Mica facts for kids

Mica is a group of shiny minerals that can be easily split into thin, flexible sheets. They are made of silicates mixed with different metals. Mica crystals often look like six-sided shapes. Their ability to split into very thin layers comes from how their atoms are arranged in flat, hexagonal sheets.
Contents
What Makes Mica Special?
The mica group includes 37 different minerals that have a layered, flat texture. The most important types of mica used in industries are muscovite and phlogopite. Mica is valuable because of its many special features.
Mica's crystal structure forms layers that can be split into very thin sheets. These sheets are:
- Chemically safe (they don't react with other things).
- Good insulators (they don't let electricity pass through easily).
- Flexible and elastic.
- Lightweight.
- Shiny and reflective.
- Clear to opaque (you can see through some, but not others).
Mica stays strong when exposed to electricity, light, moisture, and very hot or cold temperatures. It's an excellent electrical insulator and can handle high voltages without losing much energy as heat. It can be split incredibly thin (less than a hair's width) while still keeping its electrical properties. Muscovite mica is often used in electronics, especially in capacitors for high-frequency radio equipment. Phlogopite mica can handle even higher temperatures (up to 900°C or 1650°F), making it useful where both heat resistance and electrical insulation are needed. Both muscovite and phlogopite are used as sheets and as a ground-up powder.
Ground Mica: Uses in Everyday Products
Ground mica is mica that has been crushed into a powder. It's used in many different products.
- Wallboard Joint Compound: The main use for dry-ground mica in the US is in the paste used to fill gaps and smooth seams in gypsum wallboard (drywall). Mica acts as a filler, makes the paste smooth, helps it spread easily, and stops it from cracking. In 2008, this use made up 54% of all dry-ground mica used.
- Paints: In paint, ground mica helps the color stay mixed, prevents the paint from cracking or shrinking, makes it more resistant to water and weather, and brightens colors. It also helps paint stick better. In 2008, paint used 22% of dry-ground mica.
- Well Drilling: Coarsely ground mica flakes are added to drilling fluids (mud) to help seal porous parts of the drill hole and prevent fluid loss. This accounted for 15% of dry-ground mica use in 2008.
- Plastics: The plastics industry uses dry-ground mica as a filler, especially in car parts like bumpers and fenders. It makes plastics stronger, stiffer, more stable, and helps reduce sound and vibration. In 2008, plastic applications used 2% of the market's dry-ground mica.
- Rubber: Ground mica is used in rubber products like tires and roofing. It helps prevent rubber from sticking to molds during manufacturing. This use was 1.5% of the dry-ground mica market in 2008. Mica also makes rubber more resilient and reduces gas leaks.
- Roofing and Decorative Coatings: Dry-ground mica is used on rolled roofing and asphalt shingles to stop them from sticking together. It's also used in decorative coatings for wallpaper, concrete, and stucco, adding a subtle sparkle.
- Other Uses: Phlogopite mica is used in car brake linings and clutch plates to reduce noise and vibration (as a replacement for asbestos). It's also used in sound-absorbing insulation, heat shields, and some industrial coatings.

Wet-ground mica keeps its natural shine and is mainly used in pearlescent paints for cars. Many metallic-looking pigments are made by coating mica with another mineral, often titanium dioxide. This creates a reflective color that changes with the coating's thickness. These pigments are used in car paint, shiny plastic containers, and high-quality inks.
In the cosmetics industry, mica's reflective properties make it a key ingredient in blushes, eye liner, eye shadow, foundation, hair and body glitter, lipstick, lip gloss, mascara, lotions, and nail polish. Some toothpastes even contain powdered white mica to gently polish teeth and add a glittery shimmer. Mica is also added to latex balloons to give them a shiny, colored surface.
Mica can also be used as insulation in concrete blocks and home attics. It can be poured into walls that aren't insulated. Sometimes, mica is used to improve soil, especially in potting mixes for gardening. Greases for axles can contain mica to make them last longer and work better.
Built-up Mica: Electrical Insulation
Muscovite and phlogopite mica can be made into "built-up" products. This involves layering thin mica pieces with binders (like glue). Built-up mica is mainly used as an electrical insulation material.
Mica insulation is found in high-temperature and fire-resistant power cables in places like aluminum plants, blast furnaces, and critical wiring circuits (such as defense systems and fire alarms). It's also used in heaters, boilers, and furnace wiring. Some special mica-insulated wires can even work for up to 15 minutes in molten aluminum, glass, and steel!
Major products made from built-up mica include:
- Flexible plates: Used in electric motors and generators.
- Heater plates: Used where high-temperature insulation is needed.
- Molding plates: Used to make V-rings for insulating parts in motors.
- Segment plates: Used as insulation between copper parts in direct-current motors and generators. Phlogopite mica is preferred for segment plates because it wears down at the same rate as the copper, preventing uneven surfaces that could affect the motor.
Some built-up mica products are reinforced with cloth, glass, or plastic, making them very flexible. These are produced in large sheets and can be rolled into ribbons or cut into tapes.
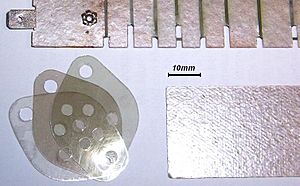
Sheet Mica: Clear and Strong Layers
Technical grade sheet mica is used in electrical and electronic parts, and as special window sheets. Other uses include parts for oxygen-breathing equipment, compass dials, optical filters, and windows for stoves and kerosene heaters. It's also used as covers for microwave oven openings and in micathermic heaters.
Mica is special because it can bend light in a certain way, so it's used to make "wave plates" in optics. Specialized uses for sheet mica are found in aerospace parts for missiles, laser devices, medical electronics, and radar systems. Mica is very strong in thin sheets and is mostly transparent to radiation (like alpha particles) while blocking most gases. Because of this, it's used as a window on radiation detectors like Geiger-Müller tubes.
In 2008, most of the sheet mica used in the United States came from India and Madagascar.
Small square pieces of sheet mica are also used in the traditional Japanese Kodo ceremony to burn incense. A piece of mica is placed on top of a burning coal, acting as a barrier between the heat and the incense. This allows the fragrance to spread without burning the incense itself.
Electrical and Electronic Uses
Sheet mica is mainly used in the electronics and electrical industries. It's useful because of its unique electrical and thermal properties, and because it can be easily cut and shaped precisely. Mica is unusual because it's a good electrical insulator but also a good heat conductor. High-quality block mica is used as an electrical insulator in electronic equipment. It's also used to line the gauge glasses of high-pressure steam boilers because it's flexible, clear, and resistant to heat and chemicals.
The highest quality muscovite mica, called India ruby mica, is used as an insulator in capacitors. The best quality mica film is used to make capacitors for very precise measuring tools.
Mica sheets are also used to hold heating wires (like those in Kanthal or Nichrome) in heating elements, and they can withstand temperatures up to 900°C (1650°F).
Peepholes and Windows
Thin, clear sheets of mica were once used for peepholes in boilers, lanterns, stoves, and kerosene heaters. They were less likely to shatter than glass when exposed to extreme temperature changes. These mica windows were also used in "isinglass curtains" in horse-drawn carriages and early 20th-century cars.
Atomic Force Microscopy
Mica is also used as a base for making super-flat, thin film surfaces. Scientists use freshly split mica surfaces as clean bases for atomic force microscopy. This allows them to create incredibly detailed images of tiny things like bismuth films, proteins, cell membranes, and DNA molecules.
Early History of Mica Use
Humans have been using mica since ancient times. People in ancient India, Egypt, Greece, Rome, and China, as well as the Aztec civilization, knew about mica.
The earliest use of mica was found in cave paintings from the Upper Paleolithic period (40,000 BC to 10,000 BC). White colors in these paintings sometimes came from mica.
Near Mexico City, the ancient city of Teotihuacan has a towering structure called the Pyramid of the Sun. This pyramid contained significant amounts of mica in layers up to 30 cm (12 inches) thick.
Native American tribes like the Taos and Picuris Pueblos in New Mexico still use natural mica to make pottery. Their pottery is made from weathered mica schist, which gives the pots tiny flecks of mica. Tewa Pueblo pottery is made by coating the clay with mica to create a dense, glittery finish.
In Pakistan, thin mica flakes (called abrak) are used to decorate women's summer clothes, especially dupattas (long, lightweight scarves). The dupatta is dipped in hot starch water with mica flakes, then hung to dry, giving it a sparkling effect.
Mica Powder for Decoration
For centuries, fine powders of mica have been used for decoration. Powdered mica glitter is used to decorate traditional water clay pots in India, Pakistan, and Bangladesh. It's also used on traditional Pueblo pottery.
The gulal and abir (colored powders) used by North Indian Hindus during the Holi festival contain fine mica crystals to create a sparkling effect. The majestic Padmanabhapuram Palace in India has colored mica windows. Mica powder is also used in traditional Japanese woodblock printmaking. When applied to wet ink and allowed to dry, it sparkles and reflects light.
Images for kids
See also
 In Spanish: Mica para niños
In Spanish: Mica para niños