Faroe Islands facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Faroe Islands
Føroyar
Færøerne |
|
|---|---|
|
Motto: Vivre Libre ou Mourir ("Live free or die")
|
|
|
Anthem: Tú alfagra land mítt
Thou, my most beauteous land |
|
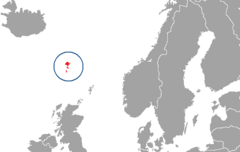
Location of the Faroe Islands in Northern Europe
|
|
| Capital and largest city
|
Tórshavn 62°00′N 06°47′W / 62.000°N 6.783°W |
| Official languages | Faroese, Danish |
| Ethnic groups | 91% Faroese 5.8% Danish 0.7% British 0.4% Icelandic 0.2% Norwegian 0.2% Poles |
| Demonym(s) | Faroese |
| Government | Parliamentary democracy within a constitutional monarchy |
|
• Queen
|
Margrethe II |
|
• High Commissioner
|
Dan M. Knudsen |
| Aksel V. Johannesen | |
| Autonomy
within the Kingdom of Denmark
|
|
| 1035 | |
| 14 January 1814 | |
|
• Home rule
|
1 April 1948 |
| Area | |
|
• Total
|
1,399 km2 (540 sq mi) (180th) |
|
• Water (%)
|
0.5 |
| Population | |
|
• July 2017 estimate
|
50,730 (211th) |
|
• 2011 census
|
48,346 |
|
• Density
|
35/km2 (90.6/sq mi) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2008 estimate |
|
• Total
|
$1.642 billion |
|
• Per capita
|
$33,700 |
| GDP (nominal) | 2008 estimate |
|
• Total
|
$2.45 billion |
|
• Per capita
|
$50,300 |
| HDI (2006) | 0.943 very high |
| Currency | Faroese króna (DKK) |
| Time zone | UTC+0 (WET) |
|
• Summer (DST)
|
UTC+1 (WEST) |
| Calling code | 298 |
| ISO 3166 code | FO |
| Internet TLD | .fo |
|
a. Danish monarchy reached the Faeroes in 1380 with the reign of Olav IV in Norway.
b. The Faeroes, Greenland and Iceland were formally Norwegian possessions until 1814 despite 400 years of Danish monarchy beforehand. |
|
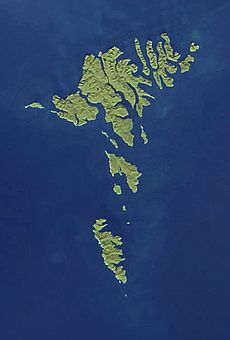
The Faroe Islands, also called Føroyar (meaning "Sheep Islands"), are a group of eighteen islands. They are located in the north Atlantic Ocean, between Scotland, Norway, and Iceland.
The Faroe Islands are part of the Kingdom of Denmark. However, they have had their own local government since 1948. This means the Faroese government controls most matters, except for military defense. People in the Faroe Islands have been able to trade with other countries since 1856. The islands share similarities with Iceland, Shetland, the Orkney Islands, the Outer Hebrides, and Greenland. The Faroe Islands became separate from Norway in 1815. They also have their own representatives in the Nordic Council.
Contents
Exploring the Faroe Islands: Regions and Towns
The Faroe Islands are divided into 34 local areas called municipalities. Within these municipalities, there are about 120 cities and villages. Historically, the islands also have six larger areas known as sýslur (regions). These regions include Norðoyar, Eysturoy, Streymoy, Vágar, Sandoy, and Suðuroy.
Geography: The Islands' Landscape
The Faroe Islands are a group of eighteen islands located off the coast of Northern Europe. They lie between the Norwegian Sea and the north Atlantic Ocean. The total area of the islands is 1,399 square kilometres (540 sq. mi). There are no large lakes or rivers on the islands. The coastline stretches for 1,117 kilometres (694 mi). The Faroe Islands do not share any land boundaries with other countries. Only one island, Lítla Dímun, has no people living on it.
How Far Are the Faroe Islands From Other Places?
- Sula Sgeir (uninhabited, Scotland): 240 km (149 mi)
- Shetland (Scotland): 280 km (174 mi)
- Scotland (British Mainland): 310 km (193 mi)
- Iceland: 450 km (280 miles)
- Norway: 675 km (419 miles)
- Ireland: 678 km (421 miles)
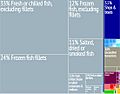
Economy: How the Islands Make Money
Fishing, raising sheep, and tourism are very important to the economy of the Faroe Islands. Around 1990, the economy faced some challenges. However, unemployment decreased in the late 1990s. By June 2008, unemployment was very low, at 1.1%. It rose slightly to 3.4% in early 2009.
Since fishing is so vital, problems with fishing can affect the entire economy. Since 2000, new businesses have started in the Faroe Islands. These projects aim to attract new investments. For example, a Burger King opened in Tórshavn, which was a big event. Moving around the islands is easy because bridges and tunnels connect 80% of the population.
Culture: Life and Traditions
Ólavsøka: The National Holiday
The national holiday of the Faroe Islands is called Ólavsøka. It is celebrated on July 29th. This day remembers the death of Saint Olaf. The main celebrations take place in Tórshavn. They begin on the evening of July 28th and continue until July 31st.
The official part of the celebration starts on July 29th. This is when the Faroese Parliament opens. During the day, there is a parade with many people from the churches across the islands.
The Nordic House: A Cultural Hub
The Nordic House in the Faroe Islands (Faroese: Norðurlandahúsið) is a key cultural place in the Faroes. It helps promote Nordic and Faroese culture. This happens both locally and in the wider Nordic region. A director manages the House, and this person changes every four years.
Music: Artists and Festivals
The Faroe Islands are home to many talented artists and musicians. Some of the most well-known musicians include:
- Eivør (Eivør Pálsdóttir)
- Lena (Lena Andersen)
- Teitur (Teitur Lassen)
- Høgni Lisberg
- Brandur Enni
Popular bands from the islands include:
- Týr
- Gestir
- 200
- Clickhaze
The islands also host music festivals where international musicians perform. These festivals are:
- Summartónar, held every summer.
- G! Festival in Gøta in July.
- Summarfestivalurin in Klaksvík in August.
Food: Traditional Dishes
Traditional Faroese food mostly uses meat and potatoes. It includes very few fresh vegetables. Lamb is a very important meat on the islands. It is the main ingredient in many dishes. Other typical foods from the islands include fresh fish, blubber, whale, seabirds, and Faroese puffins and their eggs.
Climate: Weather in the Islands
The climate in the Faroe Islands is known as Maritime Subarctic. This means summers are not very hot, and winters are cold. It is common to have fog or strong winds. These weather conditions can sometimes cause problems for air travel.
Animals and Vegetation: Nature in the Faroe Islands
Many types of birds visit the islands at different times of the year. These include the Eider, Starling, Wren, Guillemot, and Black Guillemot. Today, only a few types of wild land seals live in the Faroe Islands. These are the Grey Seals. Sometimes, visitors can see whales in the waters near the islands.
Grey Seals are very common around the Faroese shores. The natural plants of the Faroe Islands are similar to those found in the Scottish islands or Ireland. The vegetation mostly consists of wild flowers, grasses, moss, and lichen.
Images for kids
-
Ruins of the Cathedral of St. Magnus of Orkney
-
Marsh marigold (Caltha palustris) is common in the Faroe Islands during May and June.
-
Atlantic puffins are very common and a part of the local cuisine: Faroese puffin.
-
Rasmus Rasmussen, the writer who wrote the first novel in the Faroese language (poetical name: Regin í Líð) and Símun av Skarði, the poet who wrote the Faroese national hymn
-
Truck delivering chocolate in the Faroe Islands
See also
 In Spanish: Islas Feroe para niños
In Spanish: Islas Feroe para niños
 | Delilah Pierce |
 | Gordon Parks |
 | Augusta Savage |
 | Charles Ethan Porter |