dry, cool, windy, and sunny. Snowfall can happen between April and September, especially in the north. However, it's not very common, usually only one to five times a year.
See Also
 In Spanish: Altiplano (Andes centrales) para niños
In Spanish: Altiplano (Andes centrales) para niños
- Lake Tauca
- Gran Chaco
- Guatemalan Highlands
- Mexican Plateau
- Puna de Atacama
- Yungas




