State of Palestine facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
State of Palestine
|
|
|---|---|
|
Anthem: فدائي (Fidāʾī; "Fedayeen")
|
|
|
Occupied Palestinian territories (green)
Territory annexed by Israel (light green) |
|
| Status | UN observer state under Israeli occupation Recognized by 146 UN member states |
|
|
| Largest city | Gaza City (before 2023), currently in flux |
| Official languages | Arabic |
| Ethnic groups | Palestinian Arabs |
| Religion
(2014 est.)
|
|
| Demonym(s) | Palestinian |
| Government | Unitary provisional semi-presidential republic |
| Mahmoud Abbas | |
| Mohammad Mustafa | |
|
• Speaker of the Parliament
|
Aziz Dweik |
| Legislature | National Council |
| Formation | |
|
• Declaration of Independence
|
15 November 1988 |
|
• UNGA observer state resolution
|
29 November 2012 |
|
• Sovereignty dispute with Israel
|
Ongoing |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
6,020 km2 (2,320 sq mi) (163rd) |
|
• Water (%)
|
3.5 |
| 5,655 km2 | |
| 365 km2 | |
| Population | |
|
• 2023 estimate
|
5,483,450 (121st) |
|
• Density
|
731/km2 (1,893.3/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2023 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| GDP (nominal) | 2021 estimate |
|
• Total
|
|
|
• Per capita
|
|
| Gini (2016) | ▼ 33.7 medium |
| HDI (2021) | high · 106th |
| Currency |
|
| Time zone | UTC+2 (Palestine Standard Time) |
|
• Summer (DST)
|
UTC+3 (Palestine Summer Time) |
| Date format | dd/mm/yyyy |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +970 |
| ISO 3166 code | PS |
| Internet TLD | .ps |
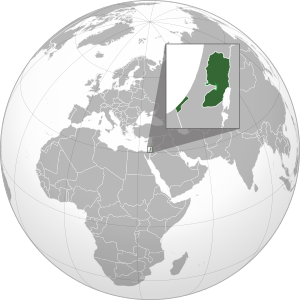
Palestine (Arabic: فلسطين, romanized: Filasṭīn), officially known as the State of Palestine (Arabic: دولة فلسطين, romanized: Dawlat Filasṭīn), is a country in Western Asia. It claims the West Bank and Gaza Strip as its territory, with Jerusalem as its capital. However, its government currently has control over parts of the West Bank and the Gaza Strip. The main administrative center is in Ramallah.
Since 1948, the land claimed by Palestine has been occupied. First, it was controlled by Egypt and Jordan, and then by Israel after the Six-Day War in 1967. As of 2020, Palestine has a population of over 5 million people.
After World War II, in 1947, the United Nations suggested a plan to divide the area into separate Arab and Jewish states, with Jerusalem as an international city. Jewish leaders accepted this plan, but Arab leaders did not. On November 15, 1988, the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) declared the establishment of the State of Palestine.
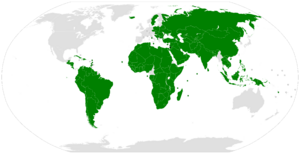
Today, Palestine is recognized as a country by 144 out of 193 member states of the United Nations. It is also a member of important groups like the Arab League and the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation.
Contents
About Palestine
What is the Name "Palestine"?
The name "Palestine" has been used for this region for a very long time, even since ancient Greek times. The Greek historian Herodotus wrote about a "district of Syria, called Palaistine" in the 5th century BC. Many believe the name "Palestine" comes from the Philistines, an ancient people who lived in the area.
How Did Palestine Become a State?
In 1947, the UN proposed a plan to create two states in the region: one Arab and one Jewish. Jewish leaders agreed, but Arab leaders did not. In 1948, the State of Israel was declared. This led to a war, and Israel gained more land. Egypt took control of the Gaza Strip, and Jordan took control of the West Bank.
In 1964, the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) was formed to work for Palestinian rights. In 1988, the PLO declared the establishment of the State of Palestine. Later, in 1993, the Oslo Accords were signed. These agreements led to the creation of the Palestinian National Authority (PNA) to govern parts of the West Bank and Gaza Strip.
In 2012, the United Nations General Assembly voted to upgrade Palestine's status to a "non-member observer state." This means Palestine can participate in UN meetings, similar to the Holy See.
Where is Palestine Located?
The areas claimed by the State of Palestine are in a region called the The Levant.
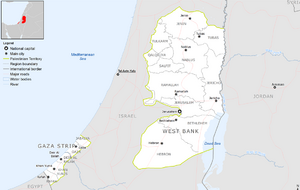
- The Gaza Strip is on the western coast, bordering the Mediterranean Sea, Egypt to the south, and Israel to the north and east.
- The West Bank is bordered by Jordan to the east, and Israel to the north, south, and west.
These two areas are not connected by land; Israel separates them. The total land area claimed by Palestine is about 6,020 square kilometers.
What is the Climate Like?
Palestine has different climates.
- The West Bank mostly has a Mediterranean climate, which means mild, wet winters and hot, dry summers. Higher areas are cooler.
- The eastern part of the West Bank includes the Judean Desert, which is very dry and hot.
- The Gaza Strip has a hot, semi-arid climate. Winters are mild, and summers are dry and hot. Rain is rare and falls mostly between November and March.
Government and People
How is Palestine Governed?
The State of Palestine has several important groups that help run the country:
- The President of the State of Palestine is chosen by the Palestinian Central Council.
- The Palestinian National Council is like the parliament that helped create the State of Palestine.
- The Executive Committee of the Palestine Liberation Organization acts like a government for Palestine, especially in its dealings with other countries.
These groups are different from the ones that manage daily life in the Palestinian territories, which are part of the Palestinian National Authority (PNA).
What are the Administrative Divisions?
Palestine is divided into sixteen administrative areas called governorates. These help manage different parts of the country.
| Name | Area (km2) | Population | Density (per km2) | Muhafazah (district capital) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jenin | 583 | 311,231 | 533.8 | Jenin |
| Tubas | 402 | 64,719 | 161.0 | Tubas |
| Tulkarm | 246 | 182,053 | 740.0 | Tulkarm |
| Nablus | 605 | 380,961 | 629.7 | Nablus |
| Qalqiliya | 166 | 110,800 | 667.5 | Qalqilya |
| Salfit | 204 | 70,727 | 346.7 | Salfit |
| Ramallah & Al-Bireh | 855 | 348,110 | 407.1 | Ramallah |
| Jericho & Al Aghwar | 593 | 52,154 | 87.9 | Jericho |
| Jerusalem | 345 | 419,108a | 1214.8a | Jerusalem (de Jure) |
| Bethlehem | 659 | 216,114 | 927.9 | Bethlehem |
| Hebron | 997 | 706,508 | 708.6 | Hebron |
| North Gaza | 61 | 362,772 | 5947.1 | Jabalya |
| Gaza | 74 | 625,824 | 8457.1 | Gaza City |
| Deir Al-Balah | 58 | 264,455 | 4559.6 | Deir al-Balah |
| Khan Yunis | 108 | 341,393 | 3161.0 | Khan Yunis |
| Rafah | 64 | 225,538 | 3524.0 | Rafah |
a. Data from Jerusalem includes occupied East Jerusalem with its Israeli population
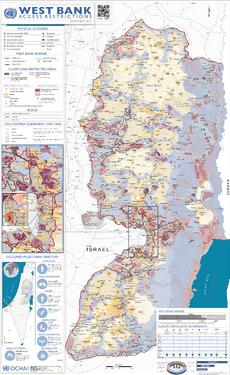
The governorates in the West Bank are divided into three areas:
- Area A (18% of the West Bank) is managed by the Palestinian government.
- Area B (22% of the West Bank) has Palestinian civil control, with shared Israeli-Palestinian security control.
- Area C (60% of the West Bank, except East Jerusalem) is managed by Israel. The Palestinian government provides education and health services to Palestinians living there.
How Does Palestine Relate to Other Countries?
The Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) represents the State of Palestine to other countries. Palestine has embassies in many countries that recognize it. Palestine is also part of various international organizations.
As of 2024, 145 out of 193 UN member states recognize the State of Palestine. In 2012, the UN General Assembly voted to make Palestine a "non-member observer state." This means Palestine can raise its flag at the UN headquarters, which happened in 2015.
What About Law and Security?
The State of Palestine has its own security forces. These include a Civil Police Force, National Security Forces, and Intelligence Services. Their job is to keep people safe and protect the Palestinian State.
How Many People Live in Palestine?
| Population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Million | ||
| 1950 | 0.9 | ||
| 2000 | 3.2 | ||
| 2018 | 4.9 | ||
In 2013, the population of Palestine was about 4.4 million people. This means there are about 827 people living in every square kilometer. This is a much higher population density than the world average.
What About Healthcare and Education?
- Healthcare: In 2017, Palestine had 743 primary health centers and 81 hospitals. Many organizations work together to provide health services.
- Education: Palestine has a high literacy rate, meaning most people can read and write. In 2014, about 96.3% of people could read. The number of women who can read has greatly increased over the years.
What Religions are Practiced?
Religion of Palestinians (est. 2014) Islam (93%) Christianity (6%) Druze and Samaritans (1%)
Most Palestinians (93%) are Muslim, mainly following the Sunni branch. About 6% of Palestinians are Palestinian Christians. There are also smaller groups like Druze and Samaritans.

Economy and Daily Life
What About Tourism?
Tourism is important in Palestine, especially in East Jerusalem and the West Bank. Many people visit historical and religious sites. In 2010, 4.6 million people visited the Palestinian territories. Most tourists come for short trips. The Palestinian government wants to encourage more visitors, but challenges exist.
How Do People Communicate?
Most Palestinian households have mobile phones, and many have smartphones. About 80% of homes have internet access, and about a third have a computer. The World Bank is helping to improve the technology sector in Palestine to create more jobs for young people.
How Do People Travel?
Roads
In 2010, the West Bank and Gaza Strip had about 4,686 kilometers of roads. The main highway in the Gaza Strip is Salah al-Din Road, which runs through its entire length.
Ports
The West Bank is landlocked, so it has no ports. The Port of Gaza is a small port used by fishing boats. Plans for a larger seaport in Gaza were stopped in 2000.
Airports
There are three airports in the Palestinian territories, but all are currently closed. These include Yasser Arafat International Airport in Gaza and Atarot Airport. Palestinians traveling abroad often use the Allenby Bridge to cross into Jordan and fly from Queen Alia International Airport in Amman.
Border Crossings
Several border crossings connect the Palestinian territories with Israel and Egypt:
- The Allenby Bridge connects the West Bank with Jordan. It is the main exit and entry point for West Bank Palestinians traveling internationally.
- The Erez Crossing is for people moving between the Gaza Strip and Israel.
- The Kerem Shalom Crossing is used for goods traveling between Israel and the Gaza Strip.
- The Rafah Crossing is the only land crossing between the Gaza Strip and Egypt.
What About Water and Sanitation?
Water supply and sanitation are big challenges in the Palestinian territories. There is often a shortage of water, and water quality is worse in the Gaza Strip. A lot of water is lost in the distribution system. Also, existing wastewater treatment plants cannot handle all the wastewater, leading to pollution.
Culture
Media
Palestine has various newspapers, news agencies, and television stations. Some examples include Ma'an News Agency and Al-Aqsa TV.
Sports
Football (soccer) is the most popular sport among Palestinians. The Palestine national football team plays in international matches. Rugby is also a popular sport.
Images for kids
-
The destroyed Palestinian Legislative Council building in Gaza City, Gaza–Israel conflict, September 2009
See also
 In Spanish: Estado de Palestina para niños
In Spanish: Estado de Palestina para niños