Treaty of St. Mary's (1818) facts for kids
| Signed | September–October, 1818 |
|---|---|
| Location | St. Marys, Ohio |
| Parties | |
| Language | English |

The Treaty of St. Mary's actually refers to six different agreements. These agreements were made in the fall of 1818. They were signed between the United States government and several Native American tribes in central Indiana. The main goal of these treaties was for the United States to buy land from the Native American tribes.
The six treaties were:
- Treaty with the Wyandot, etc.
- Treaty with the Wyandot
- Treaty with the Potawatomi
- Treaty with the Wea
- Treaty with the Delaware
- Treaty with the Miami
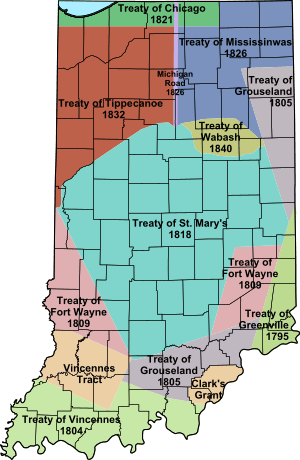
The most important of these was the treaty with the Miami tribe. They were the main Native American group in Indiana at the time. When people talk about "the Treaty of St. Mary's," they usually mean this one. These treaties helped the United States gain a large area of land in Indiana. This land was called the New Purchase. The tribes involved included the Miami, Delaware, and Potawatomi. In exchange for their land, the tribes received money, salt, sawmills, and other goods. These treaties also created special areas called reservations for the Native Americans. They continued a process of moving Native American tribes from their lands. This process had started with the Treaty of Greenville in 1795.
Understanding the Treaties
In the fall of 1818, six separate treaties were signed. They took place in St. Marys, Ohio. The United States signed agreements with several tribes. These included the Wyandot, Seneca, Shawnese, Ottawas, Potawatomi, Wea, Delaware, and Miami. Each treaty had specific terms.
The treaty with the Wyandot on September 20, 1818, involved two small land areas. These were in Wayne County, Michigan Territory. They contained the villages of Maguaga and Brownstown. Today, these are in Riverview and Flat Rock, Michigan. In return, the Wyandot received land in Huron Charter Township, Michigan.
The treaty with the Wea on October 2 meant the Wea gave up their claims. They gave up all their land in Ohio, Indiana, and Illinois.
The most important agreement was the treaty with the Miami. It was signed on October 6, 1818. Representatives from the United States and the Miami tribe signed it. Jonathan Jennings, Lewis Cass, and Benjamin Parke signed for the United States. This agreement had seven main parts.
Based on this treaty, the Miami tribe gave up land south of the Wabash River. This was a large part of central Indiana. It became known as the "New Purchase." This area covered all the land between the Wabash River and an older boundary. That older boundary was set by the Treaty of Fort Wayne (1809). The treaty also created the first Native American reservation in Indiana. This was the Great Miami Reserve. It was in the northern part of the New Purchase.
The United States also agreed to pay the Miami tribe. They would receive fifteen thousand dollars every year forever. The United States also promised to build a gristmill (for grinding grain) and a sawmill (for cutting wood). They would also provide a blacksmith and a gunsmith. The Miami would also get farming tools and one hundred sixty bushels of salt each year.
The New Purchase Area
The New Purchase was a large, unevenly shaped area. It made up most of the middle part of Indiana. It had a large "bite" taken out of its northern edge. This "bite" became the Great Miami Reserve. There was also a jagged part in the northwest. This was where the Tippecanoe and Wabash Rivers met.
The treaties described the borders of this new land. The northern and western borders were the Wabash, Tippecanoe, and Vermillion rivers. The southwestern and southeastern borders followed lines from the Treaty of Fort Wayne (1809). The far southeastern and northeastern borders used lines from the Treaty of Grouseland (1805). Parts of the eastern and western borders were the state lines. The southern tip of this area reached central Jackson County. This is near Brownstown today.
The Big Miami Reserve
The treaty with the Miami tribe meant they gave up most of their land south of the Wabash River. However, they kept some individual plots. They also kept a large area in north central Indiana. This area was between the Eel River and the Salamonie River. It was called the Big Miami Reserve.
This Reserve was huge. It covered about 760,000 acres (3,075 square kilometers). It was the largest Native American reservation ever in Indiana. It included all of today's Howard County. It also included parts of seven nearby counties. These were Wabash, Miami, Cass, Clinton, Tipton, Madison, and Grant. When it was created, this area was mostly wild. There were no settlements between Terre Haute and Fort Wayne along the Wabash River.
However, this reservation did not last long. By 1840, through more treaties, Indiana gained control of the reservation. The Native Americans living there were moved to areas west of the Mississippi River.
What Happened Next
These treaties changed things a lot. The Miami tribe was limited to their reserve area. The Delaware tribe, who had lived in central and east central Indiana, were moved west of the Mississippi River by 1820. This cleared the way for new settlers. These settlers moved north and west from places like Cincinnati and other towns along the Ohio River.
The new land was first called the Delaware New Purchase. On January 2, 1820, it was divided. The northwest part became Wabash County. The southeast part became Delaware County. These counties were later changed. The areas then became known as the "Wabash New Purchase" and "Delaware New Purchase." In 1827, the Delaware New Purchase was renamed the "Adams New Purchase." Later, 35 new counties were created from this original land. The future capital of Indiana, Indianapolis, was founded in 1822. It was located roughly in the center of the New Purchase area.
 | Jewel Prestage |
 | Ella Baker |
 | Fannie Lou Hamer |