Outline of New Zealand facts for kids
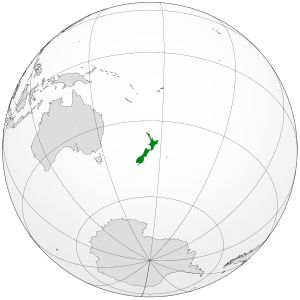
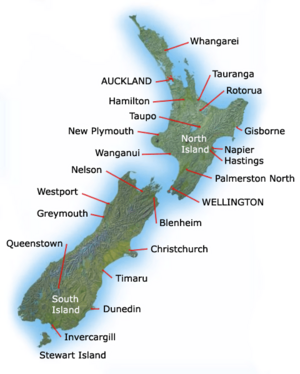
New Zealand is an island country found in the western South Pacific Ocean. It has two main islands, the North Island and the South Island. There are also many smaller islands, like Stewart Island / Rakiura and the Chatham Islands. The native Māori first called the North Island Aotearoa. This name means "The Land of the Long White Cloud." Today, Aotearoa is used as the Māori language name for the whole country.
New Zealand is about 2,000 km (1,200 mi) southeast of Australia, across the Tasman Sea. Its closest neighbors to the north are New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. Because it is so far away, it was one of the last places on Earth where humans settled. For a long time, New Zealand was isolated. This allowed it to develop unique plants, animals, and fungi. The country has many different landscapes and sharp mountains, like the Southern Alps. These were formed by land moving upwards and by volcanoes erupting. Wellington is New Zealand's capital city. Auckland is its largest city.
Most people in New Zealand are of European background. The native Māori are the biggest minority group. Asians and non-Māori Pacific Islanders also make up important groups, especially in the cities. Charles III, as the king of New Zealand, is the head of state. When he is not there, a governor-general represents him. The country is run by the New Zealand Parliament, which is chosen by the people. The prime minister leads the government. The Realm of New Zealand also includes the Cook Islands and Niue, which govern themselves but work closely with New Zealand. It also includes Tokelau and the Ross Dependency (New Zealand's land claim in Antarctica).
Geography of New Zealand
New Zealand is a group of islands and a country. It is an island country and part of the Commonwealth realm.
- Location:
* New Zealand is in the Southern Hemisphere and Eastern Hemisphere. * It is in the South Pacific Ocean, which is part of Oceania, specifically Polynesia and Australasia.
- Time Zones:
* The Chatham Islands use Chatham Standard Time (UTC+12:45) and Chatham Daylight Time (UTC+13:45). * The rest of New Zealand uses New Zealand Standard Time (UTC+12) and New Zealand Daylight Time (UTC+13) from September to April.
- Highest Point:
* The highest point is Aoraki / Mount Cook, which is 3,754 meters (12,316 ft) tall.
- Borders:
* New Zealand has no land borders with other countries. * Its coastline along the South Pacific Ocean is 15,134 km (9,404 mi) long. This makes it the 10th longest coastline in the world.
- Population:
* As of June 2023, New Zealand's population was estimated to be 5,223,100 people.
- Area:
* New Zealand covers an area of 268,680 square kilometers (103,738 sq mi).
Environment and Nature

New Zealand has a special natural environment.
- Plants and Animals:
* It has unique plants and animals. * You can find many different plants. * Its animals include special birds and mammals. The kiwi is a famous bird from New Zealand!
- Climate:
* New Zealand has a varied Climate of New Zealand. * Like many places, it is affected by Climate change in New Zealand.
- Protected Areas:
* New Zealand has many Protected areas of New Zealand to keep its nature safe. * These include Marine reserves of New Zealand in the ocean and National parks on land.
- Renewable Energy:
* The country uses a lot of Renewable energy in New Zealand, which is good for the environment.
Natural Geographic Features
New Zealand is known for its amazing natural features:
- Caves of New Zealand
- Fjords of New Zealand (deep, narrow inlets of the sea)
- Glaciers of New Zealand (large sheets of ice)
- Many islands
- Beautiful lakes
- Tall mountains, including active volcanoes
- Long rivers and stunning waterfalls
People of New Zealand
You can learn more about the people of New Zealand and how they live.
History of New Zealand
The History of New Zealand is rich and interesting.
- Early History:
* Archaeology helps us understand the first people who came to New Zealand.
- Becoming Independent:
* New Zealand's journey to becoming an independent country is an important part of its story.
- Military History:
* The Military history of New Zealand includes its role in different wars and conflicts.
- Key Moments in Political History:
* The Treaty of Waitangi is a very important agreement between the Māori and the British Crown. * The 1981 Springbok Tour was a big event that caused protests about apartheid in South Africa. * The 1993 electoral referendum changed how people vote in New Zealand.
Culture of New Zealand
The Culture of New Zealand is a mix of Māori traditions and European influences.
- Buildings:
* The buildings show different styles over time.
- Food:
* New Zealand food has its own unique flavors.
- Languages:
* New Zealand has three official languages: New Zealand English, Māori language, and New Zealand Sign Language.
- Māori Culture:
* Māori culture is a very important part of New Zealand's identity.
- National Symbols:
* The National symbols of New Zealand include the Coat of arms of New Zealand, the Flag of New Zealand, and the National anthems of New Zealand.
- Holidays:
* New Zealand celebrates several Public holidays in New Zealand.
- Religion:
* Many different religions are practiced, including Christianity in New Zealand, Hinduism in New Zealand, Islam in New Zealand, Judaism in New Zealand, and Sikhism in New Zealand.
Art in New Zealand
New Zealand has a lively art scene:
- Art of New Zealand
- Movies from New Zealand
- Books and writing
- Music of New Zealand
- Television in New Zealand
- Theatre in New Zealand
- Kapa haka is a traditional Māori performing art.
Sports in New Zealand
Sports in New Zealand are very popular!
- Rugby union in New Zealand is the national sport and is loved by many.
- Rugby league in New Zealand
- Football in New Zealand (soccer)
- Horse racing in New Zealand
- New Zealand competes in the Olympic Games.
- There are many stadiums and horse tracks across the country.
Economy and Infrastructure
The Economy of New Zealand is strong and diverse.
- Farming:
* Farming is a big part of the economy.
- Money:
* The currency is the Dollar (NZD). * The Reserve Bank of New Zealand manages the country's money.
- Communication:
* Communications in New Zealand include Internet in New Zealand and Telecommunications in New Zealand.
- Energy:
* Energy in New Zealand comes from various sources.
- Health Care:
* Health care in New Zealand provides services to people, including hospitals.
- Tourism:
* Tourism in New Zealand is very important, as many people visit to see its beautiful landscapes.
- Transport:
* Transport in New Zealand includes airports, trains, and a network of roads.
Education in New Zealand
- Education in New Zealand is highly valued.
- Secondary education in New Zealand is for teenagers.
- Tertiary education in New Zealand includes universities and colleges for higher learning.
|
 | Victor J. Glover |
 | Yvonne Cagle |
 | Jeanette Epps |
 | Bernard A. Harris Jr. |