Kavala facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Kavala
Καβάλα
|
|
|---|---|
|
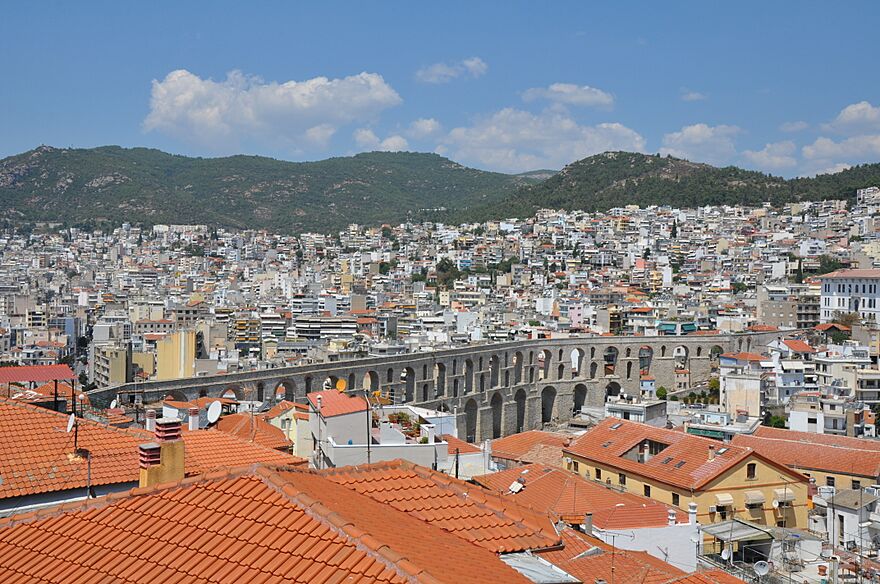
From top left: View of Kavala promenade, statue to Goddess Nike, Muhammad Ali statue, Tobacco Worker's Square, Kavala City Hall, Imaret Hotel with the Kavala Fortress in the background, view of the city's port.
|
|
| Country | Greece |
| Administrative region | Eastern Macedonia and Thrace |
| Regional unit | Kavala |
| Area | |
| • Municipality | 351.4 km2 (135.7 sq mi) |
| • Municipal unit | 112.6 km2 (43.5 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation | 53 m (174 ft) |
| Lowest elevation | 0 m (0 ft) |
| Population
(2021)
|
|
| • Municipality | 66,376 |
| • Municipality density | 188.890/km2 (489.22/sq mi) |
| • Municipal unit | 56,243 |
| • Municipal unit density | 499.49/km2 (1,293.7/sq mi) |
| Community | |
| • Population | 54,065 (2021) |
| Time zone | UTC+2 (EET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+3 (EEST) |
| Postal code |
65x xx
|
| Area code(s) | 2510 |
| Vehicle registration | KB |
| Website | kavala.gov.gr |
Kavala (Greek: Καβάλα, Kavála) is a city in northern Greece. It's a very important seaport for eastern Macedonia and the main city of the Kavala region.
The city is located on the Bay of Kavala, right across from the island of Thasos. It's also on the A2 motorway, making it easy to reach. You can drive to Thessaloniki in about an hour and a half (160 kilometers west). Drama is only a forty-minute drive (37 kilometers north), and Xanthi is 56 kilometers east. It's also about 150 kilometers west of Alexandroupoli.
Kavala is a key economic hub in Northern Greece. It's known for trade, tourism, fishing, and oil-related activities. In the past, it was also famous for its tobacco trade.
Contents
- What's in a Name?
- Why is it Called Kavala?
- A Look Back: Kavala's History
- How Many People Live Here?
- City Management
- International Connections
- Economy: How Kavala Makes Money
- Kavala's Weather
- Education and Research
- Culture and Fun
- Getting Around Kavala
- Sports in Kavala
- Religious History
- Media in Kavala
- Postage Stamps
- Consulates
- Famous People from Kavala
- Images for kids
- See also
What's in a Name?
Historically, Kavala has had several names. In ancient times, it was called Neapolis, which means 'new city'. This was a common name for new Greek settlements. Later, in the Early Middle Ages, it was renamed Christo(u)polis, meaning 'city of Christ'. During the High Middle Ages, its name changed to Morunets, a Slavic name.
Why is it Called Kavala?
The exact origin of the name Kavala is a bit of a mystery! Some people think it comes from an ancient Greek settlement called Skavala nearby. Others believe it's from the Italian word cavallo, meaning horse. Since the city was on the old Via Egnatia road, it might have been a place where imperial messengers changed horses.
A French traveler in 1547 heard a local story that Alexander the Great named it "Bukephala" after his horse, Bucephalus. Another idea is that "Kavala" is a Turkish name given by the Turks when they rebuilt the city in the early 1500s.
Finally, an archaeologist named Georgios Bakalakis suggested that the name came from a Byzantine fortress called Kavala in Asia Minor. When the Ottomans brought settlers from that area to Kavala in the 1500s, they might have brought their homeland's name with them.
Today, Kavala is often called "the cyan city" (Η γαλάζια πόλη) because of its beautiful blue waters. The city's symbol is the head of the goddess Parthenos, who was the protector of ancient Neapolis.
A Look Back: Kavala's History
Ancient Times
Kavala was founded in the late 600s BC by settlers from the island of Thassos. These settlers created many colonies along the coast to get rich from the gold and silver mines, especially in the nearby Pangaion mountain. Later, Phillip II of Macedonia took over these mines.
People in Neapolis worshipped Parthenos, a Greek goddess linked to Athena. Around 500 BC, Neapolis became independent from Thassos and started making its own silver coins. A few decades later, a large temple made of Thassian marble was built. You can see parts of it in Kavala's archaeological museum today.
During the Peloponnesian War in 411 BC, Neapolis was attacked by the Spartans and Thassians. But the city stayed loyal to Athens, and Athens rewarded its loyalty in 410 and 407 BC.
Neapolis was a town in Macedonia, located 14 kilometers from the harbor of Philippi. It was part of the Second Athenian League. Later, the Kingdom of Macedonia conquered the town.
Roman and Byzantine Eras
The important Roman military road, Via Egnatia, went through Kavala, which helped trade grow. The city became a Roman town in 168 BC. It was a base for Brutus and Cassius in 42 BC, before they were defeated in the Battle of Philippi.
The Apostle Paul landed in Neapolis during his first trip to Europe.
In the 500s, the Byzantine emperor Justinian I made the city stronger with walls to protect it from attacks. In later Byzantine times, the city was called "Christo(u)polis" (city of Christ). It was part of the theme of Macedonia and then the Theme of Strymon.
In the 8th and 9th centuries, attacks by Bulgarians made the Byzantines strengthen the city's defenses even more. Christoupolis remained under Byzantine control. In 837, Byzantine forces from Christoupolis stopped Bulgarian raids.
An old Greek inscription from 830-840 AD can still be seen on the city's defensive walls. Another inscription from 926 (now in the archaeological museum) says that General Vasilios Klaudon repaired the damaged walls.
Around the mid-1100s, an Arab geographer named Edrisi visited Christoupolis. He described it as a well-fortified city and a busy trading port. The Normans likely burned the city in 1185 after capturing Thessaloniki. Later, the Lombards took the city after the Fourth Crusade, but it was freed by Theodorus Komnenos in 1225.
In 1302, the Catalans tried but failed to capture the city. To stop them from returning, the Byzantine emperor Andronikos III Palaiologos built a new long defensive wall. In 1357, two Byzantine brothers, Alexios and John, controlled the city. Digs have found the remains of an early Byzantine church under an Ottoman mosque in the Old Town.
Ottoman Era

The Ottoman Empire first captured Kavala in 1387. It remained part of the Ottoman Empire until 1912. In the 1500s, Ibrahim Pasha, a powerful leader, helped the city grow. He rebuilt the old Roman aqueduct, which is still a famous landmark today. The Ottomans also made the Byzantine fortress on Panagia hill bigger.
Muhammad Ali, who later became the ruler of Egypt, was born in Kavala in 1769. His house is now a museum.
20th Century
Kavala was taken by the Bulgarian Army in the First Balkan War. Then, the Greek Navy captured it during the Second Balkan War, and it became part of Greece with the Treaty of Bucharest. In August 1916, during First World War, the Greek army in Kavala surrendered to the Bulgarian army. This led to a military uprising in Thessaloniki, which helped Greece join the war.
Bulgaria occupied the city from August 1916 to September 1918. Many people reported terrible events during this time.
After the Greco-Turkish War (1919–1922), many refugees from Anatolia moved to Kavala. This brought new workers and helped the city's economy grow, especially in processing and trading tobacco. Many old tobacco buildings are still in the city. Between the World Wars, Kavala was the 4th largest city in Greece.
During Second World War, Bulgaria occupied the city again from 1941 to 1944. During this time, almost all of the city's Jewish community was sent away by the Bulgarians to German authorities and sadly died in the Treblinka death camp.
After World War II, the city faced some economic challenges and many people moved away. In the late 1950s, Kavala grew by adding new land from the sea west of the port.
21st Century
On July 16, 2022, a cargo plane crashed near Kavala. The plane was carrying ammunition from Niš to Dhaka when it lost altitude and went down 35 kilometers west of Kavala Airport. All 8 crew members died.
How Many People Live Here?
Here's how Kavala's population has changed over the years:
| Year | Town | Municipal unit | Municipality |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1961 | 44,517 | 44,978 | – |
| 1971 | 46,234 | 46,887 | – |
| 1981 | 56,375 | 56,705 | – |
| 1991 | 56,571 | 58,025 | – |
| 2001 | 58,663 | 63,293 | – |
| 2011 | 54,027 | 58,790 | 70,501 |
| 2021 | 51,947 | 56,243 | 66,376 |
City Management
The Municipality of Kavala
The municipality of Kavala was created in 2011 by joining two smaller municipalities: Kavala and Filippoi. These are now called municipal units.
| Municipal unit | Population (2011) | Population (2021) | Area (km2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kavala | 58,790 | 56,243 | 112.599 |
| Filippoi | 11,711 | 10,133 | 238.751 |
The total area of the municipality is 351.35 square kilometers. In 2011, its population was 70,501, and in 2021, it was 66,376. The main office for the municipality is in Kavala city.
Some of the biggest communities within the new municipality are:
| Community | Population |
|---|---|
| Kavala | 56,371 |
| Krinides | 3,365 |
| Amygdaleonas | 2,724 |
| Nea Karvali | 2,225 |
| Zygos | 2,057 |
City Areas
Kavala is built on hills, so most residents have amazing views of the coast and sea. Some of the main areas in Kavala are:
| Agia Varvara | Agios Athanasios | Agios Ioannis | Agios Loukas | Chilia |
| Dexameni | Kalamitsa | Kentro (Centre) | Neapolis | Panagia |
| Perigiali | Potamoudia | Profitis Ilias | Timios Stavros | Vyronas |
Main Streets
|
|
International Connections
Twin Towns and Sister Cities
Kavala has special partnerships with other cities around the world, called twin towns or sister cities:
|
Partnerships
Economy: How Kavala Makes Money
For a long time, fishing was the main job for people in Kavala. The city's fishermen were famous across northern Greece.
After Greece became more industrial, Kavala also became a big center for the tobacco industry. The old Municipal Tobacco Warehouse (built in 1910) is still standing today.
In the 1970s, oil was found near the city. Now, two oil rigs (Prinos and Epsilon) are used to get the oil.
Kavala's Weather
Kavala has a hot-summer Mediterranean climate. This means it has hot, dry summers and mild, wet winters. Snow doesn't fall often, but it usually happens at least once a year. The air is usually quite humid.
The hottest temperature ever recorded was 38.0°C, and the coldest was -8.0°C.
| Climate data for Kavala Weather Station 2006-2018 | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 9.7 (49.5) |
10.9 (51.6) |
13.7 (56.7) |
18.0 (64.4) |
22.9 (73.2) |
27.3 (81.1) |
30.1 (86.2) |
30.6 (87.1) |
25.6 (78.1) |
19.9 (67.8) |
15.7 (60.3) |
11.3 (52.3) |
19.6 (67.3) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 6.8 (44.2) |
7.9 (46.2) |
10.5 (50.9) |
14.6 (58.3) |
19.4 (66.9) |
23.8 (74.8) |
26.6 (79.9) |
27.1 (80.8) |
22.2 (72.0) |
16.7 (62.1) |
12.7 (54.9) |
8.4 (47.1) |
16.4 (61.5) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 4.2 (39.6) |
5.5 (41.9) |
7.8 (46.0) |
11.6 (52.9) |
16.3 (61.3) |
20.5 (68.9) |
23.1 (73.6) |
23.7 (74.7) |
19.1 (66.4) |
14.0 (57.2) |
10.1 (50.2) |
5.7 (42.3) |
13.5 (56.3) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 57.5 (2.26) |
65.4 (2.57) |
68.2 (2.69) |
37.8 (1.49) |
48.7 (1.92) |
51.8 (2.04) |
25.4 (1.00) |
21.4 (0.84) |
49.8 (1.96) |
64.7 (2.55) |
48.6 (1.91) |
62.0 (2.44) |
601.3 (23.67) |
| Average precipitation days | 9.2 | 9.1 | 11.6 | 7.9 | 8.5 | 7.7 | 4.2 | 2.8 | 5.4 | 7.4 | 7.9 | 9.3 | 91 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 64.9 | 65.0 | 66.6 | 65.8 | 67.8 | 67.8 | 68.4 | 68.8 | 67.7 | 65.8 | 66.1 | 67.7 | 66.9 |
| Source: meteokav.gr [1] | |||||||||||||
| Climate data for Kavala, "Alexander the Great" airport near Chrysoupoli | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 9.5 (49.1) |
10.3 (50.5) |
12.9 (55.2) |
17.5 (63.5) |
22.8 (73.0) |
27.4 (81.3) |
30.1 (86.2) |
30.2 (86.4) |
25.7 (78.3) |
20.4 (68.7) |
15 (59) |
10.6 (51.1) |
19.4 (66.9) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 1.8 (35.2) |
2.1 (35.8) |
4.7 (40.5) |
8.8 (47.8) |
13.4 (56.1) |
17.3 (63.1) |
19.5 (67.1) |
19.2 (66.6) |
15.2 (59.4) |
11 (52) |
6.9 (44.4) |
3.3 (37.9) |
10.3 (50.5) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 41.3 (1.63) |
49.3 (1.94) |
36.6 (1.44) |
33.2 (1.31) |
30.2 (1.19) |
26.2 (1.03) |
22.4 (0.88) |
17 (0.7) |
24.8 (0.98) |
44.5 (1.75) |
62.3 (2.45) |
78.4 (3.09) |
466.2 (18.39) |
| Source: http://www.hnms.gr/emy/en/climatology/climatology_city?perifereia=East%20Macedonia%20and%20Thrace&poli=Kavala_Chryssoupoli (1985-2010 averages) | |||||||||||||
Education and Research
- The International Hellenic University (IHU) has five departments in Kavala. These include Computer Science, Physics, Chemistry, Management Science, and Accounting. The campus is large, covering about 132,000 square meters.
- The Fisheries Research Institute (FRI) studies fishing and helps develop new technologies in this area. It's located 17 kilometers from Kavala, in Nea Peramos. This area is rich in fish and has many lagoons, lakes, and rivers.
- The Institute of Mohamed Ali for the Research of the Eastern Tradition (IMARET) is a non-profit group in Kavala. It studies the influence of Egyptian culture in Greece and promotes cultural exchange through art. They work with the Bibliotheca Alexandrina to document architectural history. Each year, the institute hosts an International Roman Law Moot Court Competition.
- The Historical & Literary Archives of Kavala is a public foundation that keeps historical records. It is supported by its founders and occasional local government help.
- Egnatia Aviation is a private school that trains pilots. It started in Greece in 2006. Its main facilities are at the former passenger terminal of the Kavala International Airport "Alexander the Great".
Culture and Fun
Festivals and Events
Kavala has many cultural events, especially in the summer. One of the most important is the Festival of Philippi. It runs from July to September and includes plays and music concerts. This festival has been a major event in Kavala since 1957.
The Kavala AirSea Show is an exciting annual air show held in late June.
"Cosmopolis" is an international festival in Kavala's Old Town. It lets you experience cultures from around the world through dancing, music, food, movies, and exhibits. It started in 2000 and was held every year from 2002 to 2009. It came back in 2016 with 250 artists and musicians from all over the world.
The Yiannis Papaioannou's Festival features concerts and music workshops.
"Ilios kai Petra" (Sun and Stone) is a festival in July held in Nea Karvali. It's a folk festival with traditional dance groups from all over the world.
The Wood Water Wild Festival is an outdoor festival inspired by nature. It includes live music, DJ sets, wellness activities, a book fair, outdoor theater, and discussions about ecology.
Many other cultural events happen in all parts of Kavala during the summer.
Delicious Food
Kavala's food is mostly about fresh fish and seafood. Local farm products and livestock are also very important. The city's traditional recipes have also been influenced by the food of refugees from Pontus and Asia Minor.
Some famous dishes in Kavala and nearby coastal towns include fresh fish and seafood, especially sardines. You can also try shrimp salad (garidosalata), sun-dried mackerel "goúna" (grilled), kavouropilafo (crab rice), mussels with rice, herring saganáki, anchovies wrapped in grape leaves, and stuffed eggplants. For meat lovers, lamb with spinach is popular.
The grapes, wine, and tsipouro (a strong drink) made in the area are well-known. Don't forget to try the famous kourabiedes (sugar-coated almond biscuits) from Nea Karvali!
Getting Around Kavala
Roads
European route E90 goes through Kavala, connecting it to other cities. The Egnatia Odos (A2 motorway) is north of the city. You can enter Kavala from two main exits: Kavala West and Kavala East. Kavala has regular bus connections (KTEL) to and from Thessaloniki and Athens.
Airport
The Kavala International Airport "Alexander the Great" is 27 kilometers from Kavala. It has regular flights to Athens and many European cities.
Port
Kavala's port connects the city to all the islands of the Northern Aegean Sea with frequent ferry services.
City Buses
The city is connected to all major Greek cities like Thessaloniki and Athens by bus. All local villages are also connected by bus lines. Bus tickets are usually very cheap. Kavala also has a local shuttle bus service with these lines:
- Vironas – Kallithea
- Dexameni
- Cemetery
- Kipoupoli – Technological Institute
- Agios Loukas
- Profitis Ilias
- Stadium
- Kalamitsa – Batis (only in summer)
- Agios Konstantinos
- Neapoli
- Hospital – Perigiali
Trains
Kavala does not currently have a train connection. However, there are plans to build a new train line between Thessaloniki and Xanthi that will go through Kavala. This project is part of the Egnatia Railway and will cost about €1.25 billion. In 2019, the contract was given to build the first 31.8-kilometer section between Xanthi and Kavala.
Hiking Trails
The Kavala Water Trail is a hiking path that connects the village of Palaia Kavala with the Agios Konstantinos neighborhood in Kavala.
Sports in Kavala
- Kavala F.C.: This is Kavala's professional football (soccer) club. They play at the municipal Kavala Stadium "Anthi Karagianni".
- Kavala B.C.: This is Kavala's professional basketball club. They are also known as E.K. Kavalas and compete in the Greek League.
- Kavala '86: This is a women's football club, started in 1986. They have won national titles in Greek women's football.
- Kavala Chess Club: Chess is very popular here! The local chess club is one of the best in Greece and has had a lot of success. Every August, they host an International Open tournament that attracts top chess players from around the world.
- Nautical Club of Kavala (founded 1945): This club offers maritime sports like swimming, yachting, and water polo.
- Kavala Table Tennis Club (ΑΣΕΑ Καβάλας): This club focuses on table tennis.
- Kavala Titans (founded 2009): This team plays rugby union and rugby league.
Religious History
In ancient times, Neapolis was an important religious center. Later, in the 8th century AD, a bishopric (area managed by a bishop) was mentioned for Christoupolis. By 1260, Christoupolis became a metropolis, which is a higher-ranking religious center.
After the Greek army freed Kavala during the Balkan Wars, the local church was re-established. It is now called the "Metropolis of Philippi, Neapolis and Thasos." The Metropolis of Kavala has a conference center dedicated to Saint Paul in the village of Lydia. This is near the spot where, according to tradition, Paul baptized Saint Lydia in the Zygaktis river. At the same spot, there is an open-air baptistery and a unique octagonal baptistery with beautiful mosaic and stained-glass decorations.
Media in Kavala
- TV: ENA Channel, Center TV
- Newspapers: Proini, Kavala (newspaper), Chronometro
- Online: Kavala.com
Postage Stamps
Austria had a post office in Kavala before 1864. Between 1893 and 1903, the French post office in the city made its own postage stamps. At first, they were French stamps with "Cavalle" and a value in piasters printed over them. Then, in 1902, they used French designs with "CAVALLE" written on them.
Consulates
In the past, Kavala hosted consulates from various European countries. Currently, it has a consulate from:
Famous People from Kavala
- Ilarion Karatzoglou, a Greek rebel during the Greek War of Independence (1821–1829) against the Ottoman Empire.
- Muhammad Ali Pasha of Kavala, who became the ruler of Egypt from 1805 to 1848 and started the modern state of Egypt.
- Mohamed Sherif Pasha, a former Prime Minister of Egypt.
- Anna-Maria Botsari, a chess player.
- Nasos Galakteros, a basketball player.
- Giorgos Georgiadis, a footballer.
- Anthi Karagianni, a silver medalist in the Athens 2004 and Beijing 2008 Paralympic Games. The city's stadium is named after her!
- Vasilis Karras, a singer.
- Kostas Mitroglou, a footballer.
- Yiannis Papaioannou, a composer.
- Mitsos Partsalidis, the first elected communist mayor in modern Greek history, in 1934.
- Sofoklis Schortsanitis, a basketball player.
- Despina Vandi, a singer.
- Anna Verouli, a javelin thrower who won a Gold Medal in the 1982 European Championship.
- Vassilis Vassilikos, a writer and diplomat.
- Theodoros Zagorakis, a former footballer and captain of the Greek national team that won the European Championship in 2004.
Images for kids
-
Statue of Muhammad Ali of Egypt, a gift from Egypt (sculpted by Konstantinos Dimitriadis)
See also
 In Spanish: Kavala para niños
In Spanish: Kavala para niños
 | Victor J. Glover |
 | Yvonne Cagle |
 | Jeanette Epps |
 | Bernard A. Harris Jr. |