East Lothian facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
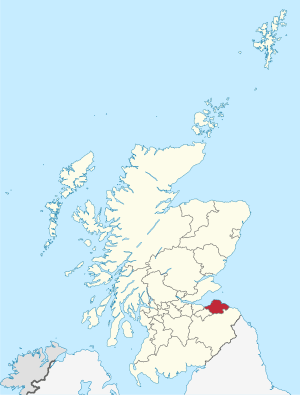
East Lothian
Aest Lowden
Lodainn an Ear Haddingtonshire
|
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
|||||
|
|||||
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom | ||||
| Country | Scotland | ||||
| Lieutenancy area | East Lothian | ||||
| Admin HQ | Haddington | ||||
| Government | |||||
| • Type | Unitary authority | ||||
| • Body | East Lothian Council | ||||
| Area | |||||
| • Total | 262.2 sq mi (679.2 km2) | ||||
| Area rank | Ranked 18th | ||||
| Population
(2020)
|
|||||
| • Total | 105,790 | ||||
| • Rank | Ranked 21st | ||||
| • Density | 403.41/sq mi (155.757/km2) | ||||
| ONS code | S12000010 | ||||
| ISO 3166 code | GB-ELN | ||||
| Largest city | Musselburgh | ||||
East Lothian is a beautiful area in eastern Scotland. It is one of Scotland's 32 council areas, which are like local government regions. It's also a historic county, meaning it has a long history as a distinct area.
East Lothian is located south of the Firth of Forth, which is a large bay. It borders Edinburgh to the west, Midlothian to the southwest, and the Scottish Borders to the south. The main town and administrative center is Haddington, while the largest town is Musselburgh.
This area was known as Haddingtonshire until 1921. It has very old roots, being mentioned in old documents from the 1100s. Three of its towns – Haddington, Dunbar, and North Berwick – were once special "royal burghs," which were important towns with special rights from the king.
East Lothian was part of the Anglo-Saxon kingdom of Bernicia a long time ago. Later, it became part of the Kingdom of Northumbria. A famous legend says that the flag of Scotland was created in the East Lothian village of Athelstaneford after a battle in 823. From the 900s, Lothian became part of Scotland. It was a key place for battles between England and Scotland. Later, a big victory for the Jacobites (supporters of the Stuart kings) happened here at the Battle of Prestonpans. In the 1800s, East Lothian was known for its farms, fishing, and coal mining.
Contents
Exploring East Lothian's Past
How East Lothian Began
After the Romans left Britain, the area now known as Lothian was home to people who spoke a language called Brythonic. This area was part of a kingdom called Gododdin. In the 600s, the Angles took over this land, and Lothian became part of the kingdom of Bernicia.
Bernicia later joined with other areas to form the Kingdom of Northumbria, which was part of early England. However, by the 900s, the Scottish kings gained control of Lothian. The first mention of the "shire" (or county) of Haddington, or Haddingtonshire, was in the 1100s. It covered the eastern part of Lothian.
Castles and Conflicts in History
Haddingtonshire was a busy place during many old wars. You can still see many strong castles and buildings from this time, like Dunbar Castle, Tantallon Castle, and Dirleton Castle.
In the 1100s and 1200s, the Palace of Haddington was one of the homes for the Kings of Scotland. King William the Lion stayed there, and his son, Alexander II, was born there in 1198. Sadly, the palace and town were burned by an English army in 1216. In 1296, a big battle happened at Dunbar, where the English army won against the Scottish king.
East Lothian also saw fighting during a war called the Rough Wooing in the 1500s. Many homes and villages were burned by the English. Later, during the War of the Three Kingdoms, another Battle of Dunbar took place in 1650. English forces won this battle and then marched on to take Edinburgh.
After the kings returned to power and Scotland joined with England to form Great Britain, there were still conflicts. The Jacobites fought against the government. In September 1745, a major battle happened at Prestonpans in the west of the county. The Jacobites won a big victory there, but they were later defeated in another battle in 1746.
East Lothian in Modern Times
In 1890, the Haddingtonshire County Council was created to manage local affairs. This council was based at the County Buildings in Haddington.
In 1921, the council decided to change the county's name from Haddingtonshire to "East Lothian." The government agreed, and the change became official in November 1921.
Later, in 1975, Scotland's local government system changed. East Lothian became a "district" within a larger "region" called Lothian. Then, in 1996, Scotland changed its system again, creating 32 new local authorities. This is when the modern council area of East Lothian was officially formed, much like it is today.
East Lothian's Natural Beauty
East Lothian is mostly countryside. It has about 40 miles (64 km) of coastline along the Firth of Forth. Many towns are located along this coast, including Musselburgh, Prestonpans, Cockenzie and Port Seton, Longniddry, Gullane, North Berwick, and Dunbar. The coast has many interesting features like bays and headlands. There are also small islands off the coast near North Berwick, such as Fidra and Bass Rock.
Only two towns in East Lothian are not on the coast: Tranent and Haddington. To the south, you'll find the Lammermuir Hills, which form the border with Berwickshire. The highest point in the county, Meikle Says Law, is in these hills, standing at 535 meters (1,755 feet) tall. The River Tyne flows through Haddington and other villages, reaching the Firth of Forth near Belhaven. The River Esk flows through Musselburgh before emptying into the Firth of Forth.
Getting Around East Lothian
Roads
The main road, the A1, runs through East Lothian. It connects to the Scottish Borders in the south and Edinburgh in the north. The A1 is a dual carriageway (meaning it has two lanes in each direction) in East Lothian, with major exits for towns like Dunbar, Haddington, Tranent, Prestonpans, and Musselburgh.
Another important road is the A199, which starts in Leith and goes through Musselburgh, Wallyford, Tranent, Macmerry, and Haddington.
Public Transport
East Lothian has several railway stations. You can catch trains at East Linton, Dunbar, and Musselburgh on the East Coast Main Line. There are also stations at North Berwick, Drem, Longniddry, Prestonpans, and Wallyford on the North Berwick Line. Train companies like ScotRail, CrossCountry, and London North Eastern Railway serve these stations.
Buses are also a popular way to travel. Lothian Buses and its company East Coast Buses provide most of the services, connecting towns and villages in East Lothian to Edinburgh.
People of East Lothian
In 2019, the population of East Lothian was about 105,790 people. This number has been growing and is expected to reach over 120,000 by the 2030s. The area around Tranent, Wallyford, and Macmerry is growing the fastest.
Fun Places to Visit
East Lothian has many interesting places to explore:
- Aberlady Bay
- Bass Rock
- Dirleton Castle
- Dunglass Collegiate Church
- Fa'side Castle
- Fenton Barns Retail & Leisure Village
- Hailes Castle
- Hopetoun Monument
- Lennoxlove historic house
- Longniddry Bents
- Muirfield Golf Links
- Museum of Flight, East Fortune
- North Berwick Harbour
- North Berwick Law
- Preston Mill
- Prestongrange Industrial Heritage Museum
- Scottish Seabird Centre, North Berwick
- Seacliff Beach
- Seton Collegiate Church
- Tantallon Castle
- Chesters Hill Fort
- Torness Nuclear Power Station
- Traprain Law
- Yellowcraigs, a beach and conservation area
Towns and Villages
Here are the largest towns and villages in East Lothian by population:
| Settlement | Population (2020) |
|---|---|
| Musselburgh | 21100 |
| Tranent | 11910 |
| Prestonpans | 10460 |
| Haddington | 10360 |
| Dunbar | 10270 |
| North Berwick | 7840 |
| Cockenzie | 5370 |
| Wallyford | 3370 |
| Gullane | 2810 |
| Longniddry | 2340 |
Learning in East Lothian
East Lothian has many schools. There are six state-run high schools:
- Dunbar Grammar School
- Knox Academy in Haddington
- Musselburgh Grammar School
- North Berwick High School
- Preston Lodge High School in Prestonpans
- Ross High School in Tranent
There are also two private schools:
- Loretto School in Musselburgh, which was founded in 1827.
- Belhaven Hill School in Dunbar, a smaller school established in 1923.
In 2007, Queen Margaret University moved to a new campus in Musselburgh, making it the first university in East Lothian.
Culture and Community
East Lothian's Flag

In 2017, East Lothian held a competition to design an official county flag. Many people entered, and in December 2018, the winning design was announced. It was created by Archie Martin, a local man from Musselburgh.
The flag features a saltire (a cross shape) to show that East Lothian is believed to be where Scotland's flag was first thought of. A gold cross represents the rich farmlands and East Lothian's history as a "granary" (a place that produces a lot of grain). A lion in the middle stands for the Haddington lion, and blue stripes represent the River Esk and River Tyne.
Local News and Radio
East Lothian has a local newspaper called the East Lothian Courier. It started in 1859 as the Haddingtonshire Courier and changed its name in 1971.
There are also two local community radio stations: East Coast FM, based in Haddington, and Radio Saltire, based in Tranent.
Famous People from East Lothian
Many interesting people have connections to East Lothian:
- Alexander II (1198–1249), a King of Scots.
- John Knox (c.1510-1572), a very important leader of the Protestant Reformation in Scotland.
- Andrew Fletcher of Saltoun (1655–1716), a writer and politician.
- Andrew Meikle (1719–1811), who invented the threshing machine, which helped farmers.
- Rev. Dr. John Witherspoon (1723–1794), who signed the United States Declaration of Independence.
- Robert Moffat (1795–1883), a missionary to Africa and father-in-law of David Livingstone.
- Jane Welsh Carlyle (1801–1866), a famous letter-writer.
- Samuel Smiles (1812–1904), author of the book Self-Help.
- John Muir (1838–1914), known as the "father of the US National Parks" because he helped create them.
- Arthur Balfour (1848–1930), who was a Prime Minister of the United Kingdom.
- Mollie Hunter (1922–2012), a Scottish writer.
- John Bellany (1942–2013), a famous painter.
- Rhona Cameron (born 1965), a comedian.
Many sports stars also have ties to East Lothian:
- Willie Anderson, a golfer who won the U.S. Open Golf Championship four times.
- Catriona Matthew, a professional golfer.
- Gary Anderson, a darts player.
- Euan Burton, a judoka (judo athlete) who competed in the 2012 Olympics.
- Josh Taylor, a professional boxer.
Special Honors
The "Freedom of the County" is a special honor given to people or groups who have done great things for East Lothian.
- John Bellany: 2004
- Catriona Matthew: 2009
Military units that have received this honor include:
- 1st Battalion The Royal Scots Borderers: 2012
- E Squadron The Scottish and North Irish Yeomanry: 6 July 2019
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: East Lothian para niños
In Spanish: East Lothian para niños