British entry into World War I facts for kids
The United Kingdom joined World War I on August 4, 1914. This happened when King George V declared war after Germany ignored Britain's warning. The main public reason was to protect Belgium, a neutral country. However, a big secret reason was to stop Germany from defeating France. If France lost, Germany would control much of Western Europe.
The Liberal Party was in charge, led by Prime Minister H. H. Asquith and Foreign Minister Edward Grey. Even though many Liberals were against war, the cabinet decided to join. The Conservative Party wanted war. The Liberals knew that if they didn't agree on the war, they might lose power to the Conservatives.
Contents
How Britain Prepared for War
For most of the 1800s, Britain followed a policy called "splendid isolation." This meant staying out of formal alliances to keep a balance of power in Europe. But by the 1890s, Europe was splitting into two main groups. The British government realized this left Britain vulnerable.
So, Britain started making new friends. In 1902, they signed the Anglo-Japanese Alliance with Japan. Then, in 1903, King Edward VII visited Paris. This helped improve relations with France and led to the 1904 Entente Cordiale. This agreement helped Britain support France against Germany during the First Moroccan Crisis in 1905.
In 1907, the new Liberal government made another agreement, the Anglo-Russian Convention, this time with Russia. Like the agreement with France, it helped solve problems over colonies. This allowed Britain to focus its navy more on the growing German navy.
By 1911, after another crisis in Morocco (the Agadir Crisis), Britain and France began secret military talks. They planned for a British army of 100,000 soldiers to go to France within two weeks if war broke out. The French Navy would handle the Mediterranean Sea, while the Royal Navy would protect the North Sea and the English Channel. This meant Britain was pretty much committed to helping France if Germany attacked. However, most people outside the government didn't know this.
Why Britain and Germany Didn't Get Along
One big reason Britain went to war with Germany was that Germany was quickly becoming much stronger economically. Britain worried that Germany, with its fast-growing industries and powerful army and navy, would control the English Channel and northern France. British leaders believed this would be a disaster for their country's safety.
Germany often used military force, while Britain preferred to talk about what was right and wrong. This difference became very clear when Germany invaded neutral Belgium. Germany saw it as a necessary military move. Britain saw it as a terrible crime.
Historians point out that on July 29, 1914, the British government decided that an old treaty from 1839, which protected Belgium, didn't force them to fight if Germany invaded Belgium. But things changed quickly.
The Decision to Go to War
On June 28, 1914, Archduke Franz Ferdinand, the heir to the Austro-Hungarian throne, was killed in Sarajevo. At first, British newspapers were sympathetic to Austria-Hungary and blamed the Serbian assassin. They used strong words against "fanatics" and "reckless agitators."
But by July 27, opinions started to change. Newspapers began to criticize Austria-Hungary. Conservative papers said Britain had to support France. Liberal papers argued Britain should stay neutral.
As Germany supported Austria-Hungary and Russia supported Serbia, British leaders felt more and more committed to defending France. They worried that if Germany defeated France again, like in the 1870 Franco-Prussian War, Germany would become a huge threat to Britain.
Also, politics played a role. The Liberal Party was known for wanting peace and free trade. The Conservative Party was seen as the party of national pride and war. Liberal voters initially wanted peace. But they became very angry when Germany invaded Belgium and called the 1839 treaty protecting Belgium a "scrap of paper."
Germany invaded northern France through Belgium early on August 4. Belgium asked Britain for military help under the 1839 treaty. Britain then gave Germany a warning, which expired at 11 pm London time. Germany ignored it. That evening, King George V declared war on Germany.
Before the war was declared, British newspapers had many different ideas about what Britain should do. Some, like Manchester Guardian, strongly argued against war. They called it a "crime against Europe."
David Lloyd George, a politician, said that just a few days before the war, only two cabinet members wanted to join. But Germany's invasion of Belgium completely changed everyone's minds.
Once war was declared, defending Belgium became the main public reason for fighting. Propaganda posters showed that Britain had to protect Belgium's neutrality.
Even on August 1, 1914, most Liberals were against war. But the German invasion of Belgium was such a clear violation of international rules that the Liberal Party agreed to war on August 4. Historian Zara Steiner noted that Belgium was the spark. It brought out strong anti-German feelings that had been building up for years. Having a moral reason to fight helped unite the government and public opinion.
The Liberal government managed to overcome its deep disagreements. If they didn't act against Germany's invasion of France, top leaders like Prime Minister Asquith and Foreign Minister Grey would resign. This could have led to the pro-war Conservative Party taking over. While Belgium's mistreatment wasn't the only reason Britain entered the war, it was used a lot in wartime messages to encourage the British people.
The German military leaders knew that invading Belgium might bring Britain into the war. But they thought the risk was worth it. They expected the war to be short. Germany's ambassador in London even thought that a civil war in Ireland would stop Britain from helping France.
Most of the Labour Party had been against the war. But after Germany invaded Belgium, they also changed their minds and supported the war. Some members, like Ramsay MacDonald, still opposed it. But the Labour Party leaders thought the war would be short. They also believed that opposing it would hurt the party in the next election.
The Irish Problem Put on Hold
Before late July 1914, British politics was completely focused on the risk of a civil war in Ireland. In 1912, the government had proposed a law called Irish Home Rule. This law would give Ireland more control over its own affairs. It was supposed to become law in 1914.
However, Protestants in Ulster (Northern Ireland) wanted to be treated separately. By mid-1914, the government offered them a six-year break from the law. But Ulster wanted a permanent break. Both sides in Ireland had brought in weapons and formed their own armies. They were ready to fight. Even the British Army was divided. Some officers threatened to quit rather than fight against Ulster.
On July 25, when Austria's warning to Serbia became known, the government realized war with Germany was likely. The Government of Ireland Act 1914 became law, but it was put on hold until the war ended. The issue of Ulster was still not solved.
Foreign Minister Grey told the British Parliament on August 3 that Ireland was "the one bright spot in the whole of this terrible situation." He meant that Ireland's situation would not stop Britain from going to war.
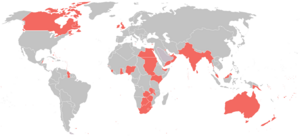
The Empire Joins the War
When the King declared war, all of Britain's dominions (like Canada and Australia), colonies, and protectorates around the world automatically joined too. Many of them sent a lot of soldiers and workers to help the Allied war effort.
See also
- Causes of World War I
- Austro-Hungarian entry into World War I
- French entry into World War I
- German entry into World War I
- Ottoman entry into World War I
- Russian entry into World War I
- Allies of World War I
- Triple Entente
- France–United Kingdom relations
- Germany–United Kingdom relations
- British military history
- History of the United Kingdom, since 1707
- International relations of the Great Powers (1814–1919)
- Diplomatic history of World War I
- Color book
- International relations (1919–1939)
- Timeline of British diplomatic history
- History of the foreign relations of the United Kingdom