Chicken as food facts for kids
| Course | Starter, main meal, side dish |
|---|---|
| Serving temperature | Hot and cold |
| Nutritional value per 100 g (3.5 oz) | |
|---|---|
| Energy | 916 kJ (219 kcal) |
|
0.00 g
|
|
|
12.56 g
|
|
| Saturated | 3.500 g |
| Monounsaturated | 4.930 g |
| Polyunsaturated | 2.740 g |
|
Protein
|
24.68 g
|
| Tryptophan | 0.276 g |
| Threonine | 1.020 g |
| Isoleucine | 1.233 g |
| Leucine | 1.797 g |
| Lysine | 2.011 g |
| Methionine | 0.657 g |
| Cystine | 0.329 g |
| Phenylalanine | 0.959 g |
| Tyrosine | 0.796 g |
| Valine | 1.199 g |
| Arginine | 1.545 g |
| Histidine | 0.726 g |
| Alanine | 1.436 g |
| Aspartic acid | 2.200 g |
| Glutamic acid | 3.610 g |
| Glycine | 1.583 g |
| Proline | 1.190 g |
| Serine | 0.870 g |
| Vitamins | Quantity
%DV†
|
| Vitamin A equiv. |
6%
44 μg |
| Pantothenic acid (B5) |
13%
0.667 mg |
| Minerals | Quantity
%DV†
|
| Iron |
9%
1.16 mg |
| Sodium |
4%
67 mg |
| Other constituents | Quantity |
| Water | 63.93 g |
|
Not including 35% bones
|
|
| †Percentages estimated using US recommendations for adults. | |
Chicken is the most common type of poultry in the world. It's easy and cheap to raise chickens compared to animals like cattle or pigs. Because of this, chicken meat (often just called "chicken") and chicken eggs are popular in many different cuisines.
You can cook chicken in many ways, such as baking, grilling, barbecuing, frying, and boiling. Since the mid-1900s, cooked chicken has become a main part of fast food. People sometimes say chicken is healthier than red meat. It has less cholesterol and saturated fat.
The poultry farming industry, which produces chicken, works differently around the world. In richer countries, chickens are often raised using intensive farming methods. In other areas, people use more traditional ways. The United Nations estimates there are 19 billion chickens on Earth today. That's more than two chickens for every person!
Contents
History of Chicken
The chickens we see today came from red junglefowl and grey junglefowl. These birds were first raised thousands of years ago in northern India.
Ancient carvings from Babylon around 600 BC show chicken as a food. Chicken was a very common meat during the Middle Ages. For thousands of years, different kinds of chicken, like capons and hens, have been eaten across most of the Eastern hemisphere. It was even a main ingredient in blancmange, a stew made with chicken, onions, milk, spices, and sugar.
In the United States in the 1800s, chicken was more expensive than other meats. It was seen as a special dish for the wealthy. Chicken eating in the U.S. grew a lot during World War II. This was because there wasn't enough beef and pork. In Europe, people started eating more chicken than beef and veal in 1996. This was partly because of concerns about mad cow disease.
-
Chicken wings being barbecued
How Chickens are Bred
Modern types of chicken, like the Cornish Cross, are bred especially for meat. Farmers focus on how much meat the chicken produces compared to the food it eats. The most common chicken breeds eaten in the U.S. are Cornish and White Rock.
Chickens raised just for food are called broilers. In the U.S., broilers are usually butchered when they are young. For example, modern Cornish Cross chickens are ready for frying at 8 weeks. They are ready for roasting at 12 weeks.
Capons are male chickens that have been castrated. They produce more meat and it's fattier. Because of this, they were considered a special food, especially popular in the Middle Ages.
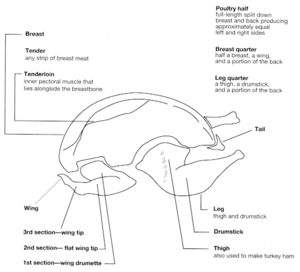
Parts of a Chicken You Can Eat

- Main Parts
- Breast: This is white meat and can be a bit dry. The breast has two parts:
- The main "breast" piece, sold without bones.
- Two "tenderloin" pieces, found under the breast meat near the ribs. These are often sold separately.
- Leg: This part has two sections:
- The "drumstick"; this is dark meat and is the lower part of the leg.
- The "thigh"; also dark meat, this is the upper part of the leg.
- Wing: Often eaten as a snack or appetizer. Buffalo wings are a good example. It has three parts:
- The "drumette", which looks like a tiny drumstick and is white meat.
- The middle "flat" part, with two bones.
- The tip, which is usually thrown away.
- Breast: This is white meat and can be a bit dry. The breast has two parts:
- Other Parts
- Chicken feet: These have little meat but are eaten for their skin and cartilage. They are popular in the Caribbean, China, and Vietnam.
- Giblets: These are organs like the heart, gizzards, and liver. They might be inside a whole chicken or sold separately.
- Head: In China, the head is a special dish. It's split open, and the brains and other soft parts are eaten.
- Kidneys: These are usually left inside the chicken when it's processed. They are found deep near the backbone.
- Neck: Used in various Asian dishes. Ashkenazi Jews stuff it to make helzel.
- Oysters: These are small, round pieces of dark meat found on the back near the thigh. Many people think they are a special treat.
- Pygostyle (chicken's buttocks): This is commonly eaten in East Asia and parts of Southeast Asia.
- By-products (Other useful parts)
- Blood: After a chicken is butchered, its blood can be collected. In many Asian countries, it's made into disc-shaped cakes for sale. These are often cut into cubes and used in soups.
- Carcass: After the meat is removed, the bones and remaining parts are used to make chicken stock for soups.
- Chicken eggs: These are the most well-known product from chickens, besides the meat itself.
- Heart and gizzard: In Brazilian churrascos (barbecues), chicken hearts are often seen as a tasty treat.
- Liver: This is the largest organ of the chicken. It's used in dishes like Pâté and chopped liver.
- Schmaltz: This is chicken fat that has been melted down. It's used in many different dishes.
Buying and Selling Chicken
You can buy chicken as a whole bird or cut into pieces.
In the United Kingdom, very young chickens (less than 28 days old) are sold as poussin. Older chickens are sold as small, medium, or large.
In the United States, whole adult chickens are sold as fryers, broilers, and roasters. Fryers are the smallest (about 2.5-4 pounds) and most common. Broilers are larger than fryers. Roasters are the biggest chickens commonly sold (6-8 pounds) and are usually more expensive. Even larger, older chickens are called stewing chickens, but you don't often find these in stores anymore. These names suggest the best way to cook them based on their size.
Chicken is also sold in pieces. These pieces usually come from smaller birds. A chicken is often cut into two leg quarters and two breast quarters. Each quarter has two common pieces. A leg quarter includes the thigh, drumstick, and part of the back. A breast quarter has the breast, wing, and part of the back. You can buy packages with all the same pieces, or mixed packages. "Whole chicken cut up" means the whole bird is cut into 8 pieces.
Many fast food restaurants around the world sell mostly chicken. Examples include KFC and Red Rooster in Australia. Most of their chicken dishes are fried or breaded and served with french fries.
Cooking Chicken Safely
Raw chicken can have bacteria called Salmonella. To prevent foodborne illness, the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services suggests cooking chicken to at least 165 °F (74 °C). However, in Japan, some dishes like torisashi use raw chicken slices, similar to sashimi. Another dish, toriwasa, is lightly seared on the outside but raw inside.
You can cook chicken in many ways. It can be made into sausages, put on skewers, added to salads, grilled, deep-fried with breading, or used in different curries. Cooking methods vary a lot between cultures. Historically, common ways include roasting, baking, and frying. Western fast food often features deep frying for things like fried chicken, chicken nuggets, or Buffalo wings. Chicken is also often grilled for salads or tacos.
Chicken bones can be dangerous if eaten because they can break into sharp pieces. However, you can simmer them with vegetables and herbs for hours to make chicken stock. This stock is great for soups.
In Asian countries, you can buy just the bones because they are very popular for making healthy chicken soups. In Australia, the rib cages and backs of chickens are often sold cheaply as "chicken frames" or "chicken carcasses" for making soup or stock.
-
Marination of chicken
-
Chicken tikka masala, a popular dish adapted from Indian chicken tikka.
-
A chicken curry from Maharashtra, India with rice flour chapatis.
-
Peking chicken from the Philippines
-
Butter chicken from India
Freezing Chicken
Raw chicken stays good longer in the freezer than fresh chicken. Its nutritional value doesn't change much when frozen. For the best quality, it's recommended to store uncooked whole chicken for up to 12 months in the freezer. Uncooked chicken parts can be stored for 9 months, and cooked chicken for 4 months. Freezing usually doesn't change the color of poultry. However, bones and nearby meat can turn dark. This happens when pigment from the bones of young poultry seeps into the meat when it's frozen and thawed.
It's safe to freeze chicken in its original packaging. But for longer storage, it's best to wrap it again with another layer. If a package tears in the freezer, the food is still safe, but you should rewrap it. Keep chicken away from other foods so that if it thaws, its juices won't drip onto them. If you buy chicken that was already frozen, you can refreeze it if it has been handled correctly.
Bacteria can survive in freezing temperatures, but they don't grow. However, if frozen cooked foods are not thawed properly and not reheated to a temperature that kills bacteria, you have a much higher chance of getting a foodborne illness.
See also
 In Spanish: Carne de pollo para niños
In Spanish: Carne de pollo para niños