Fort Pitt (Pennsylvania) facts for kids
Fort Pitt was a strong fort built by British forces. It was constructed between 1759 and 1761 during the French and Indian War. The fort was located where the Monongahela and Allegheny rivers meet to form the Ohio River. This area is now Pittsburgh in western Pennsylvania. Fort Pitt was built near, but not exactly on, the site of Fort Duquesne. Fort Duquesne was a French fort built in 1754 as tensions grew between Great Britain and France. The French destroyed Fort Duquesne in 1758 when they had to retreat from British attacks.
Protecting this area helped lead to the growth of Pittsburgh and Allegheny County, Pennsylvania. British-American colonists and immigrants settled here.
Contents
Building Fort Pitt: Location and Construction
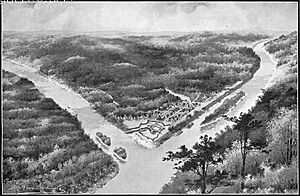
In April 1754, the French started building Fort Duquesne. They built it on the spot of a small British fort called Fort Prince George. This happened at the start of the French and Indian War, also known as the Seven Years' War. In 1755, the Braddock expedition, a British attempt to capture Fort Duquesne, failed. They were defeated at the Battle of the Monongahela. Later, in September 1758, the French soldiers at the fort defeated another British attack.
However, in late November 1758, French Colonel de Lignery ordered Fort Duquesne to be destroyed and left. This happened as British General John Forbes' expedition got closer.
Why the French Left Fort Duquesne
Several things caused the French to leave Fort Duquesne. In August 1758, the British captured Fort Frontenac in Canada. This cut off supplies to French forts along the frontier. Fort Duquesne was the furthest south of these forts. Without enough supplies, the French commander had to send some of his soldiers away. Some went down the Ohio River to bases in Illinois and Louisiana. Others went north to Fort Presque Isle. Any Native American allies who were still at Fort Duquesne likely wanted to go home for winter. This left the fort with very few soldiers, maybe as few as 200.
Another important event was the Treaty of Easton in late October 1758. This treaty largely ended the alliance between the French and several Native American tribes. Chiefs from 13 American Indian nations agreed to make peace. They negotiated with the governments of Pennsylvania and New Jersey. They also agreed to stop helping the French. These nations included the Iroquois League, the Lenape (Delaware), and the Shawnee. They agreed because the colonial governments promised to respect their hunting rights and land in the Ohio Country. They also promised not to build new settlements west of the Appalachian Mountains. Finally, they agreed to remove British and colonial troops after the war.
The French commander expected an attack along Braddock's road. He had spent time making defenses there. However, he learned from captured British soldiers that a strong British camp was only 50 miles away. This camp was at Ligonier, Pennsylvania, with many more troops behind it. He also knew about the British raid on the Native village of Kittanning two years earlier. This meant a British attack from the north was also possible.
Building the New Fort
The French commander found his fort was in a bad spot. It was often flooded and easy to attack from three sides. He was also running low on food and supplies. So, he retreated north. He destroyed the supplies and many buildings as 1500 British troops got within 10 miles. The French never came back to the area.
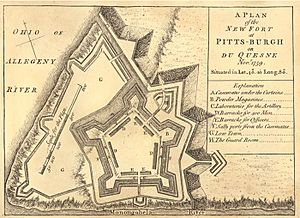
After building a temporary fort called Mercer's Fort, the British built a new, permanent fort. They named it Fort Pitt, after William Pitt the Elder, a British leader. The fort was built from 1759 to 1761 during the French and Indian War. It was right next to where Fort Duquesne used to be. Captain Harry Gordon, a British engineer, designed the fort. It was built in a popular five-pointed star shape, with strong points called bastions.
Pontiac's War and Changes

After the war, European settlers continued to break treaties and move onto Native American land. Because of this, in 1763, the western Lenape and Shawnee tribes joined an uprising. This was known as Pontiac's War. It was an effort to make settlers leave Native American territory.
The Native Americans began their siege of Fort Pitt on June 22, 1763. But they found the fort was too strong to capture by force. During talks, Captain Simeon Ecuyer, the commander of Fort Pitt, gave two Delaware messengers blankets. These blankets had been exposed to smallpox. It was understood that this act could cause a disease outbreak among the Native Americans. The effectiveness of this attempt to spread the disease is not fully known. It is hard to tell if it caused new outbreaks or if they were already happening naturally from earlier contact with colonists.
During and after Pontiac's War, smallpox outbreaks greatly affected Native American tribes. This happened in the Ohio Valley and Great Lakes areas. On August 1, 1763, most of the Native Americans stopped the siege. They left to stop a British force led by Colonel Henry Bouquet. In the Battle of Bushy Run, Bouquet fought off the Native American attack. He then reached and helped Fort Pitt on August 10.
In 1772, after Pontiac's War, the British commander sold Fort Pitt to two colonists. Their names were William Thompson and Alexander Ross. At that time, both Virginia and Pennsylvania claimed the Pittsburgh area. They fought for control of the region. After Virginians took control of Fort Pitt, they renamed it Fort Dunmore. This was to honor Virginia's Governor, Lord Dunmore. The fort was used as a base during Dunmore's War in 1774.
Fort Pitt in the American Revolutionary War
During the American Revolutionary War, Fort Pitt became a main base for the western part of the war. In 1778, the United States Congress sent representatives to the western frontier. They wanted to check on the security of the American border. Congress had learned that British governor Henry Hamilton was trying to turn local Native American tribes against the American border. They feared an attack.
From Fort Pitt, the committee reported back to Congress that the threat was serious. This led Congress to send 3,000 militiamen to the western frontier. One of these was George Rogers Clark. Clark later captured Hamilton in the winter of 1779. This success helped encourage the alliance with France. In present-day Michigan, the British had a fort called Fort Detroit.
Later, during the Northwest Indian War, General Anthony Wayne built a fort next to the site. He called it Fort Lafayette. Even later, it was used again during the War of 1812. It served as a starting point and supply center for trips against British forts to the north. Both Fort Pitt and Fort Lafayette became part of the growing town of Pittsburgh.
Fort Pitt in the 20th Century

In the 1900s, the city of Pittsburgh ordered archaeological digs. They wanted to find the foundations of Fort Pitt. After the digging, some parts of the fort were rebuilt. This helps visitors at Point State Park understand how big the fort was. The Fort Pitt Museum is located in this rebuilt section, inside what was the Monongahela Bastion. The parts of the fort that were dug up were then filled in.
A small brick building called the Blockhouse still stands in Point State Park. It is the only part left of Fort Pitt. Built in 1764, it is thought to be the oldest building still standing in Pittsburgh. For many years, it was used as a private home. Later, a local group called the Daughters of the American Revolution bought and saved the blockhouse.
The Fort Pitt Foundry was a very important place for making weapons. It supplied the government during the American Civil War. William Metcalf was in charge of it.
Fort Pitt in Popular Culture
- The movie Allegheny Uprising (1939) starred John Wayne and Claire Trevor.
- In Cecil B. DeMille's Unconquered (1947), starring Gary Cooper and Paulette Goddard, Howard Da Silva played a gunrunner. Boris Karloff played a Seneca chief who led a Native American uprising in 1763. Cooper and Goddard save Fort Pitt in the film.
- The video game Assassin's Creed III (2012) features Fort Pitt. However, it is called "Fort Duquesne" in the game. Some of the game's events happen after Fort Pitt was built to replace Duquesne.
- Conrad Richter's youth novel, The Light in the Forest (1953), has parts of its story set at Fort Pitt.
- You can see aerial views of the fort in the opening credits of the 1993 film Groundhog Day. This happens as a TV news truck leaves downtown Pittsburgh on its way to Punxsutawney.
 | Janet Taylor Pickett |
 | Synthia Saint James |
 | Howardena Pindell |
 | Faith Ringgold |