Australian Alps facts for kids
Quick facts for kids Australian AlpsAustralia |
|||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Mount Feathertop, Victoria
|
|||||||||||||||
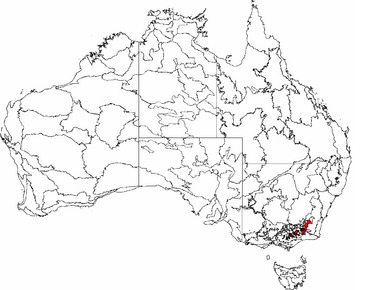
The interim Australian bioregions,
with the Australian Alps in red |
|||||||||||||||
| Area | 12,330 km2 (4,760.6 sq mi) | ||||||||||||||
| State electorate(s) |
|
||||||||||||||
| Federal Division(s) | |||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||
The Australian Alps are a big mountain range in southeast Australia. They are the highest mountains in Australia. They stretch across parts of eastern Victoria, southeastern New South Wales, and the Australian Capital Territory. These mountains are the only place in mainland Australia where peaks are higher than 2,000 meters. It's also the only area on the mainland where a lot of snow falls every year. The whole area is huge, covering about 1.2 million hectares.
The Australian Alps are part of the Great Dividing Range. This is a long chain of mountains and hills that runs for about 3,000 km. It goes from northern Queensland, through New South Wales, and into northern Victoria. This mountain chain acts like a natural wall. It separates rivers that flow east into the Pacific Ocean from those that flow west. The western rivers flow into the Murray–Darling Basin and then to the Southern Ocean. Some even flow into inland lakes like Lake Eyre, which are below sea level or dry up quickly.
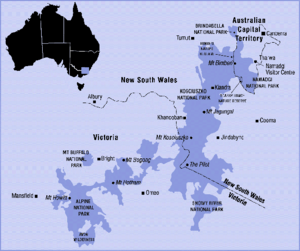
The Australian Alps have two main parts. These are the Snowy Mountains (including the Brindabella Range) in New South Wales and the Australian Capital Territory. The other part is the Victorian Alps in Victoria. People sometimes call the Victorian Alps the "High Country." This name is often used when talking about its history or culture.
Contents
How Were the Australian Alps Formed?
Unlike giant mountain ranges such as the Rockies (4,401 m high), the European Alps (4,808 m high), or the Himalayas (8,848 m high), the Australian Alps were not formed by two continental plates crashing together. When plates collide, they push up the Earth's rocky surface to create sharp, jagged peaks.
Instead, the Australian Alps are a high, wide plateau. They have softer, rolling hills. This plateau was lifted thousands of feet up. This happened because of magma moving underground. It occurred when the supercontinent Gondwana started to break apart about 130 to 160 million years ago. The highest peak in the Australian Alps is Mount Kosciuszko, which is 2,228 meters tall.
Most of the Australian Alps were formed about 100 million years ago. But over the last 90 million years, there have been smaller lifts of the land. Sometimes, basalt lava erupted from small volcanoes. This lava flowed across the land and into some valleys. It filled in low areas, creating the flat landscapes of these high plains.
About 2 million years ago, during the Pleistocene ice age, small glaciers formed. These were on the highest parts of the Australian Alps, especially near Mount Kosciuszko. Today, there are no glaciers left. But you can still see signs of them. There are many small lakes (called tarns) and bowl-shaped hollows (called cirques). Examples include Club Lake, Blue Lake, and Hedley Tarn.
Nature and Wildlife in the Alps
The Australian Alps are very important for protecting nature. They are also great for recreation like hiking and skiing. Plus, they are a key area for collecting water. Much of the water from the eastern slopes is sent into the Murray River and its branch, the Murrumbidgee River. This is done through a huge engineering project called the Snowy Mountains Scheme.
The natural environment of the Alps is protected by large national parks. These include the Kosciuszko National Park in New South Wales and the Alpine National Park in Victoria. These parks are managed together by the Australian government and the state governments.
The Australian Alps also have the only skiing areas on mainland Australia. The town of Cabramurra, New South Wales and the ski resorts are almost the only permanent settlements here. Some medium-sized towns are found in the valleys below the mountains. These include Jindabyne, New South Wales, Corryong, Victoria, and Mount Beauty.
The Australian Alps are not as high or steep as the European Alps, New Zealand's Southern Alps, or the Andes Mountains. Most of their peaks can be reached without special mountaineering gear.
Animals of the Alps
Hundreds of different animals live in the Australian Alps. These include about 40 types of mammals, 200 bird species, 30 reptile species, 15 amphibians, and 14 native fish species. There are also many different kinds of insects. Sadly, many non-native animals have also been brought to the Alps. These include rabbits, deer, mice, foxes, dogs, cats, horses, and pigs.
All these different animals, both native and introduced, need different things to survive. They need places to live, like rock outcrops and decaying logs. They also need plants for food and shelter. So, the type of land, soil, and temperature decide what kinds of plants grow there. This also affects where different animal groups live.
Birds of the Alps
BirdLife International has named the Australian Alps an Important Bird Area. This means it's a very important place for birds. The forests and woodlands in the mountains are home to many breeding flame robins and pilotbirds.
Insects of the Alps
The bogong moth travels very long distances each year. It flies to and from the Australian Alps. During summer, these moths gather in caves and other spots in the mountains. They do this to avoid the heat and because there isn't enough food for their young in the lowlands. The moth is a food source for many animals in the region. This includes the endangered mountain pygmy possum.
However, the moth can also carry arsenic. It picks up arsenic from its feeding sites in the lowlands. Then it carries it long distances into the mountains. This has led to arsenic building up in the environment and in animals in the mountain range.
Bushfires in the Alps
Australia has a mostly hot, dry climate. Because of this, bushfires in Australia happen often. This is especially true in the heavily forested areas of the Australian Alps. The Alps, particularly on the Victorian side (known as the Victorian Alps), often experience large bushfires. The area has been almost completely burned by fires many times. This happened notably during Black Thursday in 1851, Black Friday (1939), and in 2003 and 2006-07.
Some native plants in Australia have actually evolved to need bushfires to reproduce. Fire events are a natural and important part of Australia's environment. For example, in some eucalypt and banksia species, fire causes their seed pods to open. This allows the seeds to grow. Fire also helps new grassland plants to grow. Other species have adapted to recover quickly after a fire.
However, bushfires can cause huge damage to homes and native animals. This damage can sometimes be terrible. The 2003 Canberra bushfires badly affected almost 70% of the Australian Capital Territory's pastures, pine forests, and nature parks. After burning for a week through the Brindabella Ranges above Canberra, the fires entered the city's suburbs on January 18, 2003. Four people died, and over 500 homes were destroyed or badly damaged.
The Victorian Black Saturday bushfires were very strong in parts of the Victorian High Country. They destroyed several towns, including Kinglake and Marysville. These fires killed 173 people. This was Australia's highest-ever loss of life from a bushfire. Across the state, the fires burned over 400,000 hectares and destroyed 2,029 properties.
Mountain Huts
In the Australian Alps, there are about 120 active alpine huts. Most of these huts were built a long time ago. Some were for early cattlemen, others for early skiers, and some for research and surveying. Many of these huts are still used today by fly fishers (in season), hikers, and skiing groups all year round. Most huts are looked after by volunteers from groups like the Kosciuszko Huts Association and the local National Parks and Wildlife Service.
Some of the well-known huts include Moscow Villa Hut, Valentine Hut, Seaman's Hut, and Mawsons Hut. In recent years, some huts have been lost due to not being maintained or because of bushfires. For example, the Pretty Plain Hut and Mount Franklin Chalet were destroyed by the Canberra bushfires in 2003.
Things to See and Do
- The Australian Alps Walking Track is a long walking trail. It goes through the alpine areas of Victoria, New South Wales, and the ACT. It is 655 km long. It starts at Walhalla, Victoria and goes to Tharwa, ACT near Canberra.
|
|
|
Skiing in the Alps

The Australian Alps are the main place for skiing in Australia. You can ski here from June to October. New South Wales has Australia's highest snow country, its oldest ski fields, and its largest resort. People started recreational skiing in Australia around 1861 in Kiandra, New South Wales. Norwegian gold miners brought the idea to the snowy hills there. The first and longest-running ski club in the world, the Kiandra Snow Shoe Club, was likely formed in Kiandra that year.
Steeper slopes and more reliable snow are found further south. In the 20th century, skiing in New South Wales moved south. It moved to mountains in and around the Kosciuszko Main Range region. Here you'll find Australia's best vertical drop at Thredbo. Australia's biggest resort, Perisher, is also here. The State of Victoria has the most skiing areas in Australia.
Mount Bogong is 1,986 m above sea level. It is the highest peak in Victoria. The nearby Bogong High Plains is one of the biggest snow areas in Australia. It includes popular resorts like Falls Creek and Mount Hotham. People were skiing for fun and for travel in the Victorian Alps by the 1880s and 1890s. They used skis made from local wood and single steering poles. Skiing started at Mount Buffalo in the 1890s, and a chalet was built there in 1910. Australia's first ski tow was built near Mount Buffalo in 1936.
You can go Cross-country skiing in the ACT, New South Wales, and Victoria. But downhill skiing is only possible in New South Wales and Victoria.
|
|
Images for kids
-
Summer view of the Victorian Alps from Mount Hotham
See also
 In Spanish: Alpes Australianos para niños
In Spanish: Alpes Australianos para niños