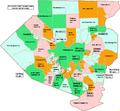
Allegheny County, Pennsylvania facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Allegheny County
|
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
|||||
|
|||||
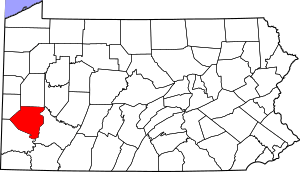
Location within the U.S. state of Pennsylvania
|
|||||
 Pennsylvania's location within the U.S. |
|||||
| Country | |||||
| State | |||||
| Founded | September 24, 1788 | ||||
| Named for | Allegheny River | ||||
| Seat | Pittsburgh | ||||
| Largest city | Pittsburgh | ||||
| Area | |||||
| • Total | 745 sq mi (1,930 km2) | ||||
| • Land | 730 sq mi (1,900 km2) | ||||
| • Water | 14 sq mi (40 km2) 1.9%% | ||||
| Population
(2020)
|
|||||
| • Total | 1,250,578 | ||||
| • Estimate
(2023)
|
1,224,825 |
||||
| • Density | 1,700/sq mi (700/km2) | ||||
| Time zone | UTC−5 (Eastern) | ||||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) | ||||
| Congressional districts | 12th, 17th | ||||
|
Pennsylvania Historical Marker
|
|||||
| Designated: | December 30, 1982 | ||||
Allegheny County is a county in Pennsylvania, United States. It's named after the Allegheny River. The name comes from a Lenape word. It might mean "fine river." Some say it refers to an old mythical tribe called "Allegewi."
In 2020, about 1.25 million people lived here. This makes it Pennsylvania's second-most populated county. Only Philadelphia County has more people. Pittsburgh is the county seat and largest city. It's also Pennsylvania's second-largest city. Allegheny County is a big part of the Greater Pittsburgh area.
Contents
History of Allegheny County
For thousands of years, Native American groups lived here. Before Europeans arrived, different tribes settled the land. These included the Seneca, Lenape, Shawnee, and Mingo.
In the early 1700s, European fur traders came to the area. They set up trading posts.
French and British Competition
In 1749, France claimed the Ohio Valley. Captain Pierre Joseph Céloron de Blainville traveled the Ohio and Allegheny rivers. He placed lead plates to mark the land for France.
Towns often grew along rivers. Rivers were important for travel and water. In the 1700s, France and Britain both wanted control. Native American tribes often sided with one country or the other.
The British sent George Washington to remove the French. He was not successful. He almost drowned in the icy Allegheny River.
In 1754, the English tried to build Fort Prince George. The French captured it and made it stronger. They renamed it Fort Duquesne.
Fort Duquesne was very important during the French and Indian War. The British tried to take it in the Braddock Expedition, but they failed. In 1758, British forces led by General John Forbes captured the fort. They destroyed it and built a new, bigger one called Fort Pitt. Today, this historic spot is Point State Park in Pittsburgh.
County Formation
Both Pennsylvania and Virginia claimed this region. This caused problems with land claims. In 1780, Pennsylvania and Virginia agreed on their border. This area became part of Pennsylvania.
Allegheny County was officially created on September 24, 1788. It was formed from parts of Washington and Westmoreland counties. More settlers were moving to the Pittsburgh area. Pittsburgh became the county seat in 1791. The county was much larger at first. It reached Lake Erie. By 1800, it had its current borders.
In the 1790s, the U.S. government taxed whiskey. Farmers in the area made money from whiskey. They refused to pay the tax. This led to the Whiskey Rebellion. President George Washington sent troops to stop the rebellion.
Industrial Growth
The area grew quickly in the 1800s. It became a major industrial center. By the late 1800s, it was the nation's top steel producer. Pittsburgh was even called "Steel Capital of the World."
In 1913, the county celebrated its 125th anniversary. A week of events included a steamboat parade. Thirty paddle wheelers traveled the Ohio River.
Geography
Allegheny County covers about 745 square miles. Most of it is land (730 sq mi), and a small part is water (14 sq mi).
Three major rivers meet in Allegheny County. The Allegheny River and the Monongahela River join in Downtown Pittsburgh. They form the Ohio River. The Youghiogheny River flows into the Monongahela River near McKeesport. All these rivers eventually drain into the Mississippi River and then the Gulf of Mexico.
Even though many forests were cut down for industry, a lot of woodland has grown back.
Neighboring Counties
Allegheny County shares borders with these counties:
- Butler County (north)
- Armstrong County (northeast)
- Beaver County (northwest)
- Westmoreland County (east and south)
- Washington County (southwest)
Major Roads
Many important roads run through Allegheny County. These include major interstates and U.S. Routes.
 Interstate 76 (Pennsylvania Turnpike)
Interstate 76 (Pennsylvania Turnpike) Interstate 79
Interstate 79 Interstate 279
Interstate 279 Interstate 376
Interstate 376 Interstate 579
Interstate 579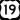 US Route 19
US Route 19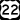 US Route 22
US Route 22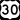 US Route 30
US Route 30
There are also many Pennsylvania State Routes that help people travel around the county.
Climate
Allegheny County has a humid continental climate. This means it has warm or hot summers.
People and Population
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1790 | 10,203 | — | |
| 1800 | 15,087 | 47.9% | |
| 1810 | 25,317 | 67.8% | |
| 1820 | 34,921 | 37.9% | |
| 1830 | 50,552 | 44.8% | |
| 1840 | 81,235 | 60.7% | |
| 1850 | 138,290 | 70.2% | |
| 1860 | 178,831 | 29.3% | |
| 1870 | 262,204 | 46.6% | |
| 1880 | 355,869 | 35.7% | |
| 1890 | 551,959 | 55.1% | |
| 1900 | 775,058 | 40.4% | |
| 1910 | 1,018,463 | 31.4% | |
| 1920 | 1,185,808 | 16.4% | |
| 1930 | 1,374,410 | 15.9% | |
| 1940 | 1,411,539 | 2.7% | |
| 1950 | 1,515,237 | 7.3% | |
| 1960 | 1,628,587 | 7.5% | |
| 1970 | 1,605,016 | −1.4% | |
| 1980 | 1,450,085 | −9.7% | |
| 1990 | 1,336,449 | −7.8% | |
| 2000 | 1,281,666 | −4.1% | |
| 2010 | 1,223,348 | −4.6% | |
| 2020 | 1,250,578 | 2.2% | |
| 2023 (est.) | 1,224,825 | 0.1% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census 1790–1960 1900–1990 1990–2000 2010–2018 |
|||
In 2020, Allegheny County had 1,250,578 people. Most residents were White (75%). About 12.9% were Black or African American. About 4.66% were Asian. About 2.74% of the population was Hispanic or Latino.
Economy
In the late 1700s, farming was very important. Farmers grew a lot of grain. It was hard to transport grain to the eastern part of the state. So, farmers made grain into whiskey. This helped them earn money.
The area quickly became a key manufacturing center. It had lots of iron and coal. Rivers made it easy to transport goods by barge. Pittsburgh became one of the world's most important steel-producing areas.
Later in the 1900s, U.S. steel production went down. Allegheny County's economy changed. Now, it's known for its hospitals, universities, and technology. Even though heavy industry changed, Pittsburgh is home to many big companies. These include U.S. Steel, PNC Financial Services, PPG Industries, and H. J. Heinz Company.
The county also has many companies that supply the U.S. military.
Education
Allegheny County has many schools and colleges.
Colleges and Universities
Here are some of the universities in the county:
- Carnegie Mellon University
- Duquesne University
- University of Pittsburgh
- Carlow University
- Chatham University
- Robert Morris University
Community and Technical Colleges
There are also colleges that offer shorter programs or job training:
- Community College of Allegheny County
- Pittsburgh Technical College
- Rosedale Technical College
Public School Districts
Many public school districts serve students in Allegheny County. Some of them are:
- Allegheny Valley School District
- Baldwin-Whitehall School District
- Bethel Park School District
- Fox Chapel Area School District
- McKeesport Area School District
- Pittsburgh School District
- Plum Borough School District
- Upper St. Clair School District
Private High Schools
The county also has many private high schools, such as:
- Central Catholic High School
- Oakland Catholic High School
- Sewickley Academy
- Shady Side Academy
Transportation
Pittsburgh Regional Transit provides public transportation in Allegheny County. This includes buses and light rail. The county also manages roads and other public structures.
You can find trails for biking and walking. The Three Rivers Heritage Trail runs along the rivers in Pittsburgh. The Great Allegheny Passage trail goes all the way to Washington, D.C.
The Allegheny County Airport is used for flight schools and private flights. Pittsburgh International Airport is the main airport for passenger flights. Both airports are managed by the Allegheny County Airport Authority.
Parks and Recreation
Allegheny County has two Pennsylvania state parks. Point State Park is in Downtown Pittsburgh. It's where the Allegheny and Monongahela rivers meet. Allegheny Islands State Park is on islands in the Allegheny River.
Pennsylvania State Game Lands Number 203 offers places for hunting and other outdoor fun.
The Allegheny Land Trust helps protect green spaces. They buy land to create public parks. This helps keep nature areas for everyone to enjoy. For example, they helped expand North Park.
Sports
Allegheny County is home to several professional sports teams:
- Pittsburgh Steelers (football)
- Pittsburgh Penguins (ice hockey)
- Pittsburgh Pirates (baseball)
- Pittsburgh Riverhounds (soccer)
Communities
Allegheny County has different types of towns and cities. These are called municipalities. They include cities, boroughs, and townships.
Cities
- Pittsburgh (the county seat)
- Clairton
- Duquesne
- McKeesport
Boroughs
Boroughs are smaller towns. Some examples are:
Townships
Townships are usually larger areas that might include smaller communities. Some examples are:
- Hampton Township
- Moon Township
- Mt. Lebanon Township
- Ross Township
- Upper St. Clair Township
Census-Designated Places (CDPs)
These are areas the U.S. Census Bureau defines for data collection. They are not official towns. Examples include:
Unincorporated Communities
These are smaller places that are not officially part of a city or borough. Some examples are:
Images for kids
-
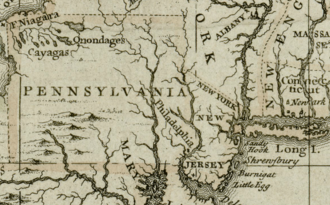
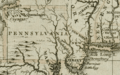
1680 British map of Western Pennsylvania and Allegheny County from the Darlington Collection
See also
 In Spanish: Condado de Allegheny para niños
In Spanish: Condado de Allegheny para niños