Assyria facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Assyria
|
|||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2500 BC–609 BC | |||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
| Capital | Aššur (2500–1754 BC) Shubat-Enlil (1754–1681 BC) Aššur (1681–879 BC) Kalhu (879–706 BC) Dur-Sharrukin (706–705 BC) Nineveh (705–612 BC) Harran (612–609 BC) |
||||||||||
| Official languages | |||||||||||
| Common languages | Akkadian Aramaic |
||||||||||
| Religion | Ancient Mesopotamian religion | ||||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||||
| King | |||||||||||
|
• c. 2500 BC
|
Tudiya (first) | ||||||||||
|
• 612–609 BC
|
Ashur-uballit II (last) | ||||||||||
| Historical era | Bronze Age | ||||||||||
|
• Kikkiya overthrown
|
2500 BC | ||||||||||
|
• Decline of Assyria
|
612 BC 609 BC | ||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||
| 194,249 km2 (75,000 sq mi) | |||||||||||
| Currency | Mina | ||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
Assyria, also known as the Assyrian Empire, was a powerful kingdom and empire in Mesopotamia. This ancient land is now part of countries like Iraq, Syria, and Turkey. Assyria existed for a very long time, from around 2500 BC until its fall between 612 BC and 609 BC.
This long history is split into different periods. These include the Early Period (2500–2025 BC), the Old Assyrian Empire (2025–1378 BC), the Middle Assyrian Empire (1392–934 BC), and the Neo-Assyrian Empire (911–609 BC).
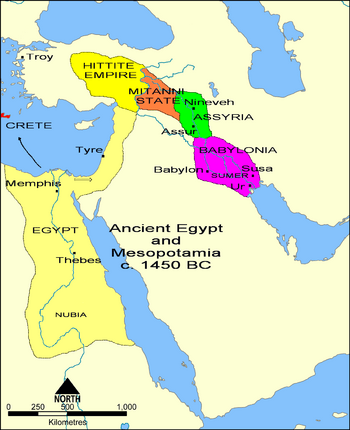
Assyria was located around the Tigris River in what is now northern Iraq. It was a big part of the "cradle of civilization" in Mesopotamia. This area also included Sumer, the Akkadian Empire, and Babylonia. Assyria became very advanced in technology, science, and culture for its time.
Around 900 BC, the Assyrians started to expand their empire. They conquered other lands and collected payments from them. They also built new fortified towns, grand palaces, and temples.
The Assyrian Empire grew to be huge. It stretched from eastern Libya and Cyprus in the Mediterranean Sea. It reached as far as Iran, and from Armenia in the north to the Arabian Peninsula and Egypt in the south.
The name "Assyria" comes from its first capital city, Aššur. This city was founded around 2600 BC. It was one of many city-states in Mesopotamia where people spoke the Akkadian language.
Contents
The Assyrian People
The Assyrians are an ethnic group with a long history. Their descendants still live in places like Iraq, Iran, Turkey, and Syria. Over the last century, many Assyrians have moved to other parts of the world.
You can find large Assyrian communities in Europe, the United States, Australia, and New Zealand. There are also many in Syria, Jordan, and Lebanon. These communities are part of the Assyrian diaspora, meaning they live outside their original homeland.
Important Places in Assyria
Assur: The First Capital
Aššur was the very first capital city of Assyria. It was founded around 2600 BC. This city was named after the chief god of the Assyrians, also called Ashur. It was a very important religious and political center for centuries.
Nineveh: A Grand Capital
Nineveh became one of the most famous capitals of the Neo-Assyrian Empire. It was a huge city with impressive walls and buildings. Many important discoveries about ancient Assyria have been made in Nineveh. It was known for its grand palaces and vast libraries.
Assyrian Achievements
Art and Architecture
The Assyrians were skilled builders and artists. They created massive palaces with detailed stone carvings called reliefs. These carvings showed kings, battles, and religious scenes. They also built large temples and ziggurats, which were pyramid-like structures.
Military Power
The Assyrian army was one of the strongest in the ancient world. They were known for their iron weapons and chariots. They used advanced military tactics to conquer new lands. Their army helped them build and maintain their large empire.
Writing and Knowledge
The Assyrians used Cuneiform writing, which was one of the earliest forms of writing. They kept detailed records on clay tablets. King Ashurbanipal created a famous library in Nineveh. This library had thousands of clay tablets, including the Epic of Gilgamesh. This shows how much they valued knowledge.
Fall of the Empire
The mighty Assyrian Empire eventually faced challenges. It became too large to control easily. Constant wars also weakened the empire. In 612 BC, the city of Nineveh was captured by a group of enemies, including the Median Empire and the Neo-Babylonian Empire. The last parts of the empire fell by 609 BC.
See Also
 In Spanish: Asiria para niños
In Spanish: Asiria para niños
Images for kids
-
Head of a female figure from the Akkadian period (c. 2334–2154 BC), found at Assur.
-
Ruins of an Old Assyrian trading colony at Kültepe.
-
A relief of Tiglath-Pileser III (r.745–727 BC). He made the Neo-Assyrian Empire stronger and larger.
-
Relief showing Naqi'a, mother of Esarhaddon (r.681–669 BC). She was a very important woman in Assyrian history.
-
A 7th-century BC relief showing Ashurbanipal (r.669–631 BC) with two royal helpers.
-
A 9th-century AD piece of papyrus with Syriac language writing.
-
A 19th-century drawing showing what Nineveh (Assyrian capital 705–612 BC) might have looked like.
-
A tablet from the Library of Ashurbanipal that tells part of the Epic of Gilgamesh.
-
A temple altar from Tukulti-Ninurta I, 13th century BC.
-
A statue of Shalmaneser III, from the 9th century BC.