Curitiba facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Curitiba
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|
|
Municipality
|
|||
| Município de Curitiba Municipality of Curitiba |
|||
|
Panoramic view of the city.
Tanguá Park
Barigui Park
24 Hour Street
Paço da Liberdade
Avenida Palace at 15 November Street
Oscar Niemeyer Museum
|
|||
|
|||
| Nickname(s):
Cidade Modelo ("Model City"); Capital Ecológica do Brasil ("Ecological Capital of Brazil"); Cidade Verde ("Green City"); Capital das Araucárias ("Capital of Araucarias"); A Cidade da Névoa Eterna ("The City of Eternal Fog")
|
|||
| Motto(s):
A Cidade da Gente (Our City; The People's City)
|
|||
 |
|||
| Country | |||
| Region | South | ||
| State | |||
| Founded | 29 March 1693 | ||
| Incorporated | 1842 | ||
| Area | |||
| • Municipality | 430.9 km2 (166.4 sq mi) | ||
| • Urban | 319.4 km2 (123.3 sq mi) | ||
| • Metro | 15,416.9 km2 (5,952 sq mi) | ||
| Elevation | 934.6 m (3,066.3 ft) | ||
| Population
(2021)
|
|||
| • Municipality | 1,963,726 (8th) | ||
| • Density | 4,062/km2 (10,523/sq mi) | ||
| • Metro | 3,731,769 (9th) | ||
| • Metro density | 210.9/km2 (546.2/sq mi) | ||
| Demonym(s) | in Portuguese: Curitibana/e/o | ||
| Time zone | UTC-3 (UTC-3) | ||
| Postal code |
80000-000 to 82999-999
|
||
| Area code | +55 (41) | ||
| HDI (2010) | 0.823 – very high | ||
| Major airport | Afonso Pena International Airport | ||
| Federal Highways | |||
Curitiba is a large city in the southern part of Brazil. It is the capital of the state of Paraná. In 2021, about 1.9 million people lived in Curitiba. This makes it the eighth most populated city in Brazil.
The city is located on a high flat area, about 932 meters (3,058 feet) above sea level. It is an important center for culture, politics, and business in Latin America. Curitiba is also home to the Federal University of Paraná, which started in 1912.
In the 1800s, Curitiba grew because it was a good place for trading cattle. Later, from 1850 to 1950, it expanded due to logging and farming. Many European immigrants came to Curitiba, especially from Germany, Italy, Poland, and Ukraine. They helped the city grow and added to its diverse culture.
After the 1960s, Curitiba grew even more thanks to smart urban planning. This helped the city's population increase from hundreds of thousands to over a million people. Curitiba's economy is strong, based on industries and services. It is the fourth largest economy in Brazil. Many people from other parts of Brazil have moved here.
Curitiba is known for its high Human Development Index, which means people generally have a good quality of life. In 2010, it won the Global Sustainable City Award for its excellent urban development. It is also considered one of the safest cities in Brazil for young people. Curitiba hosted games for the 1950 FIFA World Cup and the 2014 FIFA World Cup.
Contents
- What does the name Curitiba mean?
- How did Curitiba grow over time?
- What is Curitiba's geography like?
- How is Curitiba governed?
- Who lives in Curitiba?
- What is Curitiba's economy like?
- What are some fun places to visit in Curitiba?
- What about education in Curitiba?
- How is Curitiba planned?
- How do people get around in Curitiba?
- What sports are popular in Curitiba?
- What are Curitiba's neighborhoods like?
- Does Curitiba have international connections?
- Who are some famous people from Curitiba?
- Images for kids
- See also
What does the name Curitiba mean?
The name Curitiba might come from the Tupi words kurí tyba. This means 'many araucária seeds'. This is because there were many Paraná pines in the area.
Another idea is that it comes from kurit (pine tree) and yba (large amount).
When the Portuguese founded a settlement here in 1693, they called it Vila da Nossa Senhora da Luz dos Pinhais. This means 'Village of Our Lady of the Light of the Pines'.
The name changed to Curitiba in 1721. In 1812, it officially became a town, spelled Curityba. In 1919, the spelling was officially set as Curitiba.
How did Curitiba grow over time?
In the late 1600s, people in Curitiba mainly farmed for their own food. They also mined for minerals. After 1850, many European immigrants arrived. These included people from Poland, Italy, Germany, and Ukraine.
Cattle traders used Curitiba as an important stop. They moved their herds from Rio Grande do Sul to São Paulo.
The Paranaguá–Curitiba railroad opened in 1885. This helped the city connect with other places.
Around the early 1900s, Curitiba became wealthy from yerba mate production. The rich owners built grand houses, many of which are still standing today.
In the 1940s and 1950s, architect Alfred Agache helped create the city's first plan. It focused on wide streets, public areas downtown, and an industrial zone.
What is Curitiba's geography like?
Curitiba is located in southern Brazil, in the state of Paraná. It is part of the Brazilian Highlands, about 930 meters (3,050 feet) above sea level.
What is the climate in Curitiba?
Curitiba has a humid subtropical highland climate. This means it gets a lot of rain all year. Summers are warm but not too hot. Winters are mild because the city is not too far from the equator.
Temperatures can drop below 0°C (32°F) on the coldest winter days. But usually, winter daytime temperatures are around 19°C (66°F). In summer, the average daytime temperature is about 25°C (77°F). Snowfall is rare but has happened a few times in history.
Cold fronts often come from Antarctica and Argentina. They bring tropical storms in summer and cold winds in winter.
What kind of plants grow in Curitiba?
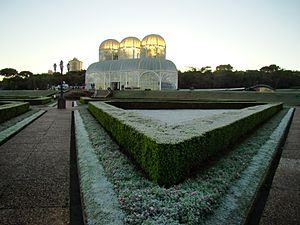
Curitiba is in an area with a special type of forest called the Ombrophilous Mixed Forest. This forest has many Paraná pines. These trees are protected from logging.
The city has a botanical garden and greenhouses that grow many native and exotic plants. Curitiba also has many purple and yellow ipês (flowering trees) that bloom in late winter. The yellow ipê is a very common tree in the city.
What are the rivers and water systems like?
Curitiba has many rivers and streams. The main rivers are the Atuba, Belém, Barigüi, Passaúna, Ribeirão dos Padilhas, and the Iguaçu River.
Since the 1970s, Curitiba has built parks with artificial lakes along its rivers. These lakes help to absorb and hold water, which reduces flooding. The city also has programs for environmental education and monitoring to protect its rivers.
What is the land like in Curitiba?
Curitiba covers about 432 square kilometers (167 square miles). It has gentle, rounded hills. The city's average height is about 934.6 meters (3,066 feet) above sea level.
Mountains and rocky hills surround parts of the city. This includes the Serra do Mar, a mountain range between the Atlantic Ocean and the plateau where Curitiba sits.
How is Curitiba governed?
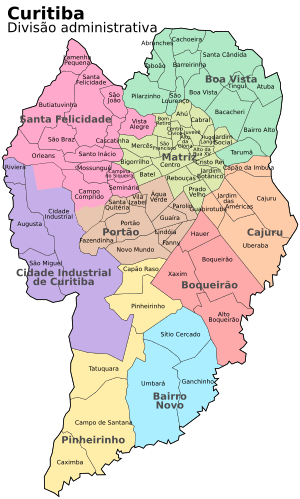
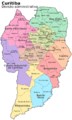
As of 2017, the mayor of Curitiba is Rafael Greca. The City Council has 38 members. Curitiba is divided into nine regional governments, which manage its 75 districts.
The Rua da Cidadania ("Street of Citizenship") is a special place. It offers many public services in one spot, often near bus terminals. This makes it easy for people to access services.
Jaime Lerner was a very famous mayor of Curitiba. He was mayor three times, starting in the 1970s. He helped make big changes to the city. For example, he encouraged building parks instead of canals to prevent floods. He also made the downtown area friendly for walking and created a special bus system.
Who lives in Curitiba?
Most people in Curitiba have European backgrounds. The first Europeans were Portuguese, who arrived in the 1600s. They mixed with native people and African slaves.
Later, in the 1800s, many immigrants came from Europe. The first non-Portuguese immigrants were Germans.
Curitiba has the largest group of Polish immigrants in Brazil. The Memorial of Polish Immigration was opened in 1980. It has wooden houses that show how Polish immigrants lived.
Italian immigrants started arriving in Curitiba in 1878. Many settled in the Santa Felicidade neighborhood, which is still a center for the Italian community.
Nearly 20,000 Ukrainian immigrants came between 1895 and 1897. Most were farmers. Paraná state has the largest Ukrainian community in Brazil.
Curitiba also has a Jewish community that started in the 1870s. Some German Jewish academics moved to Curitiba in the 1930s.
Japanese immigrants began arriving in 1915. Curitiba has the second largest Japanese community in Brazil, after São Paulo.
What are the main religions in Curitiba?
Most people in Curitiba are Roman Catholic (about 62%). Other large religious groups include Protestants (about 24%) and Spiritists (about 2.8%). About 6.7% of people do not have a religion.
What is Curitiba's economy like?
Curitiba has been a capital city since 1853. It has used smart urban planning to manage its growth. This has made it a global example for transportation and environmental solutions.
The city is Brazil's second largest car manufacturer. Its economy relies on industry, trade, and services. Many investors see Curitiba as a great place to invest in Brazil.
More than two million tourists visit Curitiba each year. Most arrive at the Afonso Pena International Airport.
Curitiba's industrial area, Cidade Industrial de Curitiba, is home to many international companies like Nissan, Renault, Volkswagen, and Volvo. It also has well-known Brazilian companies.
The city's public transport system is very efficient. This makes it easy for people to use buses instead of cars. Curitiba uses about 30% less fuel per person compared to other similar Brazilian cities. This helps keep the air cleaner.
Curitiba's economy has grown quickly. Its income per person is 66% higher than the Brazilian average. The city offers good health, education, and daycare services. It also has "Citizenship Streets" where people can find public services, sports, and cultural facilities.
There are seven large shopping malls in Curitiba. The Rua das Flores (Street of Flowers) is a pedestrian-only area with many shops. The Feira do Largo da Ordem is a popular street fair.
In 2008, Curitiba was the fourth richest city in Brazil. It is also known as a center for new technology and innovation.
What are some fun places to visit in Curitiba?
Curitiba has many interesting attractions:
- Shrine of the Divine Mercy: A peaceful place established by the Marian Fathers.
- Municipal Market: A market with many shops selling imported goods, organic products, and vegan food. It has a great food court with Asian and organic meals.
- Italian Woods: A place for local celebrations.
- Wire Opera House: A unique theater built in an old quarry.
- Oscar Niemeyer Museum: A museum showing art from Paraná and other Brazilian artists. It has rooms just for photography.
- Panoramic Tower: A 360-foot tall tower with amazing views of Curitiba. It also has a telephone museum.
- Portugal Wood: A park that honors the connection between Brazil and Portugal. It has a path with poems written on tiles and a tribute to Portuguese explorers.
- Curitiba International Ecological Marathon: A challenging marathon held in November.
- Tourism Line: A special bus that stops at all the main tourist spots in the city.
- Capão da Imbuia Wood
What about education in Curitiba?

Paraná state has over 183 universities. Curitiba has several important ones:
- Universidade Federal do Paraná (UFPR): The first university in Brazil, with over 35,000 students.
- Universidade Tecnológica Federal do Paraná (UTFPR): The first technology university in Brazil.
- Pontifícia Universidade Católica do Paraná (PUCPR): A major private university.
In the 1990s, the city started a project called Faróis do Saber ("Lighthouses of Knowledge"). These are free learning centers with libraries, free internet, and cultural resources. They work with schools and offer about 5,000 books.
Curitiba has the highest literacy rate among Brazilian capitals. It also ranks number one in education among Brazilian capitals.
How is Curitiba planned?
Curitiba is famous for its smart urban planning. It has a special transportation system with dedicated lanes for its bus rapid transit (BRT) system. These buses are very long and stop at special elevated stations. They charge one price no matter how far you travel.
The city also protects its green areas. It has about 51.5 square meters (554 square feet) of green space per person.
In the 1960s, architect Jaime Lerner led a team that created the Curitiba Master Plan. This plan aimed to control city growth, reduce traffic downtown, protect historic areas, and create good public transport.
The plan was adopted in 1968. Lerner even closed XV de Novembro St. to cars, making it a pedestrian-only area. The city also created a "Trinary Road System" to manage traffic. This system uses one-way streets around a central lane for express buses.
In areas prone to floods, old buildings were removed, and the land was turned into parks. Today, Curitiba is seen as one of the best examples of urban planning in the world.
In 1996, Curitiba was called "the most innovative city in the country" at a global summit. UNESCO has even suggested Curitiba as a model for rebuilding cities.
The city has over 400 square kilometers (154 square miles) of public parks and forests. In 2007, Grist magazine listed Curitiba as one of the top "Green Cities" in the world. Because of this, most people in Curitiba are happy with their city.
Jaime Lerner also talks about "urban acupuncture." This means making small, quick changes in specific city areas to create big positive effects.
How do people get around in Curitiba?
Curitiba's public transport uses only buses. It was one of the first cities in the world to use a bus rapid transit (BRT) system, starting in 1974. This system has made many people choose buses over cars.
About 28% of BRT riders used to travel by car. Curitiba uses about 30% less fuel per person than other similar Brazilian cities. This helps keep air pollution low.
About 1,100 buses make 12,500 trips daily, serving over 1.3 million passengers. Curitibans spend only about 10% of their income on transportation, which is much lower than the national average.
Curitiba has the world's largest bi-articulated bus. It is 28 meters (92 feet) long and can carry 250 passengers. This bus runs on soy-based biofuel, which cuts pollution by 50%.
The city government has been planning to build an underground metro system for years.
What are the roads like?
Driving in the city center can be tricky due to many one-way streets and traffic. However, the Trinary Road System helps drivers get to the city center quickly. Most avenues are wide and well-organized.
What about air travel?
Afonso Pena International Airport is Curitiba's main airport. It is in the nearby city of São José dos Pinhais. This airport handles all commercial flights. It has been rated as the best airport in Brazil.
There is also the Bacacheri Airport, which is smaller and used for private and business planes.
Are there trains?
Brazil's railway company, Rumo, has its main office in Curitiba. Serra Verde Express offers a tourist train ride through beautiful scenery to Morretes and Paranaguá.
Other ways to get around
Curitiba has 100 kilometers (62 miles) of bike paths. About 30,000 bikers use them every day. The city also has many orange taxis.
What sports are popular in Curitiba?
Curitiba has three main football teams: Athletico Paranaense, Coritiba, and Paraná Clube.
- Club Athletico Paranaense plays at Estádio Joaquim Américo Guimarães.
- Coritiba plays at Estádio Major Antônio Couto Pereira.
- Paraná Clube plays at Estádio Durival Britto e Silva.
Both Coritiba and Athletico Paranaense have won Brazil's top football league. The Estádio Joaquim Américo Guimarães hosted games for the 2014 FIFA World Cup. The traditional stadium Vila Capanema hosted games for the 1950 FIFA World Cup.
The Autódromo Internacional de Curitiba (Curitiba International Raceway) is nearby.
Curitiba also has a strong rugby union club, Curitiba Rugby Clube.
Many top mixed martial arts (MMA) fighters are from Curitiba. These include the Rua brothers, Wanderlei Silva, Anderson Silva, and Cris Cyborg. The city is known for its influential Chute Boxe Academy, which trained many of these fighters.
What are Curitiba's neighborhoods like?
Most of Curitiba's districts started as colonial settlements. They were formed by European immigrant families in the late 1800s. The centro (downtown) is the busiest area. It has most of the city's financial buildings.
Curitiba is divided into 75 neighborhoods, managed by 9 regional governments. These neighborhoods do not have their own administrative powers, but local groups work to improve their communities.
The Civic Center (Centro Cívico) is where the main government buildings are located. It was planned in 1953. This area includes important buildings like the Iguaçu Palace and the Oscar Niemeyer Museum.
Does Curitiba have international connections?
Curitiba is connected to many cities around the world through "twin city" agreements. These connections help promote cultural exchange and cooperation.
Twin towns – sister cities
Curitiba is twinned with:
- Asunción, Paraguay
- Coimbra, Portugal
- Columbus, United States
- Guadalajara, Mexico
- Hangzhou, China
- Himeji, Japan
- Jacksonville, United States
- Kraków, Poland
- Lyon, France
- Montevideo, Uruguay
- Orlando, United States
- Santa Cruz de la Sierra, Bolivia
- Suwon, South Korea
- Treviso, Italy
- Miami-Dade, United States
Cooperation agreements
Curitiba also has cooperation agreements with:
- Lisbon, Portugal
Who are some famous people from Curitiba?

Science and Math
- Newton da Costa – a famous mathematician
- César Lattes – a physicist
Sports
- Maurício "Shogun" Rua – a mixed martial arts fighter
- Wanderlei Silva – a mixed martial arts fighter
- Anderson Silva – a mixed martial arts fighter
- Cristiane "Cyborg" Justino – a mixed martial arts fighter
- Raul Boesel – a Formula One and IndyCar driver
- Ricardo Zonta – a Formula One driver
- Emanuel Rego – an Olympic medalist in beach volleyball
Arts and Entertainment
- Alfredo Andersen – a Norwegian painter and sculptor
- Dalton Trevisan – a writer
- Isabeli Fontana – a supermodel
- Marjorie Estiano – an actress and singer
- Ary Fontoura – a Brazilian actor
Images for kids
-
Frost in Curitiba
-
Federal University of Paraná was the first university opened in Brazil.
-
Landscape with Canoe on the Margin (1922). Painting by Alfredo Andersen (São Paulo Museum of Art, São Paulo).
See also
 In Spanish: Curitiba para niños
In Spanish: Curitiba para niños
- History of Paraná
- Luxembourgish Brazilians