Basis point facts for kids
Quick facts for kids ‱ |
|
|---|---|
|
per ten thousand sign
|
|
A basis point (often called a bp, pronounced "bip" or "beep") is a very small unit used to measure changes or differences. It means one hundredth of a percent, or one ten thousandth of something. Imagine dividing something into 10,000 tiny pieces; one basis point is one of those pieces! People in finance often use basis points, especially when talking about interest rates.
Contents
What is a Basis Point?
A basis point helps us talk about very small changes.
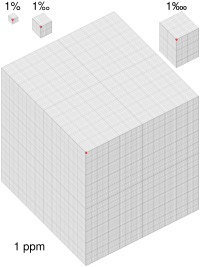
- One basis point is the same as 0.01% (that's one hundredth of a percent).
- It's also the same as 0.0001 (one ten thousandth).
- You can write it as 1‱.
- So, 1 bp = 110,000 or 0.0001.
If you have 100 basis points, that's equal to 1% (one whole percentage point).
How Do We Define It?
Basis points are super useful when we need to talk about small changes, especially when those changes are less than 1%. A great example is with interest rates. Even a tiny change in an interest rate can make a big difference over time.
For instance, if an interest rate goes up by 0.10 percentage points, we say it increased by 10 basis points. So, if a rate was 4.67% and it increased by 10 basis points, it would become 4.77%. This means that 100 basis points is exactly a 1 percentage point increase.
Why Are Basis Points Important?
Basis points help avoid confusion. When someone says an interest rate had a "1% increase," it can be tricky. Did it go from 10% to 10.1% (which is 1% of the original 10%)? Or did it go from 10% to 11% (which is 1% added to the original 10%)?
Avoiding Confusion with Percentages
Using basis points makes it clear. If a report says an interest rate of 10% had a "100 basis point increase," it means the rate went up by exactly 1.00%. So, the new rate would be 11%. This way, everyone understands the exact change.
Basis Points in Finance
In the world of finance, people often use basis points to show how much a financial product's rate changes. They also use it to show the difference between two interest rates. This includes the earnings you get from bonds and other fixed-income investments.
Sometimes, a loan or bond's interest rate is set based on another rate, like the London Interbank Offered Rate (LIBOR). If a loan's interest is 0.50% higher than LIBOR, people say it's "50 basis points over LIBOR." You might see this written as "L+50bps" or just "L+50."
Where Does the Term Come From?
The term "basis point" comes from trading. Traders often talk about the "basis," which is the difference or "spread" between two interest rates. Since this difference is usually very small, they multiplied it by 10,000 to make it easier to talk about. So, a "full point" movement in this "basis" became known as a basis point.
You'll also hear about basis points when people discuss the fees for investment funds. These fees, called "expense ratios," are often listed in basis points.
See also

- In Spanish: Punto base para niños
 | Shirley Ann Jackson |
 | Garett Morgan |
 | J. Ernest Wilkins Jr. |
 | Elijah McCoy |