Richmond County, North Carolina facts for kids
Richmond County is a place in central southern North Carolina. Its main town, or county seat, is Rockingham. The county was created in 1779 from a part of Anson County. It was named after Charles Lennox, 3rd Duke of Richmond and Lennox, who was a British leader friendly to the American colonists. In 2020, about 42,946 people lived here.
Quick facts for kids
Richmond County
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|

Richmond County Courthouse in Rockingham
|
|||
|
|||
| Motto(s): | |||
Location within the U.S. state of North Carolina
|
|||
 North Carolina's location within the U.S. |
|||
| Country | |||
| State | |||
| Founded | November 10, 1779 | ||
| Named for | Charles Lennox, 3rd Duke of Richmond and Lennox | ||
| Seat | Rockingham | ||
| Largest community | Rockingham | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 479.70 sq mi (1,242.4 km2) | ||
| • Land | 473.69 sq mi (1,226.9 km2) | ||
| • Water | 6.01 sq mi (15.6 km2) 1.25% | ||
| Population
(2020)
|
|||
| • Total | 42,946 | ||
| • Estimate
(2023)
|
42,324 |
||
| • Density | 90.66/sq mi (35.00/km2) | ||
| Time zone | UTC−5 (Eastern) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) | ||
| Congressional district | 8th | ||
| Top - 0-9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z |
History of Richmond County
Early Settlers and Beginnings
The first people to live in the area that became Richmond County were the Cheraw Native Americans. Later, European settlers arrived. Many of the first European families were Scottish Highlanders, who traveled up the Cape Fear River to find good farmland. English settlers also came, moving down the Pee Dee River. These English families eventually became the largest group of European settlers. Many early settlers raised cattle. Before Richmond County was formed, this area was part of Bladen County and then Anson County.
Forming the County and Early Growth
Richmond County was officially created in 1779. It was made from a part of Anson County. This was done to make it easier for people to reach the county courthouse. The county was named after Charles Lennox, 3rd Duke of Richmond and Lennox. He was a British politician who supported the American colonists during the American Revolution.
The county seat was first called Richmond Court House. In 1785, it was renamed Rockingham. This new name honored Charles Watson-Wentworth, 2nd Marquess of Rockingham, another British leader who was friendly to Americans. During the American Revolutionary War, the county faced attacks from those loyal to Britain. By 1790, Richmond County had 5,885 residents.
After the war, farmers in the area started growing different crops. They switched from raising cattle to growing corn, oats, indigo, and cotton. In 1837, the county's first textile mill, Richmond Manufacturing Company, was built. As cotton farming grew, the number of enslaved people in the county also increased. By the mid-1800s, about half of the local residents were enslaved. Around 1850, the eastern part of the county, known as the Sandhills, became important for making turpentine from longleaf pines. Railway service came to Richmond County in 1861.
Civil War and Reconstruction Era
During the American Civil War, soldiers from Richmond County joined different units of the Confederate States Army. In March 1865, Union troops led by General William Tecumseh Sherman entered Richmond County. Confederate troops left, and the Union forces damaged local factories before moving on. The Richmond Manufacturing Company mill, which had been burned, was rebuilt as the Great Falls Mill in 1869. That same year, the railway line reached Rockingham. More textile mills were built in the county after 1876. Cotton farming continued to be important until the mid-1900s. Farmers also started growing tobacco and peaches, especially in the Sandhills area.
By the late 1800s, many people in Richmond County were Black, and they often supported the Republican Party. However, the state of North Carolina was mostly controlled by the Democratic Party. Because of political changes and efforts by Democrats, a new county called Scotland County was formed in 1899. This new county included the town of Laurinburg and the surrounding area, which used to be part of Richmond County.
Growth and Economic Changes

In the early 1900s, Richmond County's economy relied on farming and textile mills. The town of Hamlet grew into a busy center for the Seaboard Air Line Railroad. Five railway lines crossed through Hamlet, creating many jobs. The building of Blewett Falls Dam also helped the textile industry grow by providing hydroelectric power. By the end of World War II, Richmond County had ten textile mills, employing up to 15,000 people. Over time, larger companies bought many of these mills, and they started making fabrics other than cotton. This led to less cotton being grown locally. In 1954, Seaboard built a large railway yard near Hamlet. In 1968, the school systems of the county, Rockingham, and Hamlet joined together.
Economic Challenges and Community Action
Starting in the 1960s, Hamlet's economy faced difficulties. The railroad had more competition from roads, trucking, and air travel. The railway company, which later became CSX Transportation, moved some jobs away and reduced passenger services. The textile industry also cut jobs due to foreign competition and new machines. By the 1970s, only about 5,000 people worked in textile mills in Richmond County. Job losses in textiles continued through the 1980s and 1990s. In 1986, a large manufacturing plant in Rockingham closed. Many new jobs were in service industries or food processing, and national stores replaced local small businesses.

In the late 1980s, there was a plan to build a low-level radioactive waste disposal site in Richmond County. Local residents quickly formed a group called For Richmond County Environment (FORRCE) to oppose it. This group gained strong support from people across the county, both in Hamlet and Rockingham. FORRCE collected over 26,000 signatures on a petition, which was more than 60% of the county's population. Local leaders also spoke out against the site. In 1993, the plan to build the site in Richmond County was stopped.
On September 3, 1991, a tragic fire happened at the Imperial Food Products plant in Hamlet. Many exits were locked, which was against safety rules. Twenty-four workers and one delivery driver died in the fire. This event brought national attention to the town. The county's economy continued to struggle as more textile mills closed in the 1990s and early 2000s. From 1993 to 2005, nine textile mills closed, and 1,730 jobs were lost. Unemployment rates got worse after the Great Recession started in December 2007.
Geography and Nature
Richmond County covers about 479.70 square miles. Most of this area, 473.69 square miles, is land, and 6.01 square miles is water. It is the 38th largest county in North Carolina by land area. Richmond County shares borders with Montgomery County, Moore County, Scotland County, Anson County, and Marlboro County in South Carolina.
The county is located where three different natural regions meet: the Piedmont, the Sandhills, and the Coastal Plain. The western part of the county is mostly Piedmont, while the Sandhills and Coastal Plain are in the center and east. The Uwharrie Mountains stretch along the county's western border.
Most of the county's water flows into the Great Pee Dee River. The rest mostly drains into Drowning Creek, which is the start of the Lumber River. The county has several lakes and creeks, including Blewett Falls Lake. Much of Richmond County is covered by forests. Longleaf pines grow naturally here. Large areas of longleaf pine forest are protected in the Sandhills Game Land, with more than half of it in Richmond County. The Pee Dee River Game Land is also partly in the county. Farmland in Richmond County is home to many birds, like the loggerhead shrike and vesper sparrow. The Pee Dee National Wildlife Refuge covers part of the county and has grasslands and swamps. It is home to many migratory waterfowl and white-tailed deer.
People and Population
2020 Census Information
As of the 2020 census, Richmond County had 42,946 people. There were 18,380 households and 11,783 families living in the county.
| Race | Number | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| White (non-Hispanic) | 23,610 | 54.98% |
| Black or African American (non-Hispanic) | 12,770 | 29.74% |
| Native American | 994 | 2.31% |
| Asian | 360 | 0.84% |
| Pacific Islander | 7 | 0.02% |
| Other/Mixed | 2,133 | 4.97% |
| Hispanic or Latino | 3,072 | 7.15% |
Richmond County is part of the Rockingham, NC Micropolitan Statistical Area.
Population Changes Over Time
Between 2010 and 2022, the number of people living in Richmond County decreased by about 3,900 residents.
Government and Law
How the County is Governed
Richmond County is managed by a group of seven people called the board of commissioners. These commissioners are chosen by voters for four-year terms. They pick one of their members to be the chairman and another to be the vice-chairman. The board makes county rules, passes laws, and hires the county manager. The county manager is like the chief executive of the county government. They carry out the commissioners' decisions and represent the county in dealings with other governments. The county government gets its money from a local property tax.
Richmond County is part of the Lumber River Council of Governments, which helps with planning for five counties. It is also part of specific areas for state and national elections. The United States Army has a training area called Camp Mackall that is partly in the county.
Law Enforcement and Courts
Richmond County is part of the 21st Prosecutorial District and the 16A Superior Court and District Court Districts. Voters in the county elect a sheriff. The sheriff's office provides law enforcement throughout the county. The towns of Hamlet and Rockingham also have their own police departments.
Political Trends
For a long time, the Democratic Party was very strong in Richmond County politics. However, in recent years, the county has seen a shift. While a majority of voters supported Democratic presidential candidate Barack Obama in 2012, Republican presidential candidate Donald Trump won by a clear margin in 2016. After the 2020 elections, Republicans gained more seats on the county board of commissioners. By 2022, Republicans held all the seats on the board. As of March 2022, Richmond County had 27,358 registered voters.
Economy
The North Carolina Department of Commerce considers Richmond County to be economically challenged. However, in 2022, the county had some success in attracting new businesses. Several manufacturers expanded their operations and hired more local workers. From 2017 to 2021, the average household income in the county was estimated to be $38,962.
Transportation
Richmond County has major roads like Interstate 73 and Interstate 74. Parts of these interstates are still being finished or are marked as temporary routes. The Rockingham Bypass, which is part of both interstates, is expected to be completed in 2025. Other important roads include U.S. Route 1, US 74, and US 220, as well as several North Carolina Highways. The county government also offers a public transport bus service called Area of Richmond Transportation.
For trains, CSX Transportation provides local rail service and has several facilities in Hamlet. Amtrak's Silver Star passenger train also stops in Hamlet. For air travel, the county is served by the Richmond County Airport.
Education
Public schools in Richmond County are managed by Richmond County Schools. They operate seven elementary schools, four middle schools, and four high schools. Like other places, the county's education system was affected by the COVID-19 pandemic. For the 2021/2022 school year, about 56.1 percent of tested students did not meet state standards. Richmond Community College, located in Hamlet, serves the county. In 2021, about 17.5 percent of county residents had a bachelor's degree or higher level of education.
Culture and Fun
The Rockingham Speedway opened in 1965 and hosted many NASCAR racing events until 2004. It was last used by NASCAR for truck series races in 2012 and 2013, and it is currently being fixed up. A nearby dragway is still used regularly for races. Since 1982, Hamlet has hosted the Seaboard Festival. This community event includes local sellers, running races, and music, celebrating Hamlet's history with the railroad. The Raiders, the football team of Richmond Senior High School, are very popular among county residents. The Pee Dee National Wildlife Refuge is a popular place for hunting and fishing. Quail hunting has been a popular activity in Richmond County and the wider Sandhills region for a long time. Several buildings and sites in the area are listed on the National Register of Historic Places.
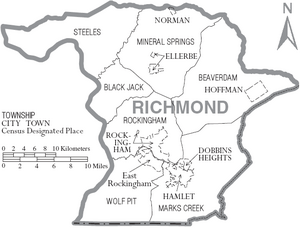
Communities in Richmond County
Towns and Cities
- Rockingham (This is the county seat and the largest community.)
- Hamlet
- Dobbins Heights
- Ellerbe
- Hoffman
- Norman
Census-Designated Places
These are areas that are like towns but are not officially incorporated.
- East Rockingham
- Roberdel
Other Unincorporated Communities
These are smaller communities that are not officially part of a town or city.
Townships
Richmond County is also divided into smaller areas called townships:
- Steeles
- Mineral Springs
- Beaverdam
- Mark's Creek
- Wolf Pit
- Rockingham
- Blackjack
Notable People from Richmond County
- Wayne Goodwin – a politician and government official
- Henry Frye – a former state lawmaker and former chief justice of the state supreme court
- Leon Levine – the person who started the Family Dollar stores
- John Coltrane – a famous jazz saxophonist
- Cameron A. Morrison – a former North Carolina governor, senator, and mayor
- Terius Youngdell Nash – a singer-songwriter and record producer
- Bucky Covington – a country music singer
- Dannell Ellerbe – a player in the NFL (National Football League)
- Melvin Ingram – a player in the NFL (National Football League)
See also
 In Spanish: Condado de Richmond (Carolina del Norte) para niños
In Spanish: Condado de Richmond (Carolina del Norte) para niños