Age of the Earth facts for kids
The age of the Earth is about 4.5 billion years old. Figuring this out was a big challenge for scientists. For most of human history, people didn't know much about how old our planet was. Earth scientists in the 1900s finally solved this puzzle.
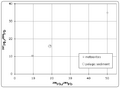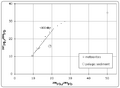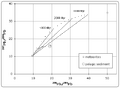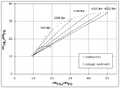
Today, we use special methods called radioactive dating to find the Earth's age. The oldest tiny minerals found on Earth are from Western Australia. These crystals are at least 4.4 billion years old. We also look at meteorites. The oldest solid pieces in meteorites formed when our Solar System began. These pieces are 4.567 billion years old. This gives us a good idea of how old the Solar System is, and it sets an upper limit for the age of Earth.
Contents
How We Figured Out Earth's Age
Orange labels: known ice ages.
Also see: Human timeline and Nature timeline
Early Ideas About Earth's Age
The first ideas about Earth's age came from the Ancient Greeks. A scientist named Eratosthenes (who lived from 276 to 194 BC) made a good guess about the Earth's size. He used math called trigonometry.
Later, a French diplomat and naturalist named Benoît de Maillet (1656–1738) tried to estimate Earth's age. He thought the Earth changed slowly over time due to natural forces. He studied geology and saw how land was worn away by erosion and how sediment built up in the sea. De Maillet believed the Earth was older than two billion years. He also understood what fossils really were and had early ideas about evolution.
The Big Debate in the 1800s
In the late 1800s, there was a big argument about the Earth's age. Charles Lyell wrote books showing that the Earth changed very slowly. This idea, called uniformitarianism, meant the Earth had to be very ancient.
His friend Charles Darwin agreed. Darwin believed that if evolution happened, it would need a very long time. Also, there's a huge amount of sedimentary rock between the oldest fossils and today's land. Darwin and Lyell thought it would take ages for so much rock to form.
However, a physicist named William Thomson (Lord Kelvin) disagreed. He calculated how long it would take for the Earth to cool down from a very hot beginning. In 1862, he estimated the Earth was between 20 and 400 million years old. Later, he changed his estimate to 20 to 40 million years. This was not enough time for Darwin's idea of evolution to happen.
Many scientists, like Thomas Henry Huxley, thought Kelvin's math was good, but his starting ideas were wrong.
The Sticky Inside of Earth
Near the end of the 1800s, someone realized something important. If the mantle (the layer under the crust) was like a very thick, sticky fluid, it would change Kelvin's calculations a lot. In 1895, John Perry, who used to work with Kelvin, suggested the Earth could be 2 to 3 billion years old. He thought the heat inside the Earth moved around much better than Kelvin believed.
Kelvin thought heat only moved slowly through solid rock. But if the inside of the Earth was moving (like convection in boiling water), it would bring a lot more heat to the surface. This would mean the Earth could be much, much older than Kelvin thought.
Today, we know that this idea of a sticky, moving fluid inside the Earth is very important. It's even more important than the discovery of radioactivity for understanding why Kelvin's age estimate was too low.
The 1900s and Modern Estimates
In 1896, Henri Becquerel discovered radioactivity. This was a huge step! Scientists soon realized that radioactivity was a major source of heat inside the Earth.
In 1921, the first modern estimate of Earth's age was made using radiometric dating. This method looks at how uranium slowly changes into lead in the Earth's crust. Henry Norris Russell estimated the Earth was between 2 and 8 billion years old.
By 1949, H.E. Suess used many different radioactive elements to estimate the age at 4 to 5 billion years. This is very close to what we believe today: about 4.56 billion years.
Modern calculations combine the idea of a sticky, moving fluid inside the Earth (from John Perry) with the heat from radioactivity. Later, the discovery of plate tectonics confirmed that the lower mantle is indeed a viscous fluid.
Our Solar System's Age
Scientists believe our whole Solar System started forming about 4.568 billion years ago. This happened when a giant cloud of gas and dust collapsed due to gravity. So, the Earth and the rest of the Solar System basically formed at the same time.
Different Views on Earth's Age
Most scientists use the scientific method to figure out the Earth's age. Some religions, like Hinduism, have ideas about Earth's age that are quite close to the scientific estimate.
Some Christians and Jews believe the Genesis creation narrative (the story of creation in the Bible) is literally true. This would mean the Earth was created between 5,000 and 10,000 years ago. They believe the methods used to calculate age might not have been the same throughout Earth's history. However, today, most people think that scientific methods are the best way to answer questions about the Earth's age.
Related pages
Images for kids
-
The Blue Marble, Earth as seen in 1972 from Apollo 17
-
Ernest Rutherford in 1908
See also
 In Spanish: Edad de la Tierra para niños
In Spanish: Edad de la Tierra para niños