Sigma facts for kids
Sigma (pronounced SIG-ma) is the eighteenth letter of the Greek alphabet. It has three main forms: a big letter (uppercase) Σ, a small letter (lowercase) σ, and a special small letter ς used only at the end of a word.
In the Greek number system, Sigma has a value of 200. You might also see the big Σ used in mathematics as a symbol for adding up a lot of numbers, which is called summation. For example, in the name Odysseus, the two small sigmas in the middle (σ) are different from the special sigma (ς) at the very end. The letter S in our Latin alphabet comes from Sigma, and the letter С in the Cyrillic alphabet (used in languages like Russian) also comes from a rounded version of Sigma.
Contents
Where Did Sigma Come From?
The shape and place of Sigma in the alphabet come from an old Phoenician letter called shin.
Sigma's first name might have been san. But because the early Greek alphabets were a bit complicated, san became its own separate letter, shown as Ϻ. The ancient Greek historian Herodotus said that the Dorians (a group of Greeks) called this letter "san," while the Ionians (another group) called it "sigma."
One idea is that the name "sigma" might come from the Phoenician letter samekh, which is related to the Greek letter Ξ. Another idea is that the Greeks made up the name "sigma" themselves, and it simply meant 'hissing', from a Greek word sízō which means 'I hiss'.
The Rounded Sigma

In ancient Greek handwriting, especially around 400-300 BC, the shape of the big Sigma (Σ) became simpler and looked more like a 'C'. This rounded shape, called lunate sigma (meaning 'moon-shaped sigma'), became very common in later ancient times and the Middle Ages.
Today, you can still see the lunate sigma (uppercase Ϲ, lowercase ϲ) in Greece, especially in old texts, religious writings, and church decorations. It looks like a crescent moon.
Ancient scholars like Aristarchus of Samothrace used special versions of the lunate sigma to mark notes in texts:
- A dotted lunate sigma (Ͼ) meant a line was in the wrong place.
- A reversed sigma (Ͻ) also meant a line was out of place.
- A dotted reversed sigma (Ͽ) could mean that lines needed to be rearranged or that there were different ways to read a text.
In some old Greek writings from the first century BC, Ͻ was a shortcut. It meant that a man's father had the same name as him. So, if a man named Dionysodoros had a father also named Dionysodoros, it would be written as Διονυσόδωρος Ͻ.
Alphabets That Came From Sigma
Sigma was used in the Old Italic alphabets starting around 800 BC. In these alphabets, a simpler version of Sigma with only three strokes (instead of four) was common. This three-stroke shape was then used in the Etruscan alphabet and early Latin writing, which is where our letter S comes from.
The early runic alphabet also used both the three-stroke and four-stroke versions of Sigma. Later runes, like those used by the Anglo-Saxons, mostly used the simpler three-stroke version.
The letter С in the Cyrillic alphabet (used for languages like Russian and Bulgarian) actually comes from the rounded, lunate form of Sigma.
How Sigma Is Used Today
In Language and Words
- In both ancient and Modern Greek, Sigma makes an 's' sound. In modern Greek, this 's' sound can sometimes become a 'z' sound if it's before certain other sounds.
- The big Sigma (Σ) was borrowed into the Latin alphabet for a special alphabet called the International African Alphabet. It's used as the uppercase for the letter esh (which looks like ʃ and makes a 'sh' sound).
- In the study of sounds in language (phonology), the small σ is used to show syllables (the parts of words we pronounce, like "sig-ma" has two syllables).
- In the study of language (linguistics), the big Σ can mean the whole set of symbols that make up an alphabet.
In Science and Math
Mathematics
- In math, the small σ is often used for unknown angles or as a short way to say "countably." The big Σ is very commonly used for summation, which means adding up a series of numbers. For example,
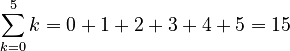 means adding numbers from 0 to 5.
means adding numbers from 0 to 5. - In statistics, σ stands for the standard deviation. This is a number that tells you how spread out a group of data is from the average.
- In topology, a σ-compact space is a type of space that can be made by joining together a countable number of smaller, "compact" parts.
- In probability theory, a σ-algebra is a special collection of sets that is used to define probabilities.
- In number theory, σ is part of different divisor functions, which are used to find the sum of a number's divisors.
Biology and Medicine
- In biology, the sigma receptor is a type of protein found on the surface of cells.
- In biochemistry, the σ factor is a protein that helps RNA polymerase (a molecule that helps make RNA) do its job.
- In the study of bones, the "sigma period" used to refer to how long a basic unit of bone remodeling lasts.
- In older physiology writings, σ was used to mean milliseconds (one-thousandth of a second).
Business and Money
- In finance, σ is the symbol for volatility. This measures how much the price of a stock changes over time.
- In accounting, Σ can show the total balance of invoices or the total amount of money owed and due.
- In the machine industry, Six Sigma (6σ) is a method used to improve quality and reduce errors in products or services.
Chemistry
- Sigma bonds (σ bonds) are the strongest type of chemical bond between atoms.
- In organic chemistry, σ is used in the Hammett equation to describe how certain chemical groups affect reactions.
Engineering and Computers
- In computer science, Σ can represent the set of all possible symbols in an alphabet.
- In machine learning, σ is used in the formula for the Sigmoid function, which is important in how some computer programs learn.
- In radar jamming, σ is used to measure the radar cross-section (RCS), which tells you how big an object appears on radar.
- In civil engineering, σ refers to the normal stress (force per unit area) on a material or structure.
Physics
- In nuclear and particle physics, σ is used for cross sections, which measure the chance of particles interacting.
- The symbol σ is also used for the Stefan–Boltzmann constant, which is important in understanding how much energy objects radiate as heat.
- In physics, σ often stands for electrical conductivity, which is how well a material conducts electricity.
- In electrostatics, σ represents the surface charge density, which is how much electric charge is on a surface.
- In quantum mechanics, σ is used for Pauli matrices, which are mathematical tools used to describe particles.
- In astronomy, σ can represent velocity dispersion, which is how much the speeds of stars or galaxies vary within a group.
- In particle physics, Σ represents a group of particles called baryons.
Organizations and Brands
- In the 1930s, the big Σ was used as a symbol by a political party in Brazil called the Ação Integralista Brasileira.
- The Sigma Corporation, a company that makes camera lenses, uses the name "Sigma."
- Sigma Aldrich, a company that sells chemicals and lab equipment, uses both the name and the character in their logo.
See also
 In Spanish: Σ para niños
In Spanish: Σ para niños
- Antisigma
- Greek letters used in mathematics, science, and engineering
- Sampi
- Sho (letter)
- Stigma (letter)
- Sibilant consonant
- Summation (Σ)
- Combining form "sigm-" (e.g. sigmodon, sigmurethra, etc.)
- Derivative "sigmoid" (e.g. sigmoid sinus, sigmoid colon, sigmoidoscopy, etc.)
 | Tommie Smith |
 | Simone Manuel |
 | Shani Davis |
 | Simone Biles |
 | Alice Coachman |


