Western diamondback rattlesnake facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Western diamondback rattlesnake |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Conservation status | |
| Scientific classification |
|
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Squamata |
| Suborder: | Serpentes |
| Clade: | Caenophidia |
| Clade: | Colubroides |
| Family: | Viperidae |
| Subfamily: | Crotalinae |
| Genus: | Crotalus |
| Species: |
C. atrox
|
| Binomial name | |
| Crotalus atrox Baird & Girard, 1853
|
|
 |
|
| Script error: The function "autoWithCaption" does not exist. | |
| Synonyms | |
|
|
Script error: No such module "Check for conflicting parameters".
The western diamondback rattlesnake (Crotalus atrox) is a type of venomous snake. It lives in the deserts of the USA and Mexico. This snake is well-known in these areas. There are no different types (subspecies) of this snake.
Contents
What Does a Western Diamondback Rattlesnake Look Like?
Adult western diamondback rattlesnakes usually grow to about 120 cm (3.9 ft) long. Some can reach 150 cm (4.9 ft) or even 180 cm (5.9 ft). The longest one ever found was 213 cm (6.99 ft) long.
Male snakes are usually bigger than females once they are fully grown. These rattlesnakes often weigh between 1.8 to 2.7 kg (4.0 to 6.0 Ib). Some larger ones can weigh up to 6.7 kg (15 Ib).
Their color is usually gray-brown. Some can be pinkish-brown or brick red. They have dark gray-brown blotches and white stripes on their bodies.
Other Names for This Rattlesnake
The western diamondback rattlesnake has many other names. People sometimes call it the "adobe snake" or the "Arizona diamond rattlesnake." Other names include "coon-tail snake" and "desert diamondback snake." It is also known as the "Texan snake" or the "Texas diamondback rattlesnake."
Where Do Western Diamondback Rattlesnakes Live?
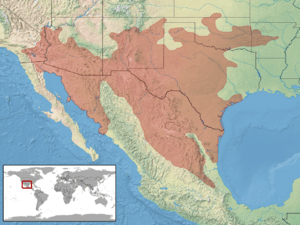
In the USA, you can find this snake in many states. These include central and western Arkansas, Oklahoma, and Texas. They also live in southern and central New Mexico and Arizona. You can find them in southern Nevada and southeastern California too.
In Mexico, they live in several states. These are Nuevo Leòn, Coahuila, and Chihuahua. They are also in Sonora, northeastern Baja California, and northern Sinaloa. Other places include northeastern Durango, Zacatecas, San Luis Potosì, northern Veracruz, Hidalgo, and Querètaro. Some have even been found on islands in the Gulf of California. These islands include San Pedro Màtir, Santa Marìa, and Tìburon.
What Kind of Places Do They Like?
Western diamondback rattlesnakes live in different types of environments. They are found in deserts and grasslands. They also live in pink-oak forests and coastal plains. You can also spot them in rocky canyons in both the USA and Mexico.
How Do Western Diamondback Rattlesnakes Behave?
These rattlesnakes are known for being quite protective. When they feel threatened, they usually coil up and rattle their tails loudly. This sound warns others to stay away.
In the winter, they go into a deep sleep called hibernation. They often share caves and burrows with other types of snakes. They are not very good at climbing trees or other tall objects.
What Do Western Diamondback Rattlesnakes Eat?
Most of what a western diamondback rattlesnake eats is small mammals. About 94% of their diet includes animals like prairie dogs, kangaroo rats, and pocket gophers. They also eat voles, wood rats, pocket mouses, white-footed mouses, and harvest mouses. Other meals include ground squirrels, rabbits, and moles.
They also eat lizards and birds. Some birds they hunt are mockingbirds, burrowing owls, black-throated sparrows, and eastern meadowlarks. The lizards they eat include whiptail liazards, spiny lizards, Texas banded geckos, and side-blotched lizards. Sometimes, they even eat insects like ants, beetles, and grasshoppers. They usually hunt in the early morning or at night.
Larger animals sometimes eat western diamondback rattlesnakes. These predators include coyotes, foxes, and hawks.
Western Diamondback Rattlesnake Reproduction and Life Cycle
Like all rattlesnakes, the western diamondback rattlesnake gives birth to live young. This means the babies grow inside the mother. A female snake is pregnant for about six to seven months.
She then gives birth to her young. A female can have around 12 to 25 babies at one time. When they are born, the young snakes are about 30 cm (12 in) long. Baby western diamondback rattlesnakes have a venomous bite from the moment they are born. They only stay with their mother for a few hours before they leave to find food on their own. These snakes can live for about 20 years.
Images for kids
-
A skeleton at the Museum of Osteology, Oklahoma City, Oklahoma
See also
 In Spanish: Crótalo diamante occidental para niños
In Spanish: Crótalo diamante occidental para niños
 | DeHart Hubbard |
 | Wilma Rudolph |
 | Jesse Owens |
 | Jackie Joyner-Kersee |
 | Major Taylor |










