Geography of Australia facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Geography of Australia |
|
|---|---|
 |
|
| Continent | Oceania (continent) |
| Region | Oceania |
| Coordinates | 27°00′00″S 144°00′00″E / 27.000°S 144.000°E |
| Area | Ranked 6th |
| • Total | 7,688,287 km2 (2,968,464 sq mi) |
| • Land | 98.21% |
| • Water | 1.79% |
| Coastline | 59,681 km (37,084 mi) |
| Borders | None |
| Highest point | Mount Kosciuszko 2,228 m (7,310 ft) |
| Lowest point | Lake Eyre, −15 m (−49 ft) |
| Longest river | Murray River, 2,375 km (1,476 mi) |
| Largest lake | Lake Eyre 9,500 km2 (3,668 sq mi) |
| Climate | Mostly desert or semi-arid, south-east and south-west corners: temperate, north: tropical climate, varied between tropical rainforests, grasslands, part desert, mountainous areas: subantarctic tundra |
| Terrain | Mostly low plateau with deserts, rangelands and a fertile plain in the southeast; mountain ranges in the east and south-east. |
| Natural Resources | Minerals, coal, and timber |
| Natural Hazards | Cyclones along the northern coasts, severe thunderstorms, droughts, occasional floods, heat waves, and frequent bushfires |
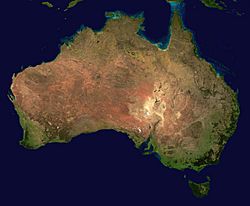
Australia is a huge country located in Oceania. It's known for its amazing and varied landscapes. Even though it's the world's smallest continent, Australia is the sixth-largest country by land area.
Most people in Australia live along the eastern and southeastern coasts. The country has everything from snowy mountains in the Australian Alps to vast deserts, thick forests, and grassy plains.
Australia shares its neighborhood with several countries. To the north are Indonesia, East Timor, and Papua New Guinea. To the east, you'll find the Solomon Islands, Vanuatu, and New Caledonia. New Zealand is located to the southeast.
Contents
Australia's Physical Features
Australia is both a country and a large island in Oceania. It sits between the Indian Ocean and the South Pacific Ocean. Its official name is the Commonwealth of Australia. The country includes the entire continent and many smaller islands around it.
This makes Australia the sixth-largest country in the world. Its total area is about 7,686,850 square kilometers. This is a bit smaller than the 48 states of the United States put together.
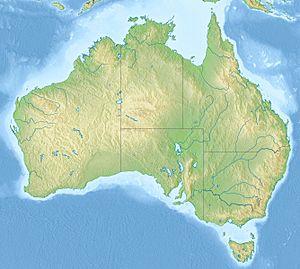
The Australian mainland has a very long coastline, stretching about 35,821 kilometers. If you add the coastlines of all its islands, it's even longer! Australia also has a huge "exclusive economic zone" in the ocean. This means it has special rights to explore and use the ocean resources in this area.
Australia doesn't share any land borders with other countries. The northernmost parts of the mainland are the Cape York Peninsula and the Top End. However, the country's most northern point is actually in the Torres Strait Islands.
Main Landform Regions
Australia can be divided into three main landform regions:
The Western Plateau
The western half of Australia is called the Western Plateau. It's mostly a flat area, but it has some mountain ranges like the Hamersley Range. There isn't much surface water here, but some larger rivers flow in the west and north.
The Eastern Highlands
Also known as the Great Dividing Range, these highlands are near Australia's eastern coast. They separate the narrow coastal plains from the rest of the continent. This area gets the most rain and has a wide variety of plants and animals. Most people in Australia live here.
The Central Lowlands
Between the Eastern Highlands and the Western Plateau are the Central Lowlands. This region includes the Great Artesian Basin, which is a huge underground water source. It also has Australia's largest river systems, like the Murray-Darling Basin.
Off the northeastern coast of Australia is the Great Barrier Reef. This is the world's largest coral reef system. The large, mountainous island of Tasmania is south of the mainland. It gets a lot of rain and has very fertile soil.
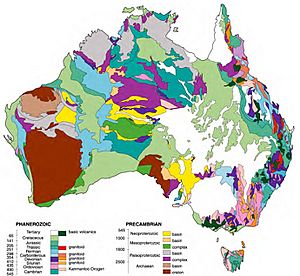
Australia's Geology
Australia is the lowest, flattest, and oldest continent on Earth. Its geological history has been quite stable. Big geological events, like mountains forming and land plates crashing, mostly happened a long time ago. This was when Australia was part of a supercontinent called Gondwana.
Australia's highest point is Mount Kosciuszko, which is 2,228 meters tall. This is quite low compared to the highest mountains on other continents.
Because Australia sits in the middle of a tectonic plate, it doesn't have any active volcanoes today. Small earthquakes happen often, but they usually don't cause any damage. Bigger earthquakes happen about every five years.
The land is mostly a low plateau with deserts and grasslands. There's also a fertile plain in the southeast. The Great Barrier Reef, the world's largest coral reef, is just off the northeast coast.
Landform Divisions
The Australian continent can be divided into six different landform areas:
- The Eastern Highlands: This includes the Great Dividing Range and fertile grasslands.
- The Eastern Alluvial Plains and Lowlands: This area covers the Murray-Darling basin and parts of the Lake Eyre Basin.
- The South Australian Highlands: This includes the Flinders Range and the Eyre Peninsula.
- The Western Plateau: This vast area includes the Nullarbor Plain.
- The Central Deserts: These are the large desert areas in the middle of the continent.
- Northern Plateau and Basins: This includes the Top End region.
Water Systems in Australia
Much of Australia's interior is very dry. Because there's little rain and high temperatures, rivers in the middle of the country are often dry. Lakes are often empty too. However, some rivers start in tropical areas where summer rains cause them to flow strongly.
When floods happen, they change the dry environment a lot. The plants and animals in central Australia have learned to adapt to these cycles of wet and dry periods.
The Great Artesian Basin is a very important source of water. It's the world's largest and deepest underground water basin. Access to this water has allowed farming and grazing to happen in areas that were once too dry.
Cities and towns in Australia sometimes face water shortages. They might put rules in place to reduce how much water people use. A "billabong" is an Australian name for a small lake that forms when a winding river changes its course.
Human Geography
Australians have mostly settled in capital cities and their surrounding areas along the long coastline. People from many different backgrounds have moved to these places. Australia has one of the lowest population densities in the world, with about 3.3 people per square kilometer.
Sport is very important in Australia. More than 90% of adults are interested in sports. English is the most common language spoken. Many Australians own their own homes.
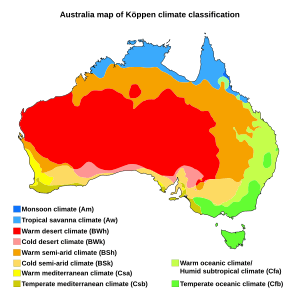
Australia's Climate
Most of Australia is either very dry (arid) or semi-dry. About 18% of the mainland is made up of named deserts. Other areas also have a desert climate due to low rainfall and high temperatures.
Only the southeastern and southwestern parts of Australia have a temperate climate with moderately fertile soil. The northern part of the continent has a tropical climate. This area includes tropical rainforests, grasslands, and some desert.
Rainfall in Australia can vary a lot. There are often droughts that last for several seasons. These droughts are thought to be partly caused by the El Niño-Southern Oscillation, a natural climate pattern. Sometimes, a huge dust storm can cover a region or even several states.
Rising levels of salt in the soil and the spread of deserts are harming the landscape in some areas. The "outback," which is the vast, dry interior of Australia, covers 70 percent of the continent.
Natural Hazards
Australia faces several natural hazards. These include cyclones along the northern coasts, severe thunderstorms, droughts, occasional floods, heat waves, and frequent bushfires.
Environment

Australia faces several environmental challenges. These include:
- Soil erosion: This happens because of too much grazing by animals, industrial growth, city development, and poor farming methods.
- Soil salinity: The salt levels in the soil are rising because of using poor quality water.
- Desertification: Deserts are spreading, partly because of animals like rabbits that were brought to Australia by European settlers.
- Introduced pest species: Animals and plants brought from other countries can harm native species.
- Habitat loss: Clearing land for farming threatens the homes of many unique Australian animals and plants.
- Great Barrier Reef: The world's largest coral reef is threatened by more shipping and tourism.
- Limited fresh water: Australia has limited natural fresh water resources.
Australia is part of many international agreements to protect the environment. These include treaties about the Antarctic, climate change, endangered species, and protecting the ozone layer.
See also
 In Spanish: Geografía de Australia para niños
In Spanish: Geografía de Australia para niños
Images for kids
-
Lake Hillier, a pink salt lake in Western Australia
-
Tropical forest, grassland, and mountains in Queensland
-
Mount Kosciuszko in the Australian Alps
-
Megalong Valley in the temperate Blue Mountains region
-
Arid parts of the Outback in Chambers Pillar, Northern Territory
 | Bessie Coleman |
 | Spann Watson |
 | Jill E. Brown |
 | Sherman W. White |