Bihor County facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Bihor County
Județul Bihor
Bihar megye
|
||
|---|---|---|
|
County
|
||

Oradea, capital of Bihor County
|
||
|
||
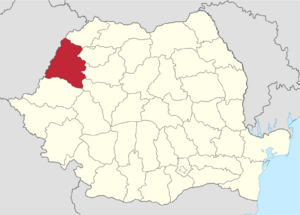
Location of Bihor County in Romania
|
||
| Country | ||
| Historic region | Crișana | |
| Capital city (Reședință de județ) | Oradea | |
| Government | ||
| • Type | County Council | |
| Area | ||
| • Total | 7,544 km2 (2,913 sq mi) | |
| Area rank | 6th in Romania | |
| Highest elevation | 1,849 m (6,066 ft) | |
| Lowest elevation | 89 m (292 ft) | |
| Population
(2021-12-01)
|
||
| • Total | 551,297 | |
| • Rank | 11th in Romania | |
| • Density | 73.078/km2 (189.270/sq mi) | |
| Time zone | UTC+2 (EET) | |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+3 (EEST) | |
| Postal Code |
41wxyz3
|
|
| Area code(s) | +40 x594 | |
| ISO 3166 code | RO-BH | |
| Car Plates | BH5 | |
| GDP | US$8.660 billion (2024) | |
| GDP per Capita | US$14,446 (2024) | |
| Website | County Council County Prefecture |
|
| 1The developing regions of Romania have no administrative role. They were formed to attract funds from the European Union 2 as of 2007, the Prefect is not a politician, but a civil servant. He (or she) is not allowed to be a member of a political party, and is banned from any political activity in the first six months after the resignation (or firing) from the civil service 3w, x, y, and z are digits that indicate the city, the street, part of the street, or even the building of the address 4x is a digit indicating the operator: 2 for the former national operator, Romtelecom, and 3 for the other ground telephone networks 5used on both the plates of the vehicles that operate only in the county limits (like utility vehicles, ATVs, etc.), and the ones used outside the county |
||
Bihor County (Romanian pronunciation: [biˈhor], Hungarian: Bihar megye) is a county, or județ, in western Romania. It covers an area of about 7,544 square kilometers (2,913 sq mi). This makes Bihor the 6th largest county in Romania by size. It is also the main county in the historical region of Crișana. The capital city of Bihor County is Oradea.
Contents
What's in a Name? The Origin of Bihor
The name Bihor likely comes from an old fortress in the area, near a place called Biharia. No one is completely sure where the name came from.
One idea is that it comes from the Serbian and Ukrainian word vihor, which means "whirlwind." Another idea is that it comes from the Slavic words biela hora, meaning "white mountain."
Some people think the name comes from the ancient Daco-Thracian language. In this theory, bi means "two" and harati means "take" or "lead." This might refer to two pieces of land.
A different idea suggests the name comes from bour, the Romanian word for aurochs. An aurochs is a type of wild ox that used to live in northwestern Romania. This theory suggests the name changed over time from buar to buhar, and then to Bihar and Bihor.
Bihor's Coat of Arms
The coat of arms for Bihor County was chosen in 1998. It shows a shield divided into four parts. On it, you can see a castle, five stalks of wheat tied with a ribbon, and a scroll. The scroll has words from Deșteaptă-te, române!, which is Romania's national anthem.
There's also a stripe across the middle with three fish. In 2013, the coat of arms had to be changed. A local teacher found that the words on the scroll were accidentally written in Greek! The original text of the anthem was in Cyrillic or Latin letters, and Bihor County has no special connection to Greece.
Exploring Bihor's Geography
Bihor County covers a total area of 7,544 square kilometers (2,913 sq mi). On the eastern side of the county, you'll find the Apuseni Mountains. The highest point in these mountains, and in the county, is Cucurbăta Mare (also called Bihor Peak), which is 1,849 meters (6,066 ft) tall.
As you move west, the land gets lower. It goes from hills down to the Romanian Western Plain, which is the eastern part of the larger Pannonian plain.
The county is mostly in the area where the Criș rivers flow. The main rivers here are the Crișul Repede, Crișul Negru, and Barcău.
Who are Bihor's Neighbors?
Bihor County shares its borders with several other places:
- To the East: Sălaj County, Cluj County, and Alba County (all in Romania).
- To the West: Hajdú-Bihar County and Békés County (both in Hungary).
- To the North: Satu Mare County (in Romania).
- To the South: Arad County (in Romania).
A Look at Bihor's History
Before World War I, the land that is now Bihor County was part of Austria-Hungary. Most of it was in the Bihar County of the Kingdom of Hungary.
After World War I ended, Austria-Hungary broke apart. In April 1919, the Romanian Army took control of the county during the Hungarian–Romanian War. In 1920, the Treaty of Trianon officially gave Bihor County to the Kingdom of Romania.
In 1938, King Carol II changed how Romania was divided. Counties were grouped into ten larger areas called ținuturi, which means "lands." These were ruled by "Royal Residents" chosen by the king. Bihor County became part of Ținutul Crișuri.
In August 1940, during World War II, part of the county was given back to Hungary. This happened because of something called the Second Vienna Award, which was influenced by Nazi Germany. But in October 1944, Romanian forces, with help from the Soviet Union, took the land back. It became part of Romania again. The Paris Peace Treaties, 1947 confirmed that the whole county belonged to Romania.
In 1950, the communist government in Romania changed the system. Bihor County was replaced by the Bihor Region. However, in February 1968, Bihor County was brought back when Romania returned to its county system.
Bihor's Economy
Bihor is one of the richest counties in Romania. Its economy is strong, and the average income per person is higher than the national average. Recently, many new buildings and projects have helped the economy grow.
Bihor has one of the lowest unemployment rates in Romania, and even in Europe. Only about 2.4% of people who want to work can't find a job, which is much lower than Romania's average of 5.1%.
The main industries in Bihor County are:
- Making clothes and other textiles.
- Producing food and drinks.
- Making parts for machines.
- Working with metals (metallurgy).
In the western part of the county, there are mines where people dig for coal and bauxite (a rock used to make aluminum). Crude oil is also found and taken out of the ground here.
Fun Places to Visit in Bihor
Bihor County has many interesting places for tourists to explore:
- The city of Oradea itself is a popular destination.
- The Apuseni Mountains offer beautiful scenery and activities:
- The Stâna de Vale resort and the Iad River valley are great for nature lovers.
- You can explore many caves around Padiș and in the Sighiștel River valley.
- Don't miss the Bear's Cave, a famous cave with ancient bear bones.
- The Băile Felix Resort is known for its thermal waters and spas.
People of Bihor: Demographics
According to the 2021 census, Bihor County had a population of 551,297 people. This means there were about 73 people per square kilometer (189 per sq mi). About 51.1% of the people in Bihor live in cities, which is a bit less than the average for all of Romania.
Ethnic composition of Bihor County (2021) Romanians (69.03%) Hungarians (22.35%) Romani (7.33%) Slovaks (0.97%) Germans (Sathmar Swabians) (0.11%) Others (0.22%)
Religious composition of Bihor County (2021) Romanian Orthodox (59.29%) Reformed (16.01%) Pentecostals (8.16%) Roman Catholics (8.01%) Baptists (4.28%) Greek Catholics (1.99%) Others (1.36%) Irreligious,atheist and agnostic (0.91%)
| Year | County population |
|---|---|
| 1948 | 536,323 |
| 1956 | 574,488 |
| 1966 | 586,460 |
| 1977 | 633,094 |
| 1992 | 634,093 |
| 2002 | 600,246 |
| 2011 | 575,398 |
| 2021 | 551,297 |
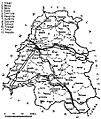
How Bihor is Divided: Administrative Divisions
Bihor County is organized into different types of areas: four municipalities, six towns, and 91 communes.
Municipalities
- Beiuș
- Marghita
- Oradea – This is the capital city, with 183,105 people as of 2021.
- Salonta
Towns
- Aleșd
- Nucet
- Săcueni
- Ștei
- Valea lui Mihai
- Vașcău
Communes
- Abram
- Aștileu
- Aușeu
- Avram Iancu
- Balc
- Batăr
- Biharia
- Boianu Mare
- Borod
- Borș
- Bratca
- Brusturi
- Budureasa
- Buduslău
- Bulz
- Buntești
- Căbești
- Câmpani
- Căpâlna
- Cărpinet
- Cefa
- Ceica
- Cetariu
- Cherechiu
- Chișlaz
- Ciumeghiu
- Cociuba Mare
- Copăcel
- Criștioru de Jos
- Curățele
- Curtuișeni
- Derna
- Diosig
- Dobreşti
- Drăgănești
- Drăgești
- Finiș
- Gepiu
- Girișu de Criș
- Hidişelu de Sus
- Holod
- Husasău de Tinca
- Ineu
- Lăzăreni
- Lazuri de Beiuș
- Lugașu de Jos
- Lunca
- Mădăras
- Măgești
- Nojorid
- Olcea
- Oșorhei
- Paleu
- Petreu
- Pietroasa
- Pocola
- Pomezeu
- Popești
- Răbăgani
- Remetea
- Rieni
- Roșia
- Roșiori
- Sâmbăta
- Sâniob
- Sânnicolau Român
- Sânmartin
- Sântandrei
- Sârbi
- Săcădat
- Sălacea
- Sălard
- Spinuș
- Suplacu de Barcău
- Șimian
- Șinteu
- Șoimi
- Șuncuiuș
- Tămășeu
- Tărcaia
- Tarcea
- Tăuteu
- Tileagd
- Tinca
- Toboliu
- Tulca
- Țețchea
- Uileacu de Beiuș
- Vadu Crișului
- Vârciorog
- Viișoara
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Distrito de Bihor para niños
In Spanish: Distrito de Bihor para niños
 | Bayard Rustin |
 | Jeannette Carter |
 | Jeremiah A. Brown |