International recognition of the State of Palestine facts for kids
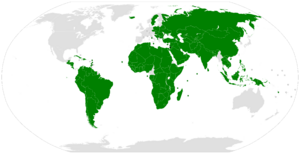
The State of Palestine is a land that many people want to see become an independent country. In November 2012, the United Nations General Assembly accepted Palestine as an "observer state." This means Palestine can join many UN meetings and discussions, but it is not a full member with voting rights. As of April 2024, 140 out of 193 countries that are full members of the United Nations (UN) have officially recognized Palestine as a state.
The Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) officially declared the State of Palestine on November 15, 1988. They claimed control over the Palestinian territories, which include the West Bank (with East Jerusalem) and the Gaza Strip. By the end of 1988, 78 countries had recognized this new Palestinian state.
To try and end the long-running Israeli–Palestinian conflict, Israel and the PLO signed agreements called the Oslo Accords in 1993 and 1995. These agreements created the Palestinian National Authority (PA). The PA is a temporary government that manages parts of the Gaza Strip and about 40% of the West Bank. After some political changes in Israel, talks between Israel and the PA stopped. This led Palestinians to seek international recognition for their state without Israel's agreement.
In 2011, the State of Palestine joined UNESCO, a UN agency focused on education and culture. In 2012, after being accepted as an observer state by the UN General Assembly (with 138 votes), the PA officially started using the name "State of Palestine" for everything.
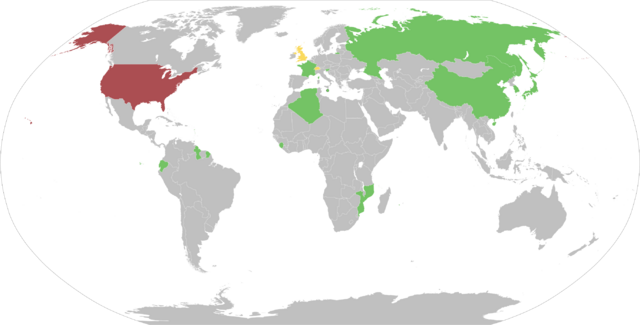
Among the G20 group of major economies, nine countries (Argentina, Brazil, China, India, Indonesia, Russia, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, and Turkey) recognize Palestine as a state. Ten other G20 countries (Australia, Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, South Korea, Mexico, the United Kingdom, and the United States) do not. These countries often support a "two-state solution" where both Israel and Palestine exist peacefully. However, they believe that recognizing a Palestinian state should happen only after direct talks between Israel and the PA.
Contents
History of Recognition
Early Steps
On November 22, 1974, the United Nations General Assembly passed a resolution. This resolution said that the Palestinian people have the right to decide their own future, become independent, and have their own country in Palestine. It also recognized the PLO as the main group representing the Palestinian people. The UN then gave the PLO "observer" status. In 1988, the UN started using the name "Palestine" for the PLO. This was because Palestine had declared its independence. However, the declared state still does not have a formal status within the UN system.
Soon after the 1988 declaration, many developing countries in Africa and Asia, and communist or non-aligned countries, recognized the State of Palestine. But the United States tried to stop other countries and international groups from recognizing Palestine. They used laws and other ways to discourage this. Even so, the Arab League and the Organisation of the Islamic Conference (OIC) quickly announced their support for Palestine. Palestine was then accepted as a member in both of these groups.
In February 1989, the PLO told the UN Security Council that 94 countries had recognized the new Palestinian state. Palestine then tried to join several UN-related organizations. But the U.S. stopped these efforts by threatening to cut off funding to any organization that accepted Palestine. For example, in April 1989, the PLO applied to join the World Health Organization. This application failed because the U.S. said it would stop funding if Palestine was admitted. In May, a group of OIC members asked UNESCO to accept Palestine as a member. They listed 91 countries that had recognized the State of Palestine.
In June 1989, the PLO sent letters to Switzerland to join the Geneva Conventions of 1949. Switzerland is the country that holds these agreements. But Switzerland said it could not decide if the letter was valid. This was because the international community was not sure if a State of Palestine existed.
Later, in November 1989, the Arab League suggested a UN General Assembly resolution to officially recognize the PLO as the government of an independent Palestinian state. But this plan was dropped. The U.S. again threatened to cut off its funding for the UN if the vote happened. The Arab states agreed not to push the resolution. But they demanded that the U.S. promise not to threaten the UN with financial cuts again.
Many early statements recognizing the State of Palestine were not very clear. Also, some countries hesitated, but this did not always mean they did not see Palestine as a state. This has caused confusion about how many countries officially recognized the state declared in 1988. The numbers reported have often been different, sometimes as high as 130. In July 2011, the Palestinian ambassador to the UN, Riyad Mansour, said that 122 countries had formally recognized Palestine. By the end of September that year, Mansour claimed the number had reached 139.
Israel's View
After the Six-Day War and before the Oslo Accords, no Israeli government suggested creating a Palestinian state. When Benjamin Netanyahu was Prime Minister from 1996 to 1999, he said that previous governments were getting too close to the "danger" of a Palestinian state. His main goal was to make sure the Palestinian Authority did not become more than a self-governing area.
In June 2003, Ariel Sharon became the first Israeli Prime Minister to say that a Palestinian state might be possible. Sharon talked about "the possibility of a Palestinian state with temporary borders, if conditions allow." He said this state would be "completely demilitarized." He also stated that it would be the home for Palestinians living outside the area, and that Palestinian refugees would not be allowed into Israeli territory.
The government led by Ehud Olmert had a similar goal. After the Netanyahu government took office in 2009, it again said that a Palestinian state was a danger to Israel. However, this position changed because of pressure from the Obama Administration. On June 14, 2009, Netanyahu for the first time supported the idea of a demilitarized and smaller Palestinian state. Some people criticized this because it did not clearly state which territories would be given to the Palestinian state. In February 2023, Netanyahu said, "I'm certainly willing to have them have all the powers that they need to govern themselves, but none of the powers that can threaten us. This means that Israel should have the overriding security responsibility."
Israel has refused to accept the 1967 borders. Israeli military experts say these borders are hard to defend. Israel also opposes Palestine's plan to go to the UN General Assembly for statehood. Israel says this does not follow the Oslo Accords agreement, where both sides agreed not to make one-sided moves.
Palestine's Journey at the United Nations
- October 14, 1974: The Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) was recognized by the UN General Assembly. It was seen as the representative of the Palestinian people. It was allowed to join discussions about Palestine in General Assembly meetings.
- November 22, 1974: The PLO was given "non-state observer" status. This allowed the PLO to take part in all Assembly sessions and other UN events.
- December 15, 1988: UN General Assembly Resolution 43/177 recognized the Palestinian Declaration of Independence from November 1988. It changed the name "Palestine Liberation Organization" to "Palestine" within the United Nations system.
- September 23, 2011: Palestinian President Mahmoud Abbas officially asked the United Nations to accept Palestine as a full member state.
- November 29, 2012: The General Assembly gave Palestine "non-member observer state" status in United Nations General Assembly resolution 67/19.
- December 17, 2012: The UN Chief of Protocol, Yeocheol Yoon, decided that the official name "State of Palestine" would be used by the UN Secretariat in all official UN documents.
Seeking Full UN Membership
After two years of stalled talks with Israel, the Palestinian Authority started a diplomatic effort. They wanted to gain recognition for the State of Palestine based on the borders before the Six-Day War, with East Jerusalem as its capital. These efforts began in late 2009. They gained a lot of attention in September 2011 when President Mahmoud Abbas applied to the United Nations for Palestine to become a full member state. If this had happened, it would have meant many countries recognized the State of Palestine. This would have allowed its government to take legal action against other states in international courts.
For a state to become a full member of the General Assembly, two-thirds of the member states must support its application. Also, the United Nations Security Council must first recommend admission. This means that none of the Security Council's five permanent members can use their veto power. Knowing that the United States might use its veto, Palestinian leaders hinted they might instead seek a smaller upgrade. They considered "non-member state" status. This only needs a simple majority vote in the General Assembly. This status would still give Palestinians the recognition they wanted.
The campaign, called "Palestine 194," was supported by the Arab League in May. The PLO officially confirmed it on June 26. The Israeli government called this decision a one-sided step. But the Palestinian government said it was necessary to overcome the current problems. Some other countries, like Germany and Canada, also criticized the decision. They called for a quick return to talks. However, many others, like Norway and Russia, supported the plan. Even Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon said, "UN members are entitled whether to vote for or against the Palestinian statehood recognition at the UN."

Diplomatic efforts to gain support for the bid grew stronger after several South American countries supported it in early 2011. High-level groups led by Palestinian officials visited many countries. Palestinian ambassadors, helped by those from other Arab states, were asked to get support from the governments where they worked. Before the vote, Russia, China, and Spain publicly promised their support for Palestine's bid. International groups like the African Union and the Non-Aligned Movement also supported it.
Israel tried to stop this effort. Germany, Italy, Canada, and the U.S. publicly announced they would vote against the resolution. Israeli and U.S. diplomats started a campaign. They pressured many countries to oppose the vote or not vote at all. However, because Palestinians had an "automatic majority" in the General Assembly, the Netanyahu government said it did not expect to stop a resolution from passing. In August, Haaretz quoted the Israeli ambassador to the United Nations, Ron Prosor, saying that Israel would not be able to block a resolution by September. Prosor wrote, "The maximum that we can hope to gain is for a group of states who will abstain or be absent during the vote. Only a few countries will vote against the Palestinian initiative."
Instead, the Israeli government focused on getting a "moral majority" of major democratic powers. They hoped this would reduce the importance of the vote. A lot of attention was on the European Union's position, which had not yet been announced. The EU foreign policy chief, Catherine Ashton, said it would likely depend on how the resolution was written. In late August, Israel's defense minister Ehud Barak said that "it is very important that all the players come up with a text that will emphasize the quick return to negotiations, without an effort to impose pre-conditions on the sides."
Both Israel and the U.S. also tried to pressure the Palestinian leadership to drop their plans and return to talks. In the U.S., Congress passed a bill that criticized the initiative. It called on the Obama administration to veto any resolution that would recognize a Palestinian state declared without an agreement between the two sides. A similar bill passed in the Senate. This bill also threatened to stop aid to the West Bank. In late August, another bill was introduced in Congress. It suggested blocking U.S. government funding for United Nations entities that supported Palestinian membership in the UN. Several top U.S. officials, including ambassador to the United Nations Susan Rice and consul-general in Jerusalem Daniel Rubinstein, made similar threats. In the same month, it was reported that the Israeli Ministry of Finance was holding back its monthly payments to the PA. Foreign Minister Avigdor Lieberman warned that if Palestine took one-sided action, Israel would consider the Oslo Accords invalid. Israel would also break off relations with the PA.

On July 11, 2011, the Quartet met to discuss returning to talks. But the meeting did not produce any results. President Mahmoud Abbas said he would stop the UN bid and return to talks if Israel agreed to the 1967 borders. He also wanted Israel to stop building settlements in the West Bank.
The PA's campaign gained more support from regular people. Avaaz started an online petition asking all UN members to support Palestine's bid. It reportedly got 500,000 online signatures in its first four days. OneVoice Palestine started a local campaign with news agencies. Their goal was to get Palestinian citizens involved and supportive. Overseas, campaigns were launched in several countries. They asked their governments to vote "yes" on the resolution. On September 7, a group of Palestinian activists, called "Palestine: State No. 194," protested outside the UN office in Ramallah. During the protest, they gave a letter to Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon. They urged him to "exert all possible efforts toward the achievement of the Palestinian people's just demands." The next day, Ban told reporters, "I support ... the statehood of Palestinians; an independent, sovereign state of Palestine. It has been long overdue." But he also said that "recognition of a state is something to be determined by the member states."
Other UN groups had previously said they were ready to see a Palestinian state. In April 2011, the UN's coordinator for the Middle East peace process released a report. It described the Palestinian Authority's progress in building a state. It said that "aspects of its administration [were] sufficient for an independent state." This was similar to a report published a week earlier by the International Monetary Fund. The World Bank released a report in September 2010. It found that the Palestinian Authority was "well-positioned to establish a state" very soon. However, the report also said that unless private businesses grew in the Palestinian economy, a Palestinian state would still rely on donations.
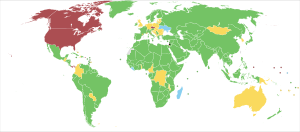
The effort to get full UN membership was tried again in 2024 during the Israel–Hamas war. The United Nations Security Council held a vote on the topic in April. The vote was 12 in favor, two countries did not vote, and one country voted against. The United States used its veto power to stop the measure.
| United Nations Security Council proposal vote on Admission of new Member Palestine (State of Palestine)
Date: 18 April 2024 |
||
|---|---|---|
| In favour (12) | Abstentions (2) | Against (1) |
- Note
Bold: Shows the permanent members of the United Nations Security Council.
P: Shows the president of the United Nations Security Council at that time.
V: The United States, as a permanent member, used its veto power to stop the proposal from passing.
Observer State Status
In September 2012, Palestine decided to try for a higher status. They wanted to go from "observer entity" to "non-member observer state." On November 27, it was announced that the request was official. It would be voted on in the General Assembly on November 29. Most countries were expected to support the status upgrade. Besides giving Palestine "non-member observer state status," the resolution also hoped that the Security Council would think positively about Palestine's application for full membership. It supported a two-state solution based on the pre-1967 borders. It also stressed the need for talks between the two sides to start again right away.
On November 29, 2012, General Assembly resolution 67/19 passed with 138 votes for, 9 against, and 41 not voting. This upgraded Palestine to "non-member observer state" status in the United Nations. This new status made Palestine's position similar to that of the Holy See (Vatican City). The Independent newspaper called this change "de facto recognition of the sovereign state of Palestine." The countries that voted "no" were Israel, Canada, the Czech Republic, the Marshall Islands, the Federated States of Micronesia, Nauru, Palau, Panama, and the United States.
This vote was a very important moment for the partially recognized State of Palestine and its people. It was a diplomatic setback for Israel and the United States. Being an observer state in the UN allows the State of Palestine to join international agreements and special UN agencies. This includes the Law of the Seas treaty and the International Criminal Court. It lets Palestine claim legal rights over its waters and airspace as a sovereign state recognized by the UN. It also gives the Palestinian people the right to sue for control over their territory in the International Court of Justice. They can also bring charges of "crimes against humanity" and war crimes against Israel in the International Criminal Court. This includes charges of unlawfully occupying Palestinian territory.
After the resolution passed, the UN allowed Palestine to call its office at the UN "The Permanent Observer Mission of the State of Palestine to the United Nations." Many saw this as the UN's way of recognizing the State of Palestine's control under international law. Palestine then started to change its name on postal stamps, official documents, and passports. The Palestinian authorities also told their diplomats to officially represent the "State of Palestine" instead of the "Palestine National Authority". Also, on December 17, 2012, UN Chief of Protocol Yeocheol Yoon decided that "the designation of "State of Palestine" shall be used by the Secretariat in all official United Nations documents." This recognized the "State of Palestine" as the official name of the Palestinian nation.
On September 26, 2013, at the United Nations, Mahmoud Abbas was allowed to sit in the General Assembly's special beige chair. This chair is usually for heads of state waiting to speak to the General Assembly.
Other Countries' Views
Official Recognition by Countries
Out of the 193 member states of the United Nations, 140 have recognized the State of Palestine. The list below is based on information from the Palestine Liberation Organization and the Permanent Observer Mission to the UN.
Some countries, marked with an asterisk (*) below, specifically recognized the State of Palestine with the borders from June 4, 1967. These borders include the West Bank, Gaza, and East Jerusalem. These areas were Arab territory before the Six-Day War.
| Countries that have official diplomatic relations with the State of Palestine |
| # | Name | Date of recognition | Diplomatic relations | Important groups or other details |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 15 November 1988 | Yes | Arab League, African Union (AU), OIC | |
| 2 | 15 November 1988 | Yes | Arab League, GCC, OIC | |
| 3 | 15 November 1988 | Yes | Arab League, OIC | |
| 4 | 15 November 1988 | Yes | Arab League, GCC, OIC | |
| 5 | 15 November 1988 | Yes | Arab League, AU, OIC | |
| 6 | 15 November 1988 | Yes | ASEAN, OIC | |
| 7 | 15 November 1988 | Yes | Arab League, AU, OIC | |
| 8 | 15 November 1988 | Yes | Arab League, AU, OIC | |
| 9 | 15 November 1988 | Yes | Arab League,AU, OIC | |
| 10 | 15 November 1988 | Yes | Arab League, AU, OIC | |
| 11 | 15 November 1988 | Yes | NATO, OIC, OTS | |
| 12 | 15 November 1988 | Yes | Arab League, OIC | |
| 13 | 16 November 1988 | Yes | OIC, SAARC | |
| 14 | 16 November 1988 | Yes | OIC, SAARC | |
| 15 | 16 November 1988 | Yes | — | |
| 16 | 16 November 1988 | Yes | ASEAN, OIC | |
| 17 | 16 November 1988 | Yes | Arab League, OIC | |
| 18 | 16 November 1988 | No | AU | |
| 19 | 16 November 1988 | Yes | EU | |
| 20 | 16 November 1988 | Yes | — | |
| 21 | 16 November 1988 | Yes | OIC, SAARC | |
| 22 | 16 November 1988 | Yes | Arab League, GCC, OIC | |
| 23 | 16 November 1988 | Yes | Arab League, GCC, OIC | |
| 24 | 16 November 1988 | Yes | Arab League, GCC, OIC | |
| 25 | 16 November 1988 | Yes | — | |
| 26 | 16 November 1988 | Yes | AU | |
| 27 | 17 November 1988 | Yes | NATO, OIC | |
| 28 | 17 November 1988 | Yes | ASEAN, OIC | |
| 29 | 17 November 1988 | Yes | Arab League, AU, OIC | |
| 30 | 17 November 1988 | Yes | AU | |
| 31 | 17 November 1988 | Yes | Arab League, AU, OIC | |
| 32 | 18 November 1988* | Yes | EU | |
| 33 | 18 November 1988 | Yes | EU, NATO | |
| 34 | 18 November 1988 | Yes | EU, NATO | |
| 35 | 18 November 1988 | Yes | Arab League, AU, OIC | |
| 36 | 18 November 1988 | Yes | AU, OIC | |
| 37 | 18 November 1988 | Yes | SAARC | |
| 38 | 18 November 1988 | Yes | AU, OIC | |
| 39 | 18 November 1988 | Yes | AU | |
| 40 | 18 November 1988 | Yes | SAARC | |
| 41 | 19 November 1988 | Yes | CSTO | |
| 42 | 19 November 1988 | Yes | AU, OIC | |
| 43 | 19 November 1988 | Yes | AU | |
| 44 | 19 November 1988 | Yes | CSTO, UNSC (permanent) | |
| 45 | 19 November 1988 | Yes | — | |
| 46 | 19 November 1988 | Yes | ASEAN | |
| 47 | 20 November 1988 | Yes | UNSC (permanent) | |
| 48 | 21 November 1988 | Yes | AU, OIC | |
| 49 | 21 November 1988 | Yes | Arab League, AU, OIC | |
| 50 | 21 November 1988 | Yes | AU, OIC | |
| 51 | 21 November 1988 | Yes | AU, OIC | |
| 52 | 21 November 1988 | Yes | ASEAN | |
| 53 | 22 November 1988 | Yes | — | |
| 54 | 22 November 1988 | Yes | AU, OIC | |
| 55 | 23 November 1988 | Yes | EU, NATO | |
| 56 | 24 November 1988 | Yes | AU | |
| 57 | 24 November 1988 | Yes | — | |
| 58 | 24 November 1988 | Yes | AU, OIC | |
| 59 | 24 November 1988 | Yes | EU, NATO | |
| 60 | 24 November 1988 | Yes | AU | |
| 61 | 25 November 1988 | Yes | EU, NATO | |
| 62 | 28 November 1988 | Yes | OIC, SAARC | |
| 63 | 29 November 1988 | Yes | AU | |
| 64 | 29 November 1988 | Yes | AU, OIC | |
| 65 | 29 November 1988 | Yes | AU | |
| 66 | 1 December 1988 | Yes | AU, OIC | |
| 67 | 2 December 1988 | Yes | ASEAN | |
| 68 | 3 December 1988 | Yes | AU, OIC | |
| 69 | 3 December 1988 | Yes | AU, OIC | |
| 70 | 5 December 1988 | Yes | AU | |
| 71 | 6 December 1988 | Yes | AU | |
| 72 | 8 December 1988 | Yes | AU, OIC | |
| 73 | 10 December 1988 | No | AU | |
| 74 | 10 December 1988 | No | AU | |
| 75 | 12 December 1988 | Yes | AU, OIC | |
| 76 | 13 December 1988 | Yes | Arab League, GCC, OIC | |
| 77 | 14 December 1988 | Yes | EU, NATO | |
| 78 | 19 December 1988 | Yes | AU | |
| 79 | 19 December 1988 | No | SAARC | |
| 80 | 22 December 1988 | No | AU | |
| 81 | 23 December 1988 | No | AU | |
| 82 | 25 December 1988 | No | SAARC | |
| 83 | 2 January 1989 | No | AU | |
| 84 | 4 February 1989 | Yes | AU | |
| 85 | 4 February 1989 | Yes | OIC | |
| 86 | May 1989 or before | Yes | AU, OIC | |
| 87 | May 1989 or before | No | AU | |
| 88 | May 1989 or before | Yes | AU | |
| 89 | 21 August 1989 | Yes | MSG, PIF | |
| 90 | September 1989 | Yes | ASEAN | |
| 91 | 1 July 1991 | Yes | AU | |
| 92 | 6 April 1992 | Yes | CSTO, OIC, OTS | |
| 93 | 15 April 1992 | Yes | OIC, OTS | |
| 94 | 17 April 1992 | Yes | OIC | |
| 95 | 25 April 1992 | Yes | — | |
| 96 | 27 May 1992 | Yes | — | |
| 97 | 6 September 1992 | Yes | CSTO, OIC | |
| 98 | 25 September 1994 | Yes | OIC, OTS | |
| 99 | 4 October 1994 | Yes | MSG, PIF | |
| 100 | 15 February 1995 | Yes | AU | |
| 101 | 12 September 1995 | Yes | CSTO, OIC, OTS | |
| 102 | 23 October 1998* | Yes | AU | |
| 103 | 1 March 2004 | Yes | — | |
| 104 | 25 March 2005* | Yes | OAS | |
| 105 | 24 July 2006 | Yes | NATO | |
| 106 | 5 February 2008 | Yes | OAS | |
| 107 | 30 November 2008 | Yes | Arab League, OIC | |
| 108 | 1 December 2008 | Yes | AU, OIC | |
| 109 | 27 April 2009 | Yes | — | |
| 110 | 14 July 2009 | Yes | OAS | |
| 111 | 1 December 2010* | Yes | OAS | |
| 112 | 6 December 2010* | Yes | OAS | |
| 113 | 17 December 2010* | Yes | OAS | |
| 114 | 24 December 2010* | Yes | OAS | |
| 115 | 7 January 2011 | Yes | OAS | |
| 116 | 13 January 2011* | Yes | CARICOM, OAS, OIC | |
| 117 | 24 January 2011 | Yes | OAS | |
| 118 | 1 February 2011* | No | CARICOM, OAS, OIC | |
| 119 | 15 March 2011 | Yes | OAS | |
| 120 | 6 June 2011* | Yes | AU | |
| 121 | 9 July 2011 | Yes | AU | |
| 122 | 18 July 2011* | Yes | Arab League, OIC | |
| 123 | 19 July 2011 | No | AU | |
| 124 | 25 August 2011 | Yes | OAS | |
| 125 | 26 August 2011* | Yes | OAS | |
| 126 | 29 August 2011* | Yes | CARICOM, OAS | |
| 127 | 9 September 2011* | Yes | CARICOM, OAS | |
| 128 | 19 September 2011 | Yes | CARICOM, OAS | |
| 129 | 22 September 2011* | No | CARICOM, OAS | |
| 130 | 15 December 2011* | Yes | EFTA, NATO | |
| 131 | 18 January 2012* | Yes | ASEAN | |
| 132 | 9 April 2013 | No | OAS | |
| 133 | 29 September 2013 | Yes | CARICOM, OAS | |
| 134 | 29 September 2013 | Yes | CARICOM, OAS | |
| 135 | 30 October 2014 | Yes | EU, NATO | |
| 136 | 14 September 2015 | Yes | CARICOM, OAS | |
| 137 | 3 August 2018 | Yes | OAS | |
| 138 | 30 July 2019 | Yes | CARICOM, OAS | |
| 139 | 19 April 2024 | No | CARICOM, OAS | |
| 140 | 23 April 2024 | No | CARICOM, OAS |
Countries Not Members of the UN
| # | Name | Date of recognition | Diplomatic relations |
Important groups or other details |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 141 | 15 November 1988 | No | AU | |
| 142 | February 2015 | Yes | — |
See also
- List of states with limited recognition
- List of positions on Jerusalem
- International recognition of Israel
- Palestinian nationalism
- Proposals for a Palestinian state
- Palestine–European Union relations
- Right to exist
 In Spanish: Reconocimiento internacional de Palestina para niños
In Spanish: Reconocimiento internacional de Palestina para niños