Mankato, Minnesota facts for kids
Quick facts for kids
Mankato, Minnesota
|
||
|---|---|---|

North Riverfront Drive Commercial District
|
||
|
||
| Nickname(s):
Key City
|
||
| Motto(s):
Leading the way...
|
||
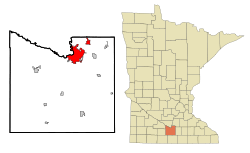
Location of Mankato in Blue Earth County,
|
||
| Country | United States | |
| State | Minnesota | |
| Counties | Blue Earth, Nicollet, Le Sueur | |
| Founded | February 1852 | |
| Incorporated | March 6, 1868 | |
| Government | ||
| • Type | City charter | |
| Area | ||
| • City | 20.229 sq mi (52.393 km2) | |
| • Land | 19.879 sq mi (51.487 km2) | |
| • Water | 0.350 sq mi (0.905 km2) | |
| Elevation | 1,007 ft (307 m) | |
| Population
(2020)
|
||
| • City | 44,488 | |
| • Estimate
(2023)
|
45,742 | |
| • Rank | US: 876th MN: 22nd |
|
| • Density | 2,299.39/sq mi (887.79/km2) | |
| • Urban | 60,206 (US: 453rd) | |
| • Metro | 104,248 (US: 352nd) | |
| Demonym(s) | Mankatoans | |
| Time zone | UTC−6 (Central (CST)) | |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−5 (CDT) | |
| ZIP Codes |
56001, 56002, 56003
|
|
| Area code(s) | 507 and 924 | |
| FIPS code | 27-39878 | |
| GNIS feature ID | 2395831 | |
| Sales tax | 7.875% | |
Mankato is a city in the state of Minnesota, USA. It is located where the Minnesota River meets the Blue Earth River. Mankato is the main city in the Mankato–North Mankato metropolitan area.
The city is the county seat of Blue Earth County, Minnesota. In 2020, about 44,488 people lived here. This makes it one of Minnesota's larger cities. Mankato is also home to Minnesota State University, which is the second-largest university in the state.
Contents
History of Mankato
Early Settlements
For a long time, different groups of indigenous peoples lived in this area. By the mid-1800s, the Dakota Sioux were the main group living here.
European Americans began settling in Mankato Township in February 1852. The city of Mankato was officially started on May 11, 1858. People like Henry Jackson helped organize the city.
There's a story that the city was supposed to be named Mahkato. But a mistake by a clerk led to the name Mankato. The Dakota people called the river Makato Osa Watapa, which means "the river where blue earth is gathered." This is why the river is now called the Blue Earth River.
Important Events
On December 26, 1862, a very sad event happened in Mankato. After the Dakota War of 1862, 38 Dakota people were executed. This was a difficult time in U.S. history. President Lincoln reviewed the cases and pardoned many others. Today, there are two statues in Mankato to remember this event. They are at the site of the hangings, which is now the Blue Earth County Library and Reconciliation Park.
By 1880, Mankato was the fourth-largest city in Minnesota. Its population was about 5,500 people.
Notable Visitors
Vice President Schuyler Colfax died in Mankato in 1885 while traveling.
Geography of Mankato
Mankato covers about 18.26 square miles (47.3 square kilometers). Most of this area is land, with a small part being water. The Minnesota River, Blue Earth River, and Le Sueur River all flow through or near the city.
Population and People
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1870 | 3,482 | — | |
| 1880 | 5,550 | 59.4% | |
| 1890 | 8,838 | 59.2% | |
| 1900 | 10,599 | 19.9% | |
| 1910 | 10,365 | −2.2% | |
| 1920 | 12,469 | 20.3% | |
| 1930 | 14,039 | 12.6% | |
| 1940 | 15,654 | 11.5% | |
| 1950 | 18,809 | 20.2% | |
| 1960 | 23,797 | 26.5% | |
| 1970 | 30,895 | 29.8% | |
| 1980 | 28,651 | −7.3% | |
| 1990 | 31,477 | 9.9% | |
| 2000 | 32,427 | 3.0% | |
| 2010 | 39,309 | 21.2% | |
| 2020 | 44,488 | 13.2% | |
| 2023 (est.) | 45,742 | 16.4% | |
| U.S. Decennial Census 2020 Census |
|||
In 2022, there were about 17,605 households in Mankato. The average household had 2.31 people. The city's median household income was $61,726. About 22.5% of the people in Mankato live below the poverty line.
Most people in Mankato have a high school diploma (93.6%). Many also have a bachelor's degree or higher (37.6%).
Population Details (2020)
| Race | Number | Percent |
|---|---|---|
| White (NH) | 34,381 | 77.3% |
| Black or African American (NH) | 3,652 | 8.2% |
| Native American (NH) | 162 | 0.4% |
| Asian (NH) | 1,698 | 3.8% |
| Pacific Islander (NH) | 21 | 0.0% |
| Some Other (NH) | 184 | 0.4% |
| Other/Mixed (NH) | 1,801 | 4.0% |
| Hispanic or Latino | 2,589 | 5.8% |
In 2020, Mankato had 44,488 people. The city had 17,576 households. The average age in the city was 26.5 years. About 16.9% of residents were under 18 years old.
Economy of Mankato
Mankato has many different types of jobs. Education and healthcare are big parts of the economy.

Major Employers
Here are some of the largest employers in Mankato:
| # | Employer | # of Employees | Percentage |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Mankato Area Public Schools ISD #77 | 2,123 | 8.06% |
| 2 | Immanuel St. Joseph's - Mayo Health System | 1,300 | 4.94% |
| 3 | Minnesota State University, Mankato | 1,300 | 4.94% |
| 4 | Walmart Distribution Center | 525 | 1.99% |
| 5 | Blue Earth County | 491 | 1.86% |
| 6 | Mankato Clinic | 425 | 1.61% |
| 7 | Mankato Rehabilitation Center Inc. Industrial Operation | 375 | 1.42% |
| 8 | Compeer Financial | 362 | 1.37% |
| 9 | Johnson Outdoors-Mankato | 360 | 1.37% |
| 10 | The City of Mankato | 313 | 1.19% |
| — | Total employers | 7,574 | 28.75% |
Arts and Culture
Fun Events
For 52 years, the Minnesota Vikings football team held their summer training camp at Minnesota State University. In 2018, they moved their camp to Eagan, Minnesota.
Places to Visit
Mankato has many interesting places:
- The Betsy & Tacy Houses: These are homes that inspired the famous children's book series.
- Blue Earth County Courthouse: A historic building listed on the National Register of Historic Places.
- Happy Chef original restaurant: You can still see the last 36-foot Happy Chef statue here!
- The Hubbard House: A beautiful historic home built in 1871.
- ISG Field: Home to the Mankato Moondogs, a summer baseball team.
- River Hills Mall: A popular shopping center.
- Sibley Park: A city park along the river.
- The Mayo Clinic Health System Event Center: An arena downtown for events and concerts.
Library Services
The Blue Earth County Library serves the city. It is part of the Traverse des Sioux Library System.
Education in Mankato
Mankato has many schools for students of all ages.
Local Schools
The Mankato Area Public Schools include Mankato, North Mankato, Eagle Lake, and Madison Lake. There are:
- Ten elementary schools (like Franklin, Kennedy, and Roosevelt)
- Two middle schools (Dakota Meadows and Prairie Winds)
- Two high schools (Mankato West High School and Mankato East High School)
There are also several private schools, such as Loyola Catholic School and Immanuel Lutheran School. Kato Public Charter School is another option.
Colleges and Universities
Mankato is a great place for higher education:
- Minnesota State University: This is the second-largest university in Minnesota. It opened in 1868.
- South Central College
- Bethany Lutheran College
- Rasmussen University
Media Outlets
Newspapers
The main daily newspaper in Mankato is the Mankato Free Press.
Television Channels
- KMNF-LD 7 (NBC/CW)
- KEYC-TV 12 (CBS/Fox)
- K14KE-D 14 (Independent)
- K26CS-D 26 (PBS)
- K29IE-D 29 (PBS)
- K30FN-D 30 (ABC)
Radio Stations
FM Radio
- 89.1 FM, KTIS (AM), Christian talk
- 89.7 FM, KMSU, college radio
- 90.5 FM, KNGA, Minnesota Public Radio
- 91.5 FM, KGAC, classical music
- 93.1 FM, KATO-FM, classic hits
- 94.1 FM, KXLP, classic rock
- 94.9 FM, KTIS-FM, Christian music
- 95.3 FM, KCMP, adult album alternative
- 95.7 FM, KMKO-FM, active rock
- 96.7 FM, KDOG, top 40
- 99.1 FM, KEEZ-FM, adult contemporary
- 100.5 FM, KXAC, country music
- 101.5 FM, KEMJ, adult contemporary
- 101.7 FM, KMKO-FM, active rock
- 102.7 FM, KTOE, news/talk
- 103.1 FM, KFSP, sports talk
- 103.5 FM, KYSM-FM, country music
- 104.5 FM, KJLY, Christian music
- 105.1 FM, KCMP, adult album alternative
- 105.5 FM, KRBI-FM, adult contemporary
- 107.1 FM, KJLY, Christian music
AM Radio
- 860, KNUJ (AM), news/talk
- 1230, KFSP, sports talk
- 1420, KTOE, news/talk
Transportation
Getting Around Mankato
The Mankato Transit System provides public transportation within the city. The Mankato Regional Airport serves the area, but it does not have commercial flights.
Main Roads
Several major highways pass through Mankato:
 U.S. Highway 14
U.S. Highway 14 U.S. Highway 169
U.S. Highway 169 Minnesota State Highway 22
Minnesota State Highway 22 Minnesota State Highway 60
Minnesota State Highway 60 Minnesota State Highway 83
Minnesota State Highway 83
Local Food History
In 2016, a cookbook from a Mankato church congregation was recognized. It had the first known recipe for a "hotdish" from 1930. A hotdish is a popular casserole dish in Minnesota. The recipe used hamburger, onions, pasta, peas, tomato soup, and tomatoes.
Famous People from Mankato
- Barry Anderson, a judge on the Minnesota Supreme Court
- Walter Jackson Bate, a writer who won a Pulitzer Prize
- Frederick Russell Burnham, known as the "father of the international scouting movement"
- Jimmy Chin, a professional climber and Academy Award-winning filmmaker
- Craig Dahl, a former NFL safety for the New York Giants
- Adolph Olson Eberhart, a former Governor of Minnesota
- Justin Hartwig, a former NFL center
- Ron Johnson, a U.S. Senator
- Sinclair Lewis, a famous author
- Maud Hart Lovelace, author of the Betsy-Tacy book series
- Adam Thielen, an NFL wide receiver for the Minnesota Vikings
- Tim Walz, the current Governor of Minnesota
- Steve Zahn, an actor and comedian
See also
 In Spanish: Mankato (Minnesota) para niños
In Spanish: Mankato (Minnesota) para niños
 | Chris Smalls |
 | Fred Hampton |
 | Ralph Abernathy |






