Predation facts for kids

In the world of ecology, predation is a special relationship between two living things. It's when one animal, called the predator, hunts, catches, and eats another animal, known as its prey. When a predator eats its prey, the prey always dies. Some predators kill their prey quickly, while others might eat them alive. Many animals can be both a predator and a scavenger (an animal that eats dead things it didn't kill).
A predator is an animal that hunts other animals for food. Think of a spider catching a fly in its web, or a group of lions working together to hunt a buffalo. The animals that predators hunt are called prey. A top predator or apex predator is an animal that is at the very top of the food chain, meaning no other animals hunt and eat it.
Most predators are carnivores, meaning they only eat meat. Some are omnivores, which means they eat both plants and other animals. Examples of predators include cats, crocodiles, snakes, raptors (like eagles), wolves, killer whales, lobsters, and sharks.
How Predators Hunt
Predators use many different ways to catch their food. Some chase their prey, while others prefer to wait quietly for an opportunity.
Ambush Predators
Ambush predators are animals that don't chase their prey. Instead, they wait quietly and hide until their prey comes close enough to attack. You might also hear them called "sit-and-wait predators." This method is used by many meat-eating animals and even some carnivorous plants.
These predators often use camouflage to blend in with their surroundings, making it hard for prey to spot them. They usually hunt alone. Waiting in ambush can be safer for the predator because it doesn't have to move around much, which means it's less likely to be seen by its own predators.
If a predator isn't faster than its prey, ambushing is often a smarter way to hunt than chasing. However, if a predator is very fast, actively hunting is usually more effective. Some predators use a mix of strategies. For example, a predator might stalk its prey quietly before a short, fast chase.
Social Hunting
Some predators work together in groups to hunt. This is called social hunting. It allows them to catch larger or faster prey that they couldn't catch alone.
-
A lioness with her prey. Lions often hunt in groups.
Images for kids
-
Spider wasps paralyse and eventually kill their hosts, but are considered parasitoids, not predators.
-
Paramecium, a tiny creature, feeding on bacteria.
-
The black-browed albatross flies long distances over the ocean to find food.
-
Seven-spot ladybirds choose good plants to find their aphid prey.
-
The chameleon catches prey by shooting out its long tongue.
-
Wolves, which are social predators, cooperate to hunt and kill bison.
-
An electric ray showing where its electric organ is located.
-
Bats use echolocation (like sonar) to hunt moths at night.
-
The Eastern coral snake is a predator itself, and its venom helps it avoid being eaten by other predators.
-
Willow plants growing back at Blacktail Creek, Yellowstone National Park, after wolves were brought back. Wolves are a keystone species and apex predator there. Left: 2002; Right: 2015.
-
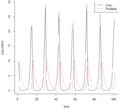
This graph shows how the numbers of snowshoe hare and Canada lynx furs sold changed over many years.
-
A San hunter in Botswana.
-
The Capitoline Wolf feeding Romulus and Remus, who were important figures in the story of Rome.
-
The large eyes, sensitive feelers, and strong jaws of a Jack jumper ant.
-
A Crab spider, an ambush predator, catching a field digger wasp.
-
A Red-tailed hawk using its sharp claws and beak to kill and eat its prey.
-
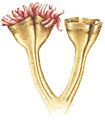
Auroralumina attenboroughii, an ancient predator from about 560 million years ago. It used stinging cells called nematocysts to catch prey.
-
This image shows how life on the sea floor changed. On the left, there was little burrowing. On the right, there were many different animals burrowing, likely to escape new predators.
-
A model of Dunkleosteus, a large fish from the Devonian period, possibly the first superpredator with a backbone.
-
Meganeura monyi, a huge predatory insect from the Carboniferous period, related to dragonflies. It could fly to escape predators. Its large size might be because there weren't many flying predators with backbones back then.
-
A model of Tyrannosaurus, a very large meat-eating dinosaur from the Cretaceous period.
See also
 In Spanish: Depredación para niños
In Spanish: Depredación para niños