Exsanguination facts for kids
Exsanguination (say: ex-SAN-gwin-AY-shun) is when someone loses so much blood that it causes them to die. You don't have to lose all your blood to exsanguinate. Losing about half to two-thirds of your blood can be deadly.
An average adult has about 5 to 6 liters of blood. This means losing 2.5 to 4 liters can be fatal. To compare, this is five to eight times the amount of blood people usually give when they donate blood.
Children and babies have much less blood than adults. They can exsanguinate by losing a lot less blood.
Exsanguination is often called bleeding to death or bleeding out. It is a serious medical emergency.
Contents
What is Exsanguination?
Doctors define exsanguination in a specific way:
- A patient has lost over 40% of their blood. For an average adult, this is 2 to 2.4 liters.
- The patient is still losing blood.
- The bleeding is so severe that if it's not stopped quickly, the patient will die.
Types of Bleeding
Bleeding can be external or internal.
External bleeding means it's happening outside the body. You can see it. For example, if you cut your hand and blood is on your skin, that's external bleeding.
Internal bleeding means it's happening inside the body. You can't see it. For example, if someone is bleeding into their brain because of a stroke, that's internal bleeding.
Sometimes, bleeding can be both internal and external. A person can exsanguinate from internal bleeding, external bleeding, or both.
What Causes Exsanguination?
Exsanguination usually happens when major blood vessels are badly injured or break open. Smaller blood vessels bleed less and slower, so they are less likely to cause exsanguination.
Injuries That Cause Bleeding
Exsanguination can be caused by injuries (also called trauma). About 30-40% of people who die from injuries die because of exsanguination. Many of these people (33-56%) die before they even reach a hospital.
Penetrating trauma is a common cause. This is an injury where something breaks the skin. Gunshot wounds to places like the heart, chest, or head are especially dangerous. These areas have many major blood vessels.
Other injuries that can cause exsanguination include:
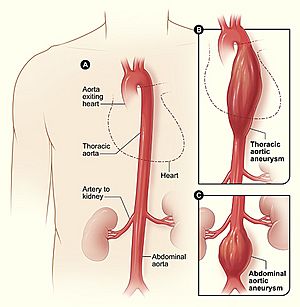
- Cuts to major arteries, like the aorta (the body's largest artery), carotid artery (in the neck), or femoral artery (in the groin and legs).
- Car accidents.
- Losing an arm or leg (Amputation).
A person can exsanguinate from internal bleeding if:
- They are bleeding into their chest or abdomen. This can happen from blunt force trauma.
- They break their pelvis.
- They break both of their femurs (thigh bones).
Exsanguination is a common cause of death for soldiers during war. It is often caused by gunshot wounds, car accidents, or explosions.
Medical Problems That Cause Bleeding
Some medical problems can cause a person to bleed internally and exsanguinate. These include:
- An aneurysm in the aorta that breaks. This can cause a person to exsanguinate in just a few minutes.
- Sepsis, a severe infection. It can cause the infection to damage blood vessel walls. Eventually, the walls break, and the blood vessels start to bleed.
- Bleeding after childbirth. Around the world, one woman dies every two minutes from exsanguination after childbirth. Most of these deaths happen in developing countries.
- Bleeding from organs like the spleen, liver, or intestines.
- A very bad peptic ulcer (a sore in the stomach or intestine).
- A tumor that grows into a major blood vessel. For example, a tumor in the neck could grow into the carotid artery and cause it to bleed.
How Exsanguination Affects the Body
If someone loses blood very quickly, they might only be awake for 20 seconds to a few minutes. If blood loss is slower, they might be conscious for a few hours. However, they will become more and more confused and tired as they lose blood. Eventually, they will go into a coma because there isn't enough blood to carry oxygen to their brain. Finally, their heart will stop, and they will die.
Exsanguination is a Syndrome
Doctors call exsanguination a syndrome. This means it's a group of symptoms and problems that happen together in the body.
Hypothermia
Blood helps keep us warm. So, losing a lot of blood causes hypothermia, which is when your body temperature drops too low.
Coagulopathy
Coagulopathy means the blood no longer clots normally. When a person loses blood, they also lose the platelets and blood-clotting proteins. These are what make blood clot. If too much blood is lost, there won't be enough platelets or proteins left to stop the bleeding.
Acidosis
Acidosis means the body makes too much acid. Normally, the body uses oxygen (from blood) and glucose (sugar) to make energy. If a person loses a lot of blood, there isn't enough oxygen. The body then makes energy without oxygen, which creates many acidic waste products. These waste products can build up and poison the body. This is called acidosis.
Arrhythmia
When the heart doesn't get enough blood, it can start beating in ways that are not normal. When this happens because of exsanguination, it usually means the patient is very close to dying.
Shock
If a person loses enough blood, they will go into shock. This means the body's most important organs are not getting the blood, oxygen, and nutrients they need to survive. It also means the body can't get rid of waste products, like acids. If shock gets too bad, it will kill the person.
Treatment for Exsanguination
First Aid for Bleeding
First aid is a very important first step in treating exsanguination. Here are things regular people can do to help:
- Call 9-1-1 or your local emergency telephone number right away.
- Try to stop the bleeding by:
* Pressing firmly against the bleeding area. * If an arm or leg is bleeding, lifting it above the person's heart. * Making a tourniquet and wrapping it tightly above the bleeding area.
- Lie the person down and raise their legs if possible.
- If the person is coughing or vomiting blood, turn them on their side so they don't choke.
- Keep the person warm.
- Try to help the person stay calm.
If possible, wear gloves if you touch someone else's blood. The injured person might have an infection that can spread through blood, like HIV or hepatitis. Gloves protect you from getting these infections.
First aid saved many lives during the Boston Marathon bombings. Ordinary people used belts as tourniquets or pressed their hands against wounds. Many people were badly hurt and could have exsanguinated. But because of the help from ordinary people and emergency medical services, everyone who didn't die right away survived.
Emergency Medical Treatments
Emergency medical treatments for exsanguination include:
- Tests like ultrasounds or CT scans to find the cause of internal bleeding.
- Surgery to fix the cause of the bleeding.
- Treatments to warm the body up.
- Blood transfusions (giving donated blood).
- Giving fluids, like saline, through a needle into a vein. This adds to the amount of fluid in the person's body.
- Giving medications to reduce acidosis.
Risk Factors for Exsanguination
Things That Increase Bleeding Risk
Some risk factors make a person more likely to exsanguinate. A few examples are:
- Taking anticoagulants (blood-thinning medications). These can make even a small wound bleed dangerously.
- Having a blood clotting disorder, like hemophilia.
- Certain health conditions that affect the liver. If the liver is damaged, it cannot make blood-clotting proteins as well. This makes people with liver problems more likely to bleed dangerously if they get hurt. Liver damage can also lead to a problem called esophageal varices, which can cause a person to exsanguinate by throwing up blood.
- Advanced cancer. Up to one in 10 people with advanced cancer who are not getting treatment have dangerous bleeding.
Things That Increase Risk of Death from Exsanguination
When a person is exsanguinating, they are more likely to die if:
- They do not get into surgery quickly enough.
- They have hypothermia, with a temperature under 34° C (93.2° F).
- Their blood is more acidic because of acidosis.
- They needed more than 4 liters of blood, or over 10 liters of fluids, to replace the blood they lost.
- They lost more than 15 mL of blood per minute. Losing blood this fast means they would exsanguinate in less than 30-40 minutes.
- They have lower numbers of platelets when they first get to the hospital.
- They are elderly.
Related pages
- Blood
- Bleeding
- Arterial bleeding (a very dangerous type of bleeding)
- Blood clotting (also called "coagulation")
- Blood vessels
- Blunt force trauma
- Aneurysm
- Platelets
- Fibrinogen (a blood-clotting protein made in the liver)